Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 11 : Hydroxy Compounds and Ethers
Preparation of ethers
Preparation of ethers:
1. Inter molecular dehydration of alcohol.
We have already learnt that when ethanol is treated with con.H2
SO4 at 443K, elimination takes place to form ethene. If the same
reaction is carried out at 413K, substitution competes over elimination to form
ethers.
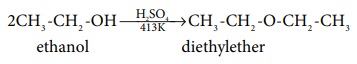
Mechanism:
This method is useful for the preparation of simple ethers and not
suitable for preparing mixed ethers. If a mixture of two different alcohols is
used, mixture of different ethers will be formed and they are difficult to
separate.
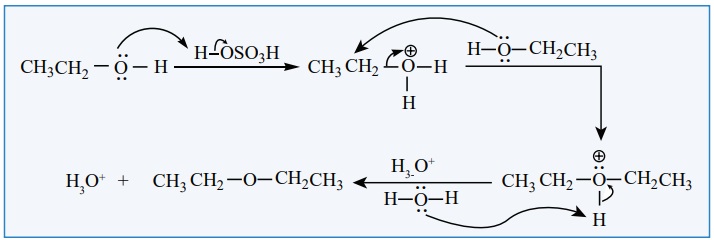
2. Williamsons synthesis:
When an alkyl halide is heated with an alcoholic solution of sodium
alkoxide, the corresponding ethers are obtained. The reaction involves SN2
mechanism.
CH3 -ONa + Br-C2H5 ---------∆→ CH3 -O-C2H5 +
NaBr
Mechanism:
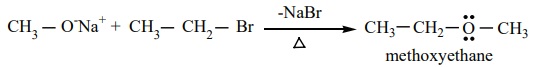
We know that primary alkyl halides are more susceptible for SN2
reaction. Hence for the preparation of mixed ether having primary and tertiary
alkyl group, primary alkyl halide and tertiary alkoxide are used. On the other
hand, if we use tertiary alkyl halide and primary alkoxide, elimination
dominates and succeeds over substitution to form an an alkene.
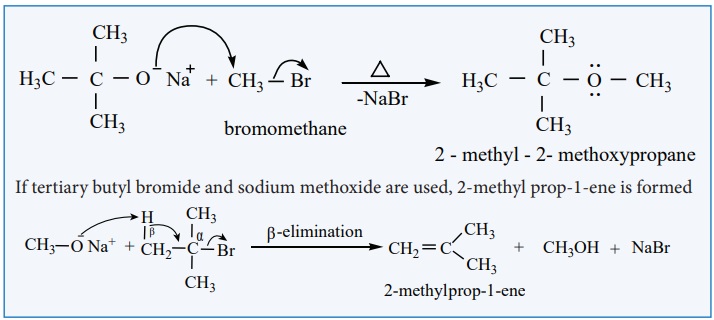
If tertiary butyl bromide and sodium methoxide are used, 2-methyl prop-1-ene is formed
Methylation of alcohol
Methyl ethers can be prepared by treating an alcohol with diazomethane
in presence of catalyst, fluoroboric acid.
CH3 -CH2 -OH+CH2N2 ---∆--HBF4→ CH3
-CH2 -O-CH3+N2
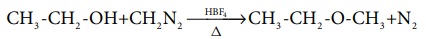
Evaluate Yourself:
1. Which of the following reaction
will give 1-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene.
a) 4-nitro-1-bromobenzene + sodium
methoxide.
b) 4-nitrosodium
phenoxide+bromomethane
2. Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order
of their acid strength. propan-1-ol, 2,4,6-trinitrophenol, 3-nitrophenol,
3,5-dinitrophenol, phenol, 4-methylphenol.
Related Topics