Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers | Chemistry - Short Answer Questions | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers
Short Answer Questions
Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers | Chemistry
Short Answer Questions
1. Identify the product (s) is / are formed when 1 – methoxy propane is heated with excess HI. Name the mechanism involved in the reaction
When
1-methoxy propane is heated with excess HI it forms methyl iodide and propyl
iodide.
CH3—O —CH2—CH2—CH3
+ 2 HI → CH3I + CH3CH2CH2I + H2O
1- methoxy
propane propyl iodide
Mechanism
It follows SN2 mechanism.
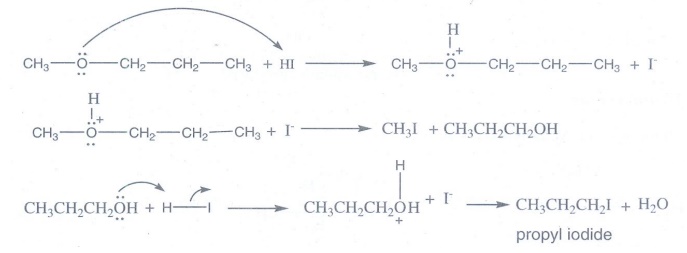
Ethers
having primary alkyl group undergo SN2 reaction.
2. Draw the major product formed when 1-ethoxyprop-1-ene is heated with one equivalent of HI
1-ethoxyprop-l-ene
is heated with one equivalent of HI gives ethyl iodide and prop-l-enol
CH3CH2 - O - CH = CH - CH3
+ HI → CH3CH2I + CH3 - CH = CH - OH
1-ethoxyprop−1-ene
Ethyl
iodide Prop−1 en ol
3. Suggest a suitable reagent to prepare secondary alcohol with identical group using Grignard reagent.
Formate
ester is used to prepare secondary alcohol with identical alkyl group
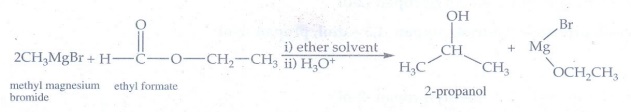
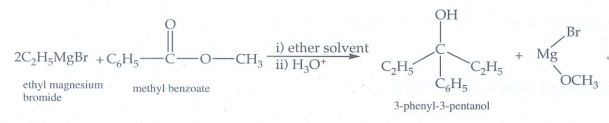
4. What is the major product obtained when two moles of ethyl magnesium bromide is treated with methyl benzoate followed by acid hydrolysis.
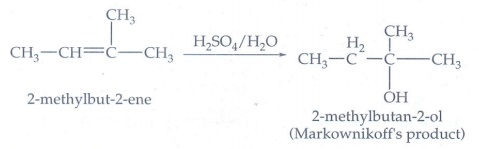
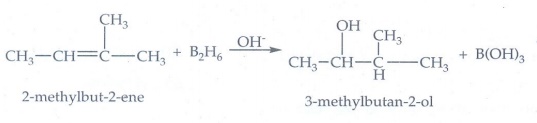
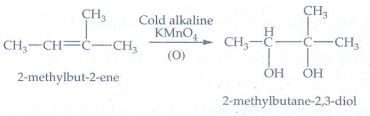
5. Predict the major product, when 2-methyl but -2-ene is converted into an alcohol in each of the following methods.
(i) Acid catalysed hydration (ii.) Hydroboration (iii.) Hydroxylation using bayers reagent
(i) Acid catalysed hydration
It
follows Markownikoff's rule.
(ii) Hydroboration
It
follows anti Markovnikov's rule
(iii) Hydroxylation using Bayers
reagent
Bayer's
reagent with alkene gives diol.
6. Arrange the following in the increasing order of their boiling point and give a reason for your ordering
(i) Butan – 2- ol, Butan -1-ol, 2 –methylpropan -2-ol
(ii) Propan -1-ol, propan -1,2,3-triol, propan -1,3 – diol, propan -2-ol
Answer:
(i) Butan - 2- ol, Butan -l-ol, 2
-methylpropan -2-ol
Hence
the boiling point decreases with increase of branching
The
van der Waals force decreases with decrease of surface area.
