Measures of central tendency - Average | 11th Business Mathematics and Statistics(EMS) : Chapter 8 : Descriptive statistics and probability
Chapter: 11th Business Mathematics and Statistics(EMS) : Chapter 8 : Descriptive statistics and probability
Average
Average
- Recall
There are several measures of
central tendency for the data. They are
┬Ę
Arithmetic Mean
┬Ę
Median
┬Ę
Mode
┬Ę
Geometric Mean
┬Ę
Harmonic
Mean
Arithmetic Mean (discrete case)
Arithmetic mean of a set of
observations is their sum divided by the number of observations. The
observation are classified into a) Ungrouped data and b) Grouped data.
a) Ungrouped data
(i) Direct Method:
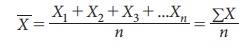
where ![]() is Arithmetic Mean, ŌłæX is sum of all the values of the variable X and n is number of
observations.
is Arithmetic Mean, ŌłæX is sum of all the values of the variable X and n is number of
observations.
(ii) Short-cut method
The arithmetic mean can be
calculated by using any arbitrary value A
as origin and write d as the
deviation of the variable X then,

b) Grouped data
Direct method
The formula for computing the
mean is
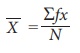
where f is frequency; X is the
variable; N = Ōłæ f i.e. total frequency.
(ii) Short-cut method
The arithmetic mean is computed
by applying the following formula:
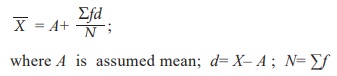
Arithmetic mean for Continuous case
The arithmetic mean may be
computed by applying any of the following methods:
(i) Direct
method
(ii) Short-cut
method
(iii) Step
deviation method
(i) Direct method
When direct method is used
arithmetic mean is defined as
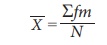
Where m = midpoint of each of the class interval,
f = the
frequency of each class interval
N = Ōłæf = total frequency
(iii) Short-cut method
The arithmetic mean is computed
by applying the following formula
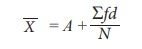
where A is assumed mean or arbitrary value, d=mŌĆōA is deviations of mid-point from assumed mean and N=Ōłæf
(iii) Step Deviation Method
In case of grouped or continuous
frequency distribution, the arithmetic mean
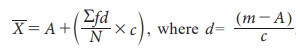
is any arbitrary value or assumed
mean and c is the magnitude of class
interval.
Mode:
Mode is the value which repeats maximum
number of times among the given observations.
Median:
Median is exactly a middle value
and it exceeds and exceeded by the same number of observations. Median is one
of the positional measure. Some other related positional measures are also
described below.
Related Topics