Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Applications of biotechnology
Regulations in Biotechnology
Regulations in
Biotechnology
Regulations apply to the production, sale and
use of biotech products and genetically modified organisms. GMOs are carefully
tested and documented before the products are available. GMOs should be
labelled and used according to instructions. These regulations are designed to
protect the people, living organisms and the environment. The Biotechnology
Regulatory Authority of India (BRAI) is a proposed regulatory body in India for
uses of biotechnology products including GMOs. The Genetic Engineering Approval
Committee (GEAC), a body under the Ministry of Environment, forests and climate
change (India) is responsible for approval of genetically engineered products
in India. If the bill is passed the responsibility will be taken over by the
Environmental Appraisal Panel, a subdivision of the BRAI. The bill also
proposes setting up an inter ministerial governing body to oversee the
performance of BRAI and a National Biotechnology Advisory Council of
stakeholders to provide feedback on the use of, import and manufacture of
biotechnology products and organisms in the society. The regulatory body is an
autonomous and statutory agency to regulate the research, transport, import and
manufacture of biotechnology products and organisms.
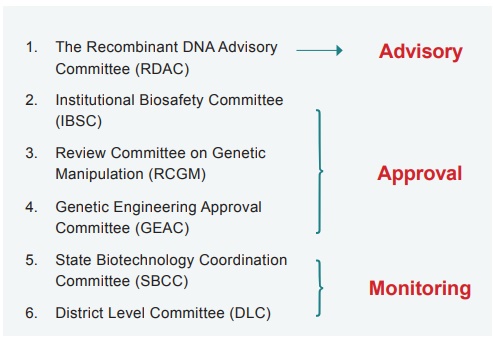
GEAC is assisted by the State Biotechnology Co- ordination Committee (SBCC) and District Level committee (DLC). The most important committees are The Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC), responsible for the local implementation of guidelines; Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) is responsible for issuing permits and the GEAC is responsible for monitoring the large scale and commercial use of transgenic materials.
Biopiracy can be defined as “the use of
bioresources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper
authorization from the countries and the people concerned without compensatory
payment”.
Bioethics is the study of the ethical issues
emerging from the advances in Biology and medicine. It is also a moral
discernment as it relates to the medical policy and practice.
The biotechnology industry is governed by
different enactments depending on their relevance / applicability on a case to
case basis. “Recombinant DNA safety guidelines, 1990” were released by the
Department of Biotechnology (DBT) which cover areas of research involving
genetically engineered organisms and these guidelines were further revised in
1994.
RCGM under the DBT comprises representatives of
DBT, Indian Council for Medical Research, Indian Council for Agricultural
research and Council for Scientific and Industrial Research.
Industrial licensing under the Industrial
(Development and Regulation) Act,1951 is compulsory for bulk drugs produced by
the use of recombinant DNA technology.
Being a signatory to the Trade Related
Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement of WTO, India has amended its
legislations pertaining to intellectual property through various legislations
including Patents (Amendment) Act, 1999.
Related Topics