Therefore
the order is 2 – methylpropan -2 – ol < Butan – 2- ol < Butan −1 - ol
(ii) Propan -l-ol, propan −1,2,3-triol,
propan −1,3 - diol, propan -2-ol
The
boiling point of the alcohol increases when the number of −OH group increases
due to strong hydrogen bonding.
propan
-2-ol < Propan -l-ol < propan −1,3 - diol < propan −1,2,3-triol
7. Can we use nucelophiles such as NH3,CH3O- for the Nucleophilic substitution of alcohols
No,
we cannot use nucleophiles such as NH3, for the nucleophilic
substitution of alcohols because nucleophilic substitution reaction reacts two
species a nucleophile (Lewis base) and a substrate in the leaving group.
8. Is it possible to oxidise t – butyl alcohol using acidified dichromate to form a carbonyl compound.
t
- butyl alcohol do not undergo oxidation reaction under normal conditions, but
at elevated temperatures, under strong oxidising agent cleavage of C -C bond
takes place to give a mixture of carboxylic acid. Therefore it is not possible
to get a carbonyl compounds from t-butyl alcohol.
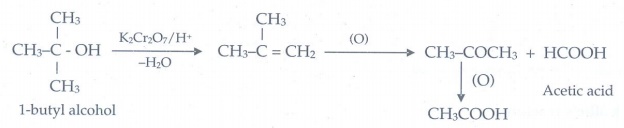
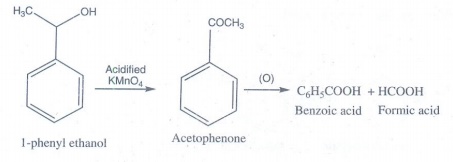
9. What happens when 1-phenyl ethanol is treated with acidified KMnO4.
1-phenyl
ethanol is treated with acidifed KMnO4 gives acetophenone and then
oxidized to give benzoic acid.
10. Write the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to give ethene.

Mechanism
It
follows E2 mechanism 
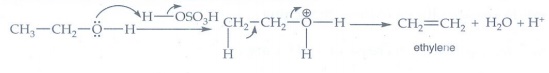
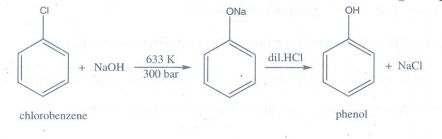
11. How is phenol prepared from
i) chloro benzene ii) isopropyl benzene
i) chloro benzene
When
chlorobenzene is hydrolysed with 6−8% NaOH at 300 bar and 633 K in a closed
vessel, sodium phenoxide is formed which on treatment with dilute HCl gives phenol.
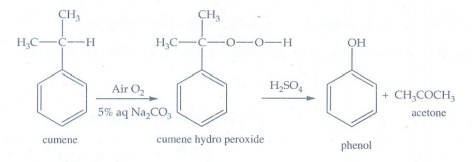
ii) isopropyl benzene
On
passing air to a mixture of cumene and 5% aqueous sodium carbonate solution,
cumene hydro peroxide is formed by oxidation. It is treated with dilute acid to
get phenol and acetone.
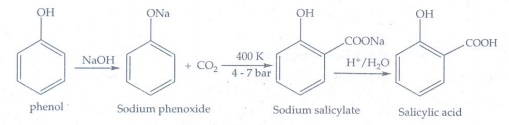
12. Explain Kolbe’s reaction
• Phenol is first converted into
sodium phenoxide which is more reactive than phenol
• It undergo electrophilic
substitution reaction with CO2 at 400K, 4-7 bar pressure gives
sodium salicylate.
• Acid hydrolysis of sodium
salicylate gives salicylic acid
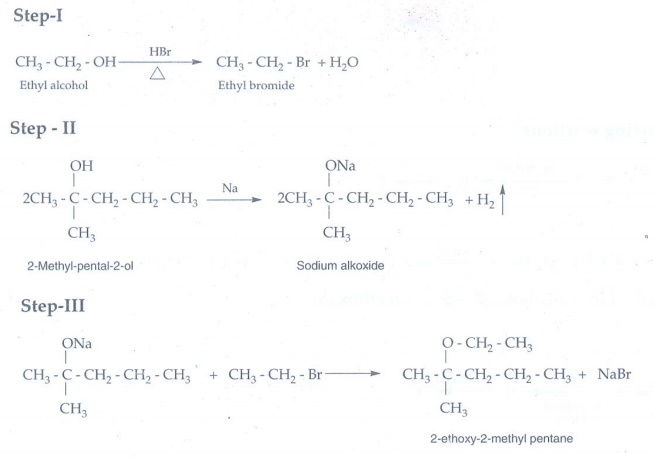
13. Write the chemical equation for Williamson synthesis of 2-ethoxy – 2- methyl pentane starting from ethanol and 2 – methyl pentan -2-ol
