Banking - Recent Advancements in Banking Sector | 12th Economics : Chapter 6 : Banking
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 6 : Banking
Recent Advancements in Banking Sector
Recent Advancements in Banking Sector
1. E- Banking
Online banking, also known as internet banking, is an electronic
payment system that enables customers of a bank or other financial institution
to conduct a range of financial transactions through the financial
institution’s website. The online banking system typically connects to or be
part of the core banking system operate by a bank and is in contrast to branch
banking which was the traditional way customers accessed banking services.
Today, “virtual banks” (or “direct banks”) have only an internet
presence, which enables them to lower costs than traditional brick-and-mortar
banks.

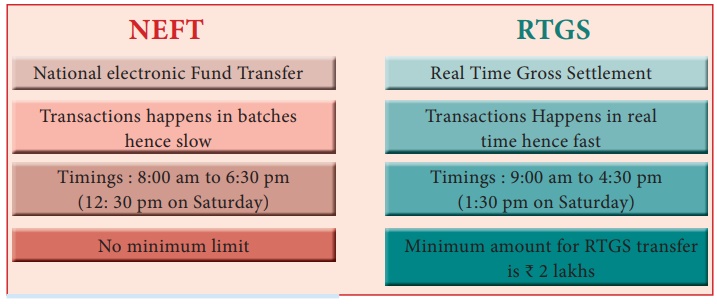
2. RTGS and NEFT
Inter Bank Transfer enables electronic transfer of funds from the
account of the remitter in one Bank to the account of the beneficiary
maintained with any other Bank branch. There are two systems of Inter Bank
Transfer - RTGS and NEFT. Both these systems are maintained by RBI. NEFT
operates in half hourly batches. Currently there are twenty three settlements
from 8 am to 7 pm on all working days including working Saturdays. Therefore,
the beneficiary can expect to get the credit for the transactions put through
between 8 am to 5.30 pm on all working days including working Saturdays on the
same day.
For transactions settled in the 6.30 and 7 pm batches on all working
days including working Saturdays, the credit will be afforded either on the
same day or on the next working day.
3. ATM (Automated Teller Machine)
ATMs transformed the bank tech system when they were first
introduced in 1967. The next revolution in ATMs is likely to involve
contactless payments. Much like Apple Pay or Google Wallet, soon we will be
able to conduct contactless ATM transactions using a smartphone.
Some ATM innovations are already available overseas. For example,
biometric authentication is already used in India, and its recognition is in
place at Qatar National Bank ATMs. These technologies can help overall bank
security by protecting against ATM hacks.

4. Paytm
Payments Bank. In August 2015, Paytm received a license from RBI
to launch a payments bank. The Paytm Payments Bank is a separate entity in
which founder Vijay Shekhar Sharma will hold 51% share, One97 Communications
holds 39% and 10% will be held by a subsidiary of One97 and Sharma.
5. Debit card and Credit Card

A Debit card is a card allowing the holder to transfer money
electronically from their bank account when making a purchase.

A credit card is a payment card issued to users (cardholders) to enable
the cardholder to pay a merchant for goods and services based on the
cardholder’s promise to the card issuer to pay them for the amounts so paid
plus the other agreed charges. The card issuer (usually a bank) creates a
revolving account and grants a line of credit to the cardholder, from which the
cardholder can borrow money for payment to a merchant or as a cash advance. In
other words, credit cards combine payment services with extensions of credit.
Complex fee structures in the credit card industry may limit customers’ ability
to shopping.![]()
6. Recent Issues
Once the borrower fails to make interest or principal payments for
90 days the loan is considered to be a non-performing asset (NPA). NPAs are
problematic for financial institutions since they depend on interest payments
for income. As on now the size of NPAs is estimated to be around 10 lakh
crores. As a result, the banks do not have adequate capital. Hence the
Government (of India) is forced to infuse capital to the banks by using poor
tax – payers money. Already more than a sum of ₹ 2 lakh crores have been
injected. During 2018 - 19, the GOI has infused ₹ 68,000 crores into the
banking system. Thus the NPAs ultimately affect the common people.
7. Merger of Banks
Union Cabinet decided to merge all the remaining five associate
banks of State Bank Group with State Bank of India in 2017. After the
Parliament passed the merger Bill, the subsidiary banks have ceased to exist.
Five associates and the Bharatiya Mahila Bank have become the part
of State Bank of India (SBI) beginning April 1, 2017. This has placed State
Bank of India among the top 50 banks in the world. The five associate banks
that were merged are State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur (SBBJ), State Bank of
Hyderabad (SBH), State Bank of Mysore (SBM), State Bank of Patiala (SBP) and
State Bank of Travancore (SBT). The other two Associate Banks namely State Bank
of Indore and State Bank of Saurashtra had already been merged with State Bank
of India. After the merger, the total customer base of SBI increased to 37
crore with a branch network of around 24,000 and around 60,000 ATMs across the
country.
Related Topics