Chapter: The Diversity of Fishes: Biology, Evolution, and Ecology: Teleosts at last II:spiny-rayed fishes
Suborder Blennioidei
Suborder Blennioidei
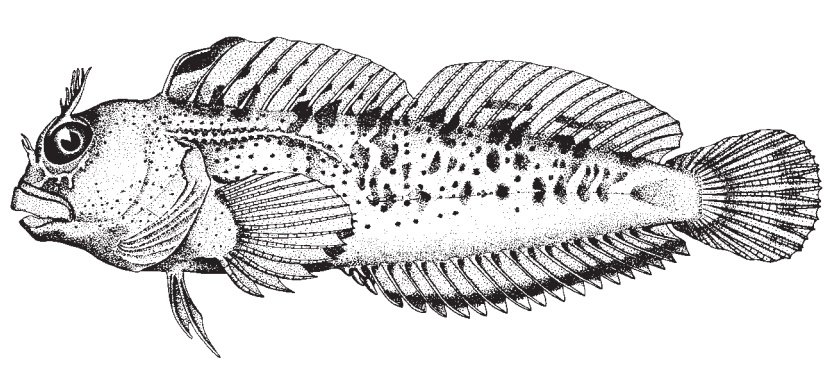
Blennioids are small, benthic, marine fishes of tropical and subtropical regions (Fig. 15.22). They generally possess long dorsal and anal fins and fleshy flaps termed cirri on some part of the head. Triplefinblennies (Tripterygiidae)derive their name from having a soft dorsal fin plus a spinydorsal fin divided into two parts (hakes and cods are the only other fishes with three distinctive dorsal fins).Dactyloscopidsand stargazers look like miniaturized (to 15 cm) uranoscopid stargazers with their oblique mouths and stalked eyes. They similarly have a specialized breathingmechanism probably related to their burying habits. Inmost fishes, water is brought into the mouth and out the gills by the combined actions of buccal and opercular pumps(see Respiration and ventilation). Sand stargazers move water via a branchiostegal rather than an opercularpump. Finger like projections inside the mouth may keeps and out of the gills. Some dactyloscopid males care for eggs by carrying them under the axil of each pectoral fin.
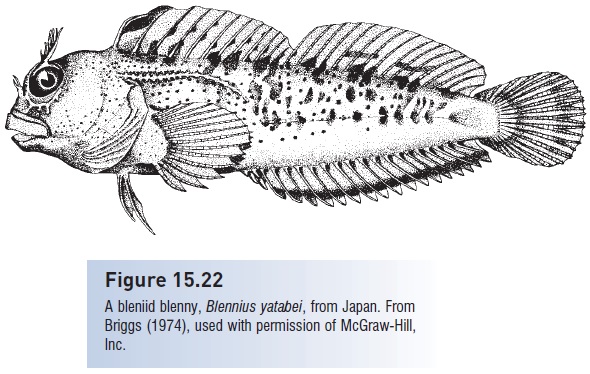
Figure 15.22
A bleniid blenny, Blennius yatabei, from Japan. FromBriggs (1974), used with permission of McGraw-Hill,Inc.
The combtooth blennies of the family Blenniidae arevery diverse, accounting for 360 species of mostly small, benthic fishes in tropical and subtropical waters worldwide.The comb like teeth are used to crop algae in many species.Many of the advanced nemophine sabre-toothed blenniids(Aspidontus, Meiacanthus) swim freely in the water column and are also involved in mimetic relationships with other fishes. The best known example is the cleaner fish mimic,Aspidontus taeniatus. This sabre-toothed blenny stronglymimics the blue and black coloration and bobbing solicitationdance of labrid cleanerfishes, particularly of the CleanerWrasse,Labroides dimidiatus. When allowed to approacha posing host fish, rather than cleaning the host, Aspidontusbites off a piece of fin (juvenile L. dimidiatus are also mimickedby juvenile fang blennies, Plagiotremus rhinorhynchos).Other sabre-toothed blennies attack passing fish and remove scales or pieces of fin (they attack prey as large asskindivers and generally attack once the diver has passedoverhead, which is always a surprising, painful, and distinctly unsettling experience). Some of the sabre-toothedspecies are referred to as poison-fanged blennies because oftheir hollow lower canines that can inject a toxin. Poisonfang blennies (Meiacanthus) may be mimicked by similarlycolored blennies (e.g., Ecsenius, Plagiotremus, Runula) andthus gain protection from predators (Losey 1972; Springer & Smith-Vaniz 1972; Moland & Jones 2004).
Clinids, also known as kelpfishes and fringeheads(including the intriguingly named Sarcastic Fringehead),vary in size from 5 cm up to the predatory Giant Kelpfish, Heterostichus rostratus, which reaches 60 cm. Clinids areshallow water, benthic forms associated closely with structurein both temperate southern and northern hemispheres.Some clinids give birth to live young. Chaenopsidpikeblennies and tube blennies are small, tropical, New Worldfishes that are most often found living in or with corals.Many tube blennies are essentially infaunal. Shortly after settling from the plankton, a tube blenny will take up residencein an available polychaete worm tube and is likely toremain there for the rest of its life.
Related Topics