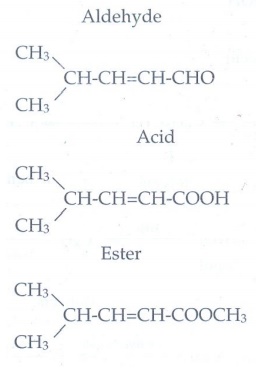
14. Write the structure of the aldehyde, carboxylic acid and ester that yield 4- methylpent -2-en-1-ol.
15. What is metamerism? Give the structure and IUPAC name of metamers of 2-methyoxy propane
Metamerism:- It is a special type of isomerism in which molecules with same formula, same functional group, differing only in the nature of the alkyl group attached to oxygen
CH3-O-CH2-CH2-CH3
Methoxy
propane
CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH3
Ethoxy
ethane
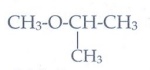
2-Methoxy
propane
16. How are the following conversions effected
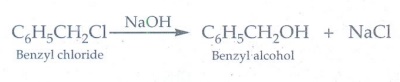
i) benzylchloride to benzylalcohol ii) benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid
Hydrolysis
of benzyl chloride with aqueous NaOH gives benzyl alcohol
ii) benzylalcohol to benzoic acid
Benzyl
alcohol is oxidised with acidified potassium dichromate or alkaline potassium
permanganate, benzaldehyde is first formed which undergoes further oxidation to
benzoic acid.
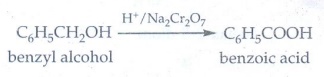
17. Complete the following reactions
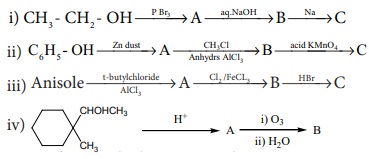
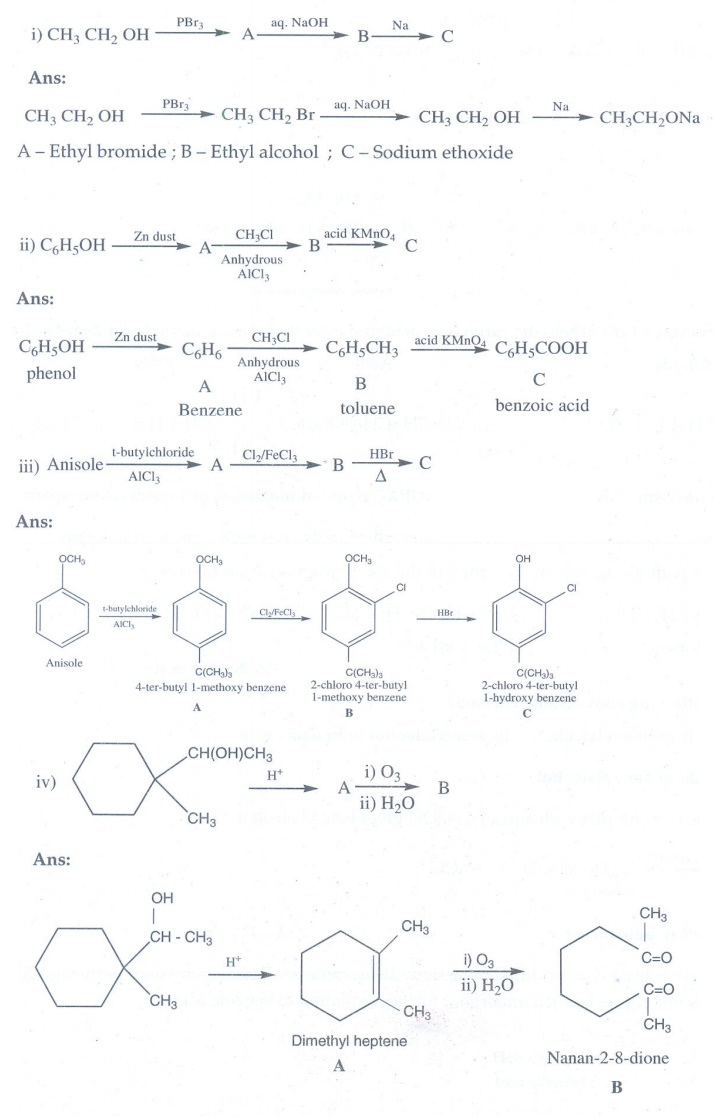
Answer:
18. 0.44g of a monohydric alcohol when added to methyl magnesium iodide in ether liberates at STP 112 cm3 of methane with PCC the same alcohol form a carbonyl compound that answers silver mirror test. Identify the compound.
