Measures of dispersion - Quartile Deviation | 11th Business Mathematics and Statistics(EMS) : Chapter 8 : Descriptive statistics and probability
Chapter: 11th Business Mathematics and Statistics(EMS) : Chapter 8 : Descriptive statistics and probability
Quartile Deviation
Quartile Deviation
Quartile
Deviation is defined as QD = ½ (Q3
– Q1) It may also be called as semi- inter quartile.
where Q1 and Q3 are the first and third quartiles of the distribution
respectively and Q3 –
Q1 is called as inter
quartile range.
(i) Relative measures for QD
Quartile
deviation is an absolute measure of dispersion. The relative measure
corresponding to this measure, called the coefficient of quartile deviation is
calculated as follows:
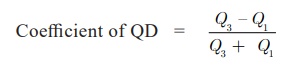
Coefficient
of quartile deviation can be used to compare the degree of variation in
different distributions.
(ii) Computation of Quartile Deviation
The
process of computing quartile deviation is very simple since we just have to
compute the values of the upper and lower quartiles that is Q3 and Q1 respectively.
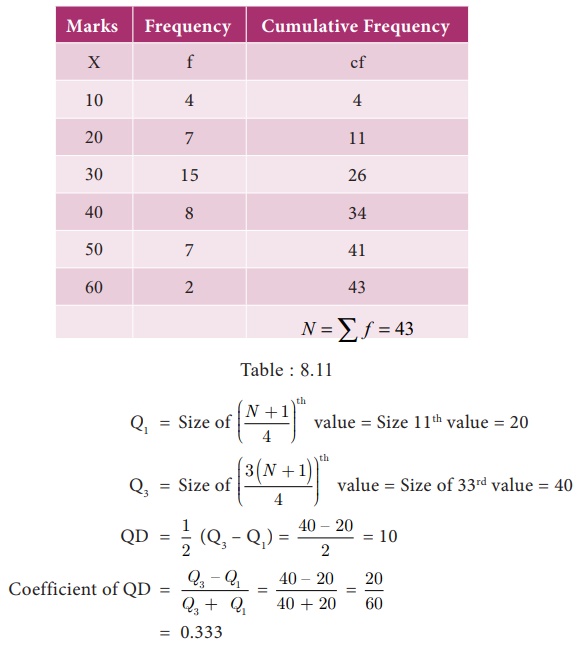
Example 8.16
Calculate
the value of quartile deviation and its coefficient from the following data
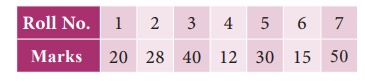
Solution :
Marks are
arranged in ascending order
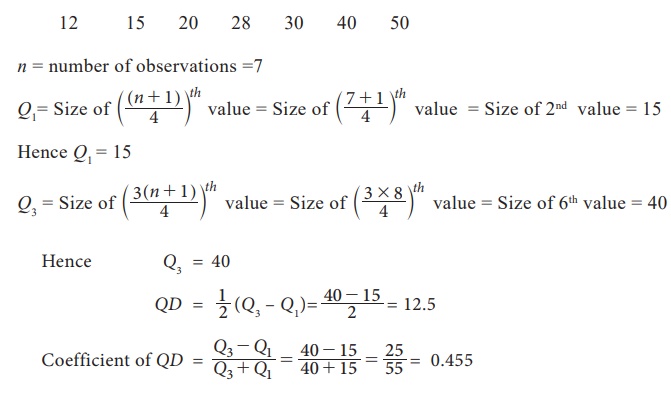
Hence
coefficient of QD = 0.455
Example 8.17
Compute
coefficient of quartile deviation from the following data
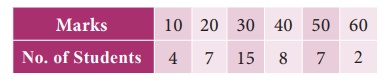
Solution :
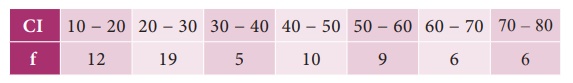
Example 8.18
Compute
Quartile deviation from the following data
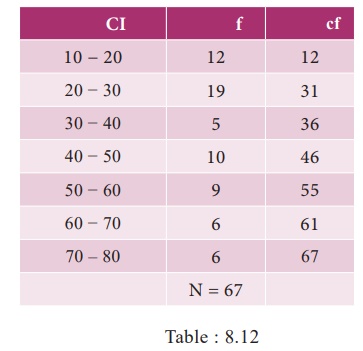
Solution :

Related Topics