Chapter: Aquaculture Engineering : Water Transport
Pumps
Pumps
Pumps are mechanical devices that add energy to fluids by transforming mechanical energy (normally from electric motors) to potential and/or kinetic energy of the fluid. Increase in potential energy is illustrated by the lifting of water to an elevated tank, while the increase in velocity and hence the flow rate through a pipeline by pumping increases the kinetic energy of the water. Pumps are commonly used in aquaculture systems, usually to increase the system pressure and thereby force the water to move against an energy gradient. In most aquaculture situations pumps are used to lift water from one level to another. Water will flow only when energy is available to create a flow, i.e. there is a positive energy gradient. In hydraulic systems pumps are used to create the pressure which is nor-mally high. This allows the fluid to do work, such as turn shafts or extend a hydraulic cylinder against a load. Oil is commonly used in such systems, but those using water are also available.
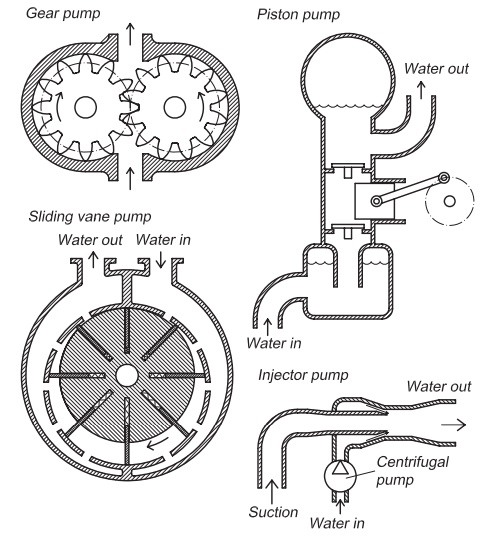
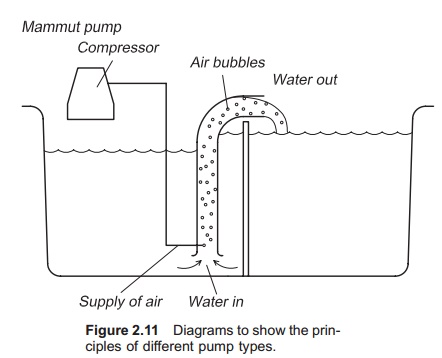
Pumps are fairly efficient machines for transfer-ring
energy to water, provided they are correctly selected for the job. The key
requirement when selecting a pump is that there shall be a close cor-relation
between the system requirements and the maximum operating efficiency of the
pump; sub-optimal pump selection may result in significantly increased
operating and maintenance costs and/or result is system failure.
Related Topics