0.44g
of a monohydric alcohol alcohol liberates 112 cm3 of methane
Mass
of monohydric alcohol which gives 22400 cm3 of methane = (22400 × 0.44
) / 112 = 88
C5H12O
molecular formula has mass number 88 and it shows eight possible isomers.
But
Neopentyl alcohol reacts with pcc to form neopentyl aldehyde which shows
positive silver mirror test.
Therefore,
compound is neopentyl alcohol.

19. Complete the following reactions
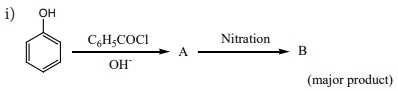
ii) C6H5 -CHCH(OH)CH(CH3 )2 ---ConH2 SO4 →
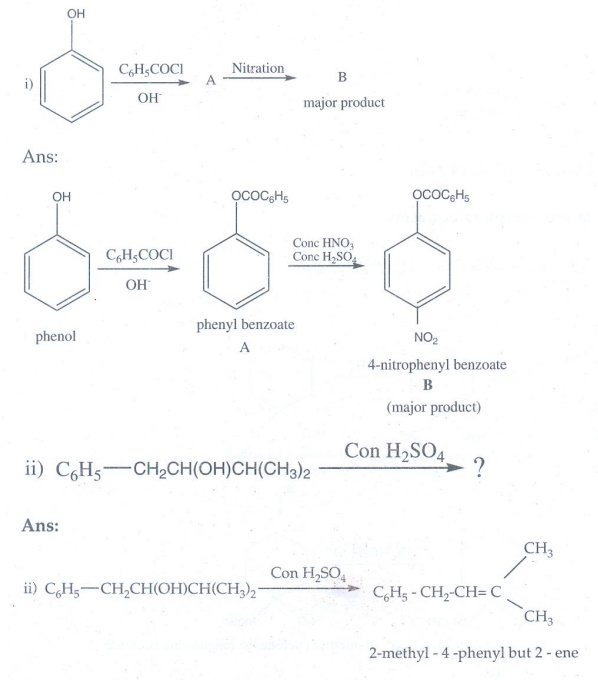
20. Phenol is distilled with Zn dust followed by friedel – crafts alkylation with propyl chloride to give a compound B, B on oxidation gives (c) Identify A,B and C.
Phenol
is distilled with Zn dust gives benzene (A)
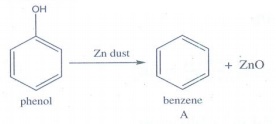
Benzene
(A) undergoes Friedel - Craft's alkylation with propyl chloride gives cumene
(B)
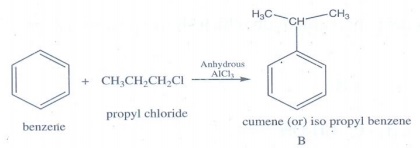
Cumene
(B) on oxidation gives phenol and acetone
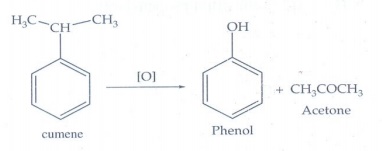
Answer:
