Applications of biotechnology - Stem Cell Therapy | 12th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Applications of biotechnology
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Applications of biotechnology
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in
most of the multi cellular animals. These cells maintain their undifferentiated
state even after undergoing numerous mitotic divisions.
Stem cell research has the potential to
revolutionize the future of medicine with the ability to regenerate damaged and
diseased organs. Stem cells are capable of self renewal and exhibit ‘cellular
potency’. Stem cells can differentiate into all types of cells that are derived
from any of the three germ layers ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
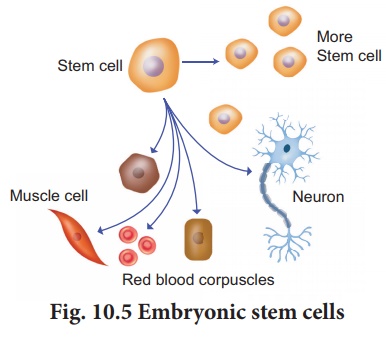
In mammals there are two main types of stem
cells – embryonic stem cells (ES cells) and adult stem cells. ES cells are
pluripotent and can produce the three primary germ layers ectoderm, mesoderm
and endoderm. Embryonic stem cells are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate
into a number of types of cells (Fig. 10.5). ES cells are isolated from
the epiblast tissue of the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. When stimulated ES
can develop into more than 200 cells types of the adult body. ES cells are
immortal i.e., they can proliferate in a sterile culture medium and maintain
their undifferentiated state.
Adult stem cells are found in various tissues of
children as well as adults. An adult stem cell or somatic stem cell can divide
and create another cell similar to it. Most of the adult stem cells are
multipotent and can act as a repair system of the body, replenishing adult
tissues.The red bone marrow is a rich source of adult stem cells.
The most important and potential application of
human stem cells is the generation of cells and tissues that could be used for
cell based therapies. Human stem cells could be used to test new drugs.
Totipotency (Toti-total) is the ability of a
single cell to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an
organism.
Pluripotency (Pluri-several) refers to a stem cell
that has the potential to differentiate into any of the three germ
layers-ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
Multipotency (multi-Many) refers to the stem
cells that can differentiate into various types of cells that are related. For
example blood stem cells can differentiate into lymphocytes, monocytes ,
neutrophils etc.,
Oligopotency (Oligo-Few) refers to stem cells
that can differentiate into few cell types. For example lymphoid or myeloid
stem cells can differentiate into B and T cells but not RBC.
Unipotency ( Uni- Single) refers to the ability
of the stem cells to differentiate into only one cell type.
Stem Cell Banks
Stem cell banking is the extraction, processing and storage of stem cells, so that they may be used for treatment in the future, when required. Amniotic cell bank is a facility that stores stem cells derived from amniotic fluid for future use. Stem cells are stored in banks specifically for use by the individual from whom such cells have been collected and the banking costs are paid. Cord Blood Banking is the extraction of stem cells from the umbilical cord during childbirth. While the umbilical cord and cord blood are the most popular sources of stem cells, the placenta, amniotic sac and amniotic fluid are also rich sources in terms of both quantity and quality.
Related Topics