Chapter: Mechanical : Total Quality Management (TQM) : Principles
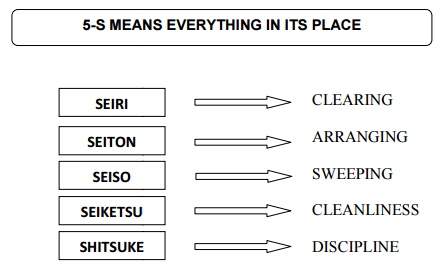
5-S: Housekeeping
5-S: HOUSEKEEPING
Ø There can
be no TQM without 5-S.
Ø A dirty
factory cannot produce quality products.
Ø Clutter
hides problems. A neat workplace promotes easy discovery of abnormalities.
The First
S : SEIRI : CLEARING
Factory
Floor
• Machines to be scrapped
• Rejected material
• Expired goods
• Broken tools, pallets, bins, trolleys.
• Old notices
Office
• Used / Broken pens
• Useless paper
• Old diaries
• Broken furniture’s
Home
• Broken toys
• Old clothes
• Broken suitcases
Flow
Chart :
Separating
the wanted and unwanted
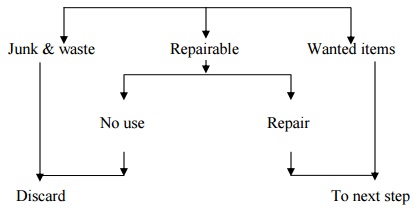
Consequences
of not practicing SEIRI
Ø The
unwanted clutters up the place and the wanted are hard to find.
Ø Every
place can only hold so much.
Ø Clutter
sometimes causes misidentification.
The Second S : SEITON : ARRANGING
Arrange everything in proper order so that it can be easily picked up for use.
Factory
Floor
• Unlabelled tool crib
• Cluttered shelves lockers etc.
• Stores – no clear location system.
• Things on the floor
Office
• Unlabelled file cabinet
• Cluttered drawer, shelves, book cases, Tables
• Records & documents Not arranged well
• File heaps and papers
Home
• Clutter
• No orderly arrangement in the rooms
Consequences
of not practicing SEITON
Ø Things
are seldom available when needed.
Ø Items
are “lost’ in stores.
Ø Items –
defectives and good ones get mixed up.
Ø Accidents
or near-accidents occur due to clutter.
Ø Visual
control of the shop floor is not possible.
Ø Sometimes,
production is lost because an item required is available but cannot be found.
Ø In some
offices, Critical Excise records or tax records may not be traceable. This can
lead to finance loss, prosecution or embarrassment.
The Third S : SEISO : SWEEPING
Sweep your workplace thoroughly so that there is
no dust anywhere.
Factory
Floor
• Dirty machines
• Dust on product parts, R.Mtls.
• Dirty jigs, fixtures
• Dirty walls, roofs
• Littered floor
Office
• Dirty table & furniture
• Dirty office equipments
• Littered floor
• Dirty windows
Home
• Dirty furniture, floor, window, grills,
bookshelves.
Consequences
of not practicing SEISO
Ø Most
machines are affected by dust & dirt and hence their performance may go
down.
Ø Dust and
dirt on products, materials, packing boxes etc. will affect either their
performance quality or their aesthetic look.
Unpleasant to work in.
The
Fourth S : SEIKETSU : CLEANLINESS
Washing with a strong overtone of keeping things
disinfected as well as free of hazardous chemicals.
Factory
Floor
• Handling hazardous Chemicals
• Control of
fumes, hazardous dust.
• Disinfecting,
Personal hygiene
Office
• Free of pests
• Personal hygiene
Home
• Pest control
• Personal hygiene
Consequences
of not practicing SEIKETSU
Ø Good
health and safety require the practice of Seiketsu.
Ø Hazardous
chemicals, dusty chemicals, fumes etc. can make it a dangerous place to work
in.
Ø Washing
thoroughly and cleaning a place makes the workplace pleasant.
Ø Personal
hygiene is essential for healthy workforce.
The Fifth
S : SHITSUKI : DISCIPLINE
Discipline especially with regard to safety rules
and punctuality.
Consequences
of not practicing SEIKETSU
Ø If
discipline is not practiced, then the first 4-S would backslide.
Ø Lack of
Shitsuki means not following the standards. Then, all activities related to
safety and quality will be affected.
IMPLEMENTING
5-S
1.
Top Management resolve and training.
2.
Formation of a top level team.
3.
Understanding current circumstances.
4.
Establishing priorities and targets.
5.
Forming sub-teams and training.
6.
Major cleaning.
7.
Establishing improvement plans in each priority
area.
8.
Implementing the plan.
9.
Verifying results.
10. Standardizing.
11. Establishing
full control.
12. Looking
for further improvements.
KAIZEN
Kaizen is a Japanese word for the philosophy that
defines management’s roles in continuously encouraging and implementing
small improvements involving everyone.
It focuses on simplification by
breaking down complex progress into their sub –
processes and then improving them.
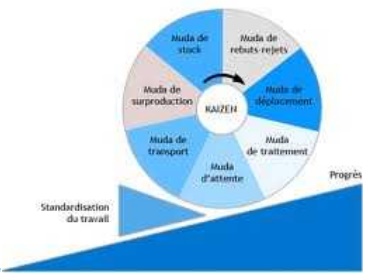
KAIZEN
WHEEL
The
Kaizen improvement focuses on the use of :
Ø Value – added
and non – value
work activities.
Ø Muda,
which refers to the seven classes of waste –
over-production, delay, transportation, processing, inventory, wasted motion,
and defective parts.
Ø Principles
of motion study and the use of cell technology.
Ø Principles
of materials handling and use of one – piece
flow.
Ø Documentation
of standard operating procedures.
Ø The
five S’s for workplace organization.
Ø Visual
management.
Ø Just – in – time
principles.
Ø Poka – Yoke.
Ø Team
dynamics.
Related Topics