A
→ Benzene; B → Cumene ; C → Phenol
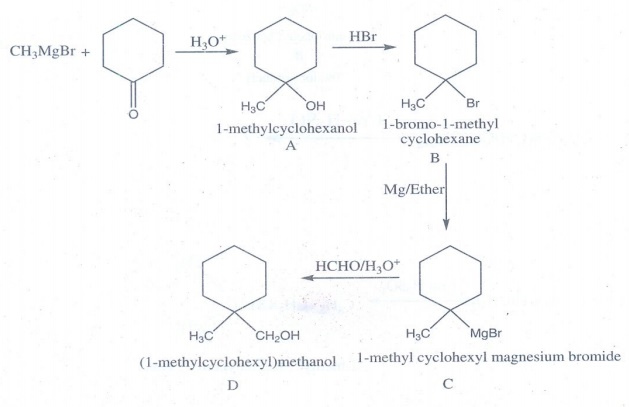
21. 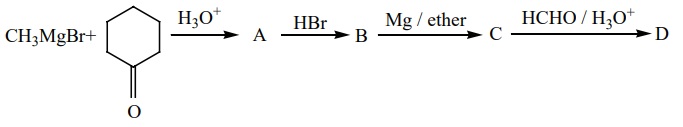
Identify A,B,C,D and write the complete equation
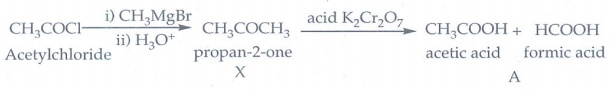
22. What will be the product (X and A)for the following reaction
Acetylchloride 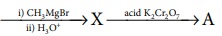
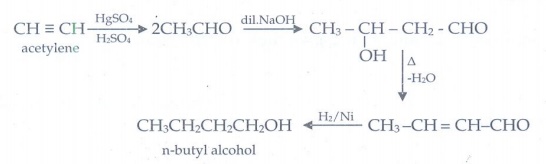
23. How will you convert acetylene into n-butyl alcohol.
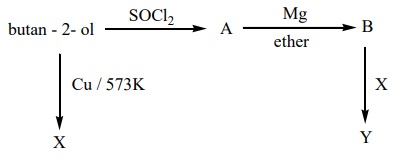
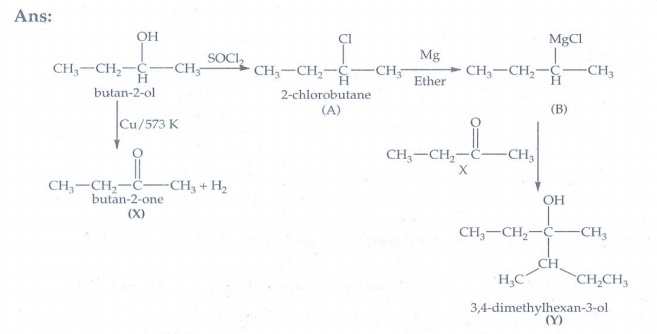
24. Predict the product A,B,X and Y in the following sequence of reaction
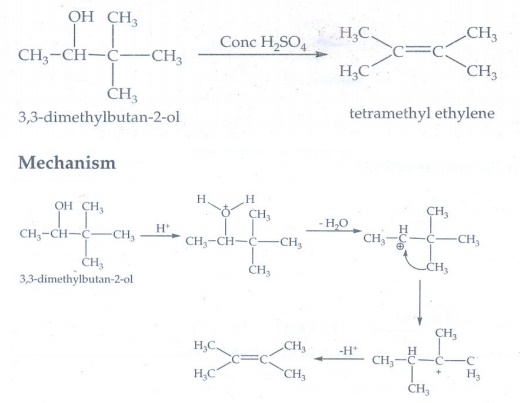
25. 3,3 – dimethylbutan -2-ol on treatment with conc. H2SO4 to give tetramethyl ethylene as a major product. Suggest a suitable mechanism
ALCOHOL
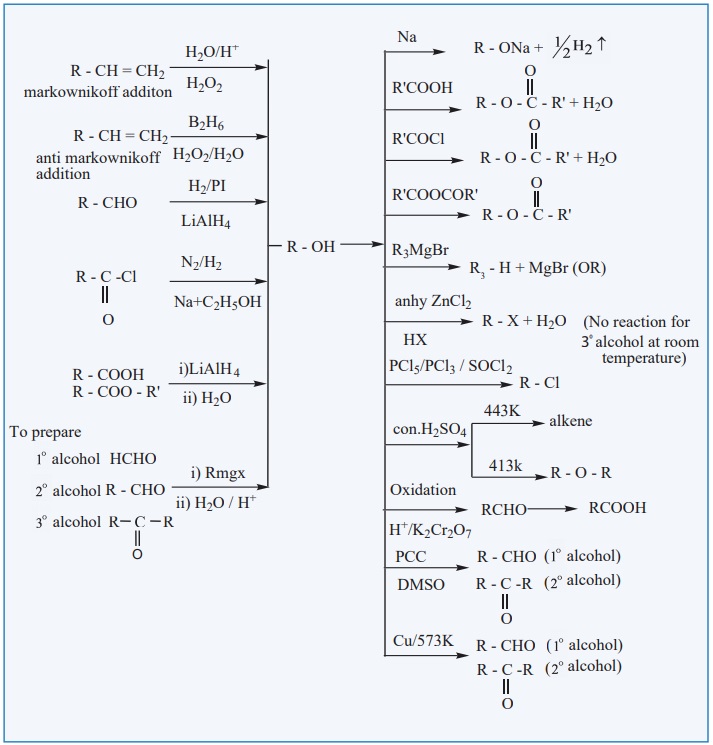
EVALUATE YOURSELF:
