Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Nonsporing Anaerobes
Providencia
Providencia
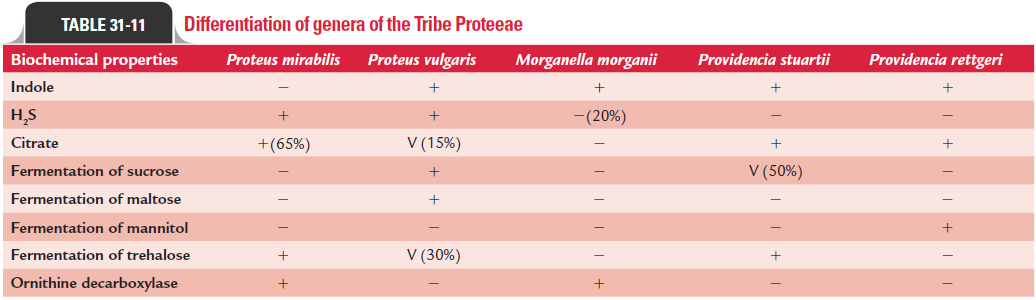
The genus Providencia consists of five species: Providencia stuartii, Providencia rettgeri, Providencia alcalifaciens, Providencia rustigianii,and Providencia heimbachae. Providencia spp. are Gram-negative, motile bacilli but do not show swarming on solid media. They produce a fruity smell and on DCA form yellow to orange colo-nies. All the species typically deaminate phenylalanine; only P.rettgeri hydrolyses urea consistently. Other biochemical proper-ties of Providencia are summarized in Table 31-11.Providencia species have been isolated from urine, stool, and blood, as well as from the throat, perineum, axilla, and wounds from humans.
P. stuartii is the most common species causing infection inhumans. P. stuartii and, to a lesser extent, P. rettgeri are commonly found in patients with long-term indwelling urinary catheters. Older people are at higher risk of infection by P. stuartii or P. rettgeri, because these infections are associated with the use of urinary catheters, and the use of such catheters is much more common in the older people. P. stuartii constitutes nearly 60% of all bacterial pathogens isolated from urine of these patients. P.stuartii possesses an adhesin, mannose-resistant/Klebsiella-like(MR/K) hemagglutinin protein, which allows it to adhere to the urinary catheter. From urine, P. stuartii may invade to blood, causing infection of the blood stream, which is common in elderly patients and in immunocompromised patients.
P. alcalifaciens, P. rettgeri, and P. stuartii also may cause inva-sive diarrhea. These species are emerging as important causes of traveler’s diarrhea in adults.
Diagnosis of UTI and diarrhea is made by routine urine and feces culture. Blood culture is useful for diagnosis of suspected blood stream infections. Antibiotics susceptibility testing is useful for treatment with suitable antibiotics, because many Providencia species show resistance to multiple antibiotics.
P. stuartii is the most resistant species of all Providencia spe-cies. It is resistant to tetracyclines, older penicillins, cephalo-sporins, fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, and TMP–SMX. It is susceptible to late-generation cephalosporins, aztreonam, and carbapenems.
P. alcalifaciens and P. rustigianii are usually susceptible toantibiotics. They usually are susceptible to fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, late-generation cephalosporins, aztreonam, carbapenems and TMP–SMX. They are resistant to tetracy-clines, older penicillins, and cephalosporins.
Related Topics