Chapter: Data Warehousing and Data Mining : Association Rule Mining and Classification
Rule Based Classification
Rule Based
Classification
Using IF-THEN Rules for
Classification
Represent
the knowledge in the form of IF-THEN rules
R: IF age
= youth AND student = yes THEN buys_computer = yes
Rule antecedent/precondition vs. rule consequent
Assessment of a rule: coverage
and accuracy
o
ncovers = # of tuples covered by R
o
ncorrect = # of tuples correctly
classified by R
o
o coverage(R) = ncovers /|D| /* D: training data set */
o
accuracy(R) = ncorrect / ncovers
If more than one rule is triggered, need conflict resolution
o
Size ordering: assign
the highest priority
to the triggering
rules that has
the
o
―toughest‖ requirement (i.e., with the most attribute test)
o
Class-based ordering: decreasing order of prevalence or misclassification cost per
class
o
Rule-based ordering (decision list): rules are
organized into one long priority list, according to some measure of rule
quality or by experts
Rule Extraction from a Decision
Tree
o
Rules are easier to understand than large trees
o
One rule is created for each path from the root to
a leaf
o
Each attribute-value pair along a path forms a
conjunction: the leaf holds the class prediction
o
Rules are mutually exclusive and exhaustive
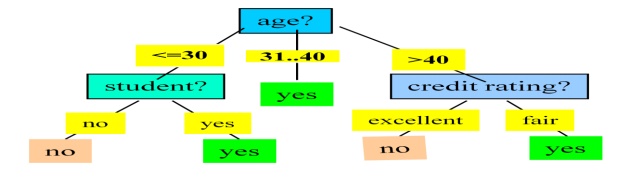
Example: Rule extraction from our
buys_computer decision-tree

Rule Extraction from the Training
Data
o
Sequential covering algorithm: Extracts rules
directly from training data
o
Typical sequential covering algorithms: FOIL, AQ,
CN2, RIPPER
o
Rules are learned sequentially, each for a given class Ci will cover many
tuples of Ci but none (or few) of the tuples of other classes
o
Steps:
·
Rules are learned one at a time
·
Each time a rule is learned, the tuples covered by
the rules are removed
·
The process repeats on the remaining tuples unless termination condition, e.g., when no
more training examples or when the quality of a rule returned is below a user-specified
threshold
o
Comp. w. decision-tree induction: learning a set of
rules simultaneously
Related Topics