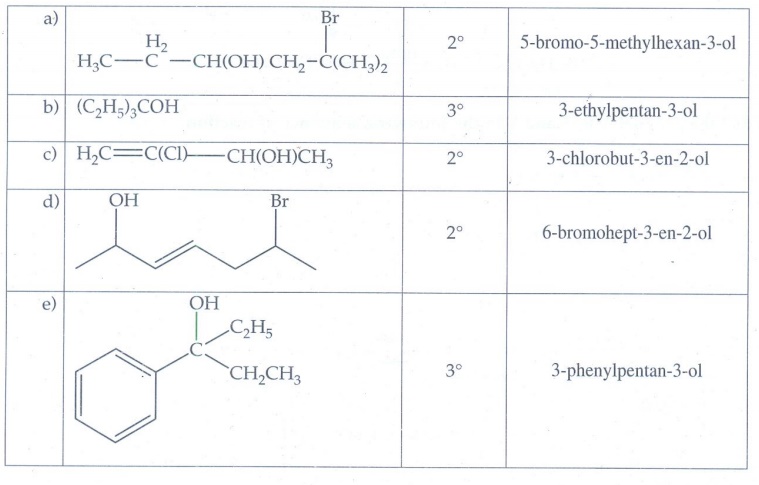
1. Classify the
following alcohols as 1°, 2°, and 3° and give their IUPAC Names.
2. Suggest a
suitable carbonyl compound for the preparation of pent-2-en-l-ol using LiAlH4-.
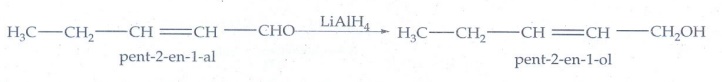
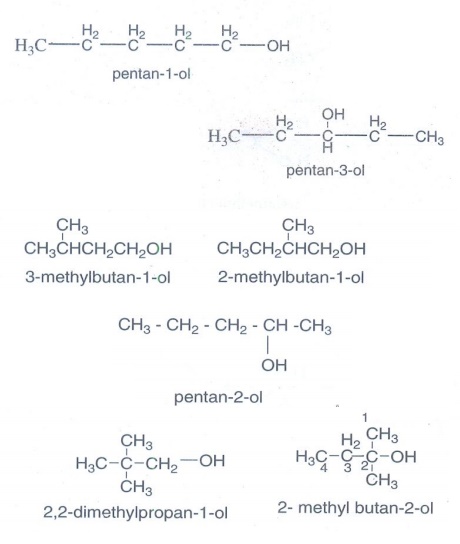
3. Write all the
possible isomers of an alcohol having the molecular formula C5H12O
and give their IUPAC names.
4. 2-methylpropan-2-ene 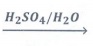
The reaction follows Markovnikov's rule
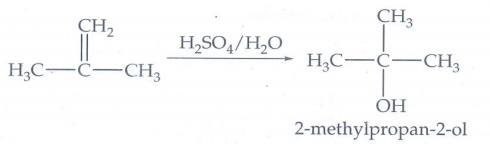
5. How will you
prepare the following using Grignard reagent?
i) t-butyl alcohol
ii) allyl alcohol
i) t-butyl alcohol
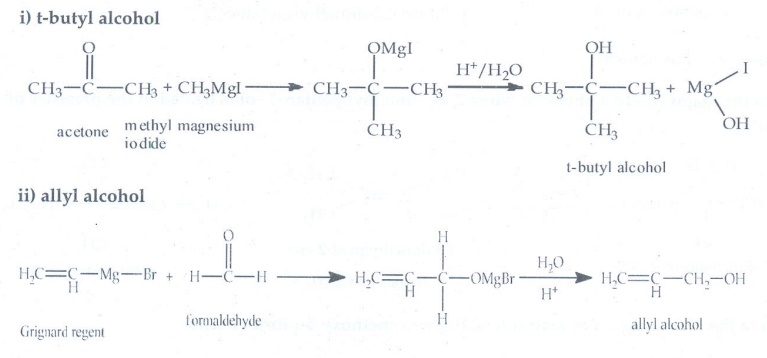
6. Identify the
products in the following reactions. Write their IUPAC names and mention the
mechanism involved in the reactions.
