Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers
Physical and Chemical Properties of ethers
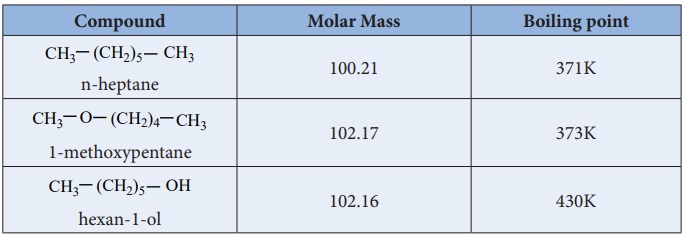
Physical Properties:
Ethers are polar in nature. The dipolemoment of ether is the vector sum
of two polar C-O bonds with significant contribution from two lone pairs of
electrons. For example, the dipole moment of diethyl ether is 1.18D. Boiling
point of ethers are slightly higher than that of alkanes and lower than that of
alcohols of comparable masses.
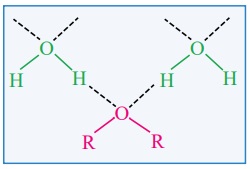
Oxygen of ether can also form Hydrogen bond with water and hence they
are miscible with water. Ethers dissolve wide range of polar and non-polar
substances.
Chemical Properties of ethers:
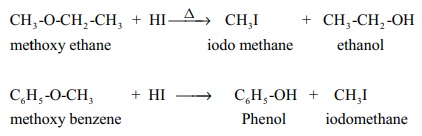
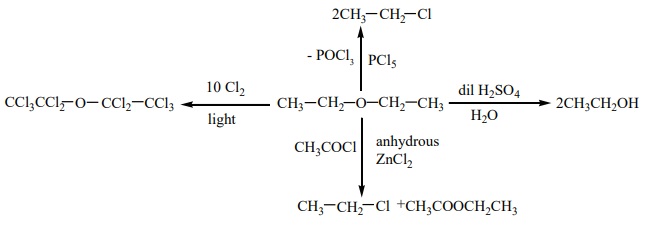
1. Nucleophilic substitution reactions of ethers.
Ethers can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with HBr or HI .
HI is more reactive than HBr .
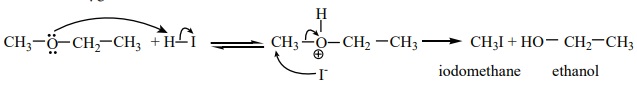
Mechanism:
Ethers having primary alkyl group undergo SN2 reaction while
tertiary alkyl ether undergo SN1 reaction.Protonation of ether is
followed by the attack of halide ion.The halide ion preferentially attacks the
less sterically hindered of the two alkyl groups which are attached to etherial
oxygen.
When excess HBr or HI is used, the alcohol formed will further react with
HBr or HI to form alkyl halides.
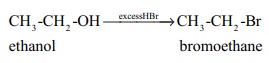
Evaluate Yourself:
1mole of HI is allowed to react with t-butyl methylether.
Identify the product and write down the mechanism of the reaction.
Autooxidation of ethers:
When ethers are stored in the presence of atmospheric oxygen, they
slowly oxidise to form hydroperoxides and dialkylperoxides. These are explosive
in nature. Such a spontaneous oxidation by atmospheric oxygen is called
autooxidation.
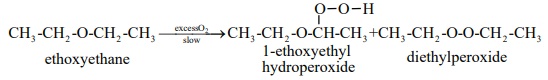
Some of the reaction of diethyl ether.
Aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions:
The alkoxy group ( -OR ) is an ortho, para directing group as well as
activating group.It activates the aromatic ring towards electrophilic
substitution.
i) Halogenation:
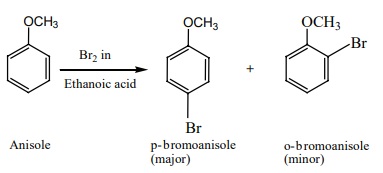
Anisole undergoes bromination with bromine in acetic acid even in the
absence of a catalyst, para isomer is obtained as the major product.
ii) Nitration:
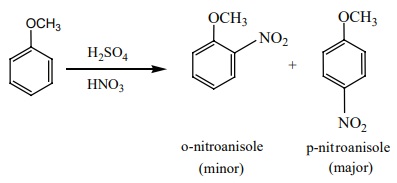
Anisole reacts with a mixture of conc. H2SO4/Conc.HNO3
to yield a mixture of ortho nitro anisole and para nitro anisole.
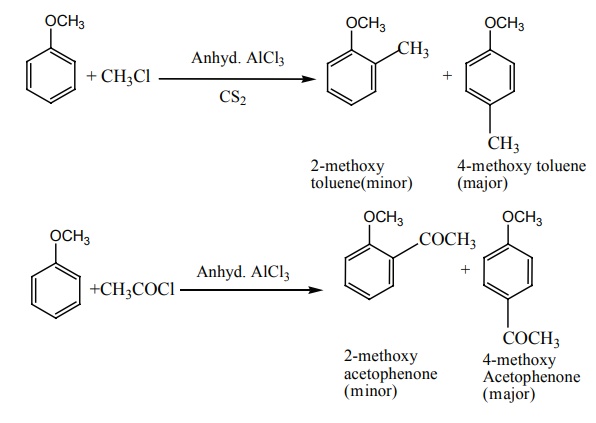
iii) Friedel Craft’s reaction:
Anisole undergoes Fridel Craft’s reaction in presence of anhydrous AlCl3
as a catalyst.
Related Topics