Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Principles of cooking and methods of Cooking
PRINCIPLES OF COOKING AND METHODS OF COOKING
Some foods like fruits, vegetables and nuts are eaten raw. It is good that they are consumed raw as in the uncooked condition they retain most of their nutritive value. However most foods are cooked before being consumed.
The process of subjecting foods to the action of heat is termed as cooking.
Objectives of cooking.
Improves the taste and food quality.
Cooking food to the required temperature for a required length of time can destroy all harmful microorganisms in food.
Cooking improves digestibility.
Cooking increases variety.
Methods of cooking
Moist heat methods
Boiling
Boiling is cooking foods by just immersing them in water at 100 o C and maintaining the water at that temperature till the food is tender. It does not require special skill and equipment. It is time consuming.
Simmering
When foods are cooked in a pan with a well fitted lid at a temperature just below the boiling point 82 o -99 o C , it is known as simmering. It is a useful method when foods have to be cooked for a long time to make it tender. (eg) vegetables.
Poaching
This involves cooking in the minimum amount of liquid at a temperature of 80 o -85 o C. Foods generally poached are eggs and fish.
Stewing
This is a gentle method of cooking in a pan with a tight fitting lid, using small quantities of liquid to cover only half the food. The liquid is brought to a boiling point and then the heat applied is reduced to maintain the cooking at simmering temperature ie., 98 o C. Apples can be cooked by this method.
Steaming
This method requires the food to be cooked in steam. This is generated from vigorously boiling water or liquid in a pan so that the food is completely surrounded by steam and not in contact with the water or liquid. Here the food gets cooked at 1000C.
Pressure cooking
In pressure cooking escaping steam is trapped and kept under pressure so that the temperature of the boiling water and steam can be raised above 100 o C thus reducing cooking time. Foods cooked in pressure cooker are rice, dhal, vegetables and meat.
Dry heat methods
In this either air or fat is used as the medium of cooking.
Air as medium of cooking
Grilling
Grilling consists of placing the food below or above or in between a red-hot surface. This results in the browning of the food.
Pan broiling or roasting
When food is cooked uncovered on heated metal or a frying pan, the method is known as pan-broiling, (e.g) chapathis.
Baking