Answer:
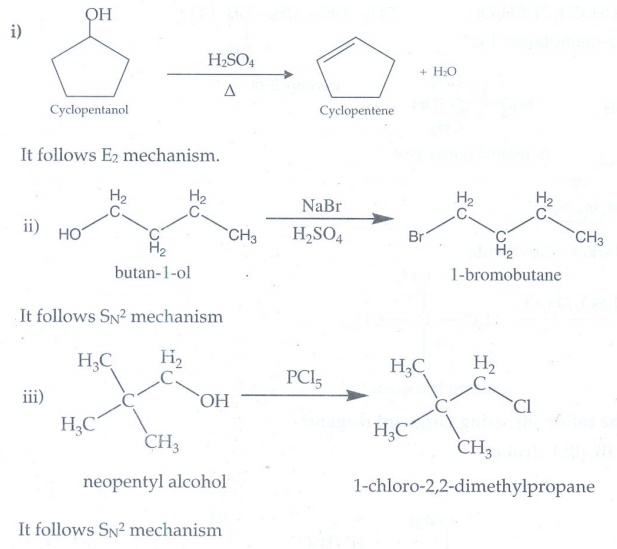
7. What is the
major product obtained when 2,3 - dimethyl pentan-3 -ol is heated in the
presence of H2SO4?
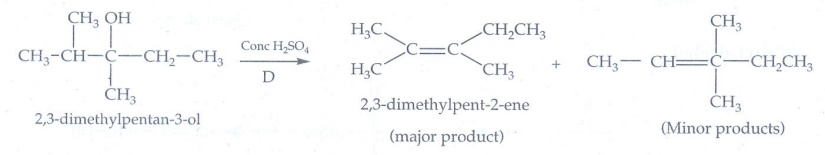
8. Which of the
following set of reactants will give l-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene.
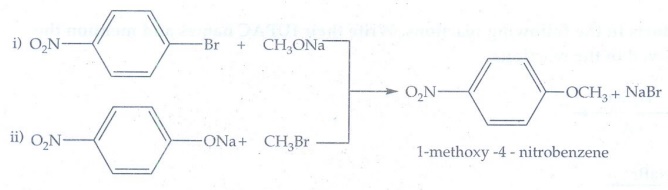
Equation
(ii) only gives l-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene. The reaction is Williamson's
synthesis. The Br atom attached to aromatic carbon atom is more strong and
hence it will not cleaved easily and does not give l-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene.
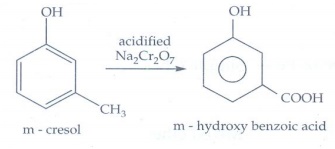
9. What happens
when m-cresol is treated with acidic solution of sodium dichromate?
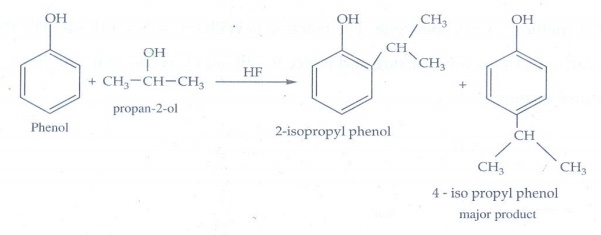
10. When phenol is
treated with propan-2-ol in the presence of HF, Friedel-Craft reaction takes
place . Identify the products.
Alkylation
takes place at ortho and para position
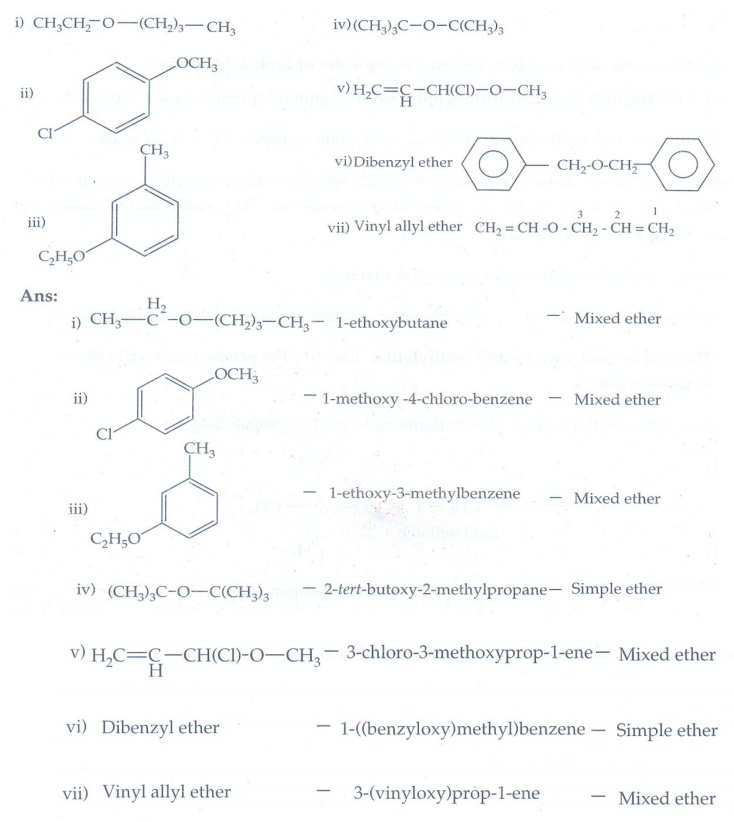
11. Give the IUPAC
name for the following ethers and classify them as simple or mixed.
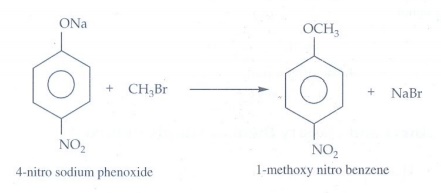
12. Which of the
following reaction will give l-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene?
a) 4-nitro-l-bromobenzene
+ sodium methoxide.
b) 4-nitrosodium
phenoxide+bromomethane
Reaction
(b) only gives l-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene. The reaction is Williamson's
synthesis. The Br atom attached to aromatic carbon atom is more strong and
hence it will not cleaved easily and does not give the
l-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene.
13. Arrange the
following compounds in the increasing order of their acid strength.
propan-l-ol, 2,4,6-trinitrophenol,3-nitrophenol,3,5-dinitrophenol,
phenol,4-methylphenol.
Aliphatic
alcohols are less acidic than aromatic alcohol. Hence propan-l-ol is least
acidic.
Electron
releasing group decreases the acidity of phenol where as electron withdrawing
group enhances the acidity of phenol. If electron withdrawing group like -NO2
is attached to phenol, the compound is more acidic than phenol.
Hence
the increasing order of their acid strength is given as
propan-l-ol
< 4-methylphenol < phenol < 3-nitrophenol < 3,5-dinitrophenol <
2,4,6-trinitrophenol
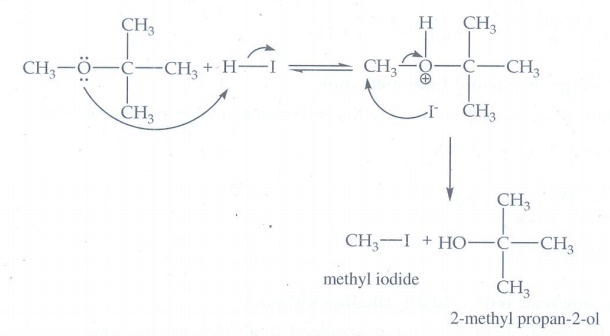
14. 1 mole of HI is
allowed to react with t-butyl methylether. Identify the product and write down
the mechanism of the reaction.
t-butyl methylether reacts with HI gives
iodomethane and 2-methylpropan-2-ol
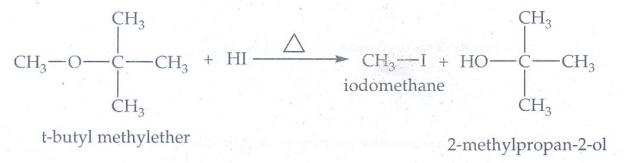
Mechanism
The
reaction involves protonation of oxygen which is following by SN1
mechanism. The products are t-butyl alcohol and methyl idodide.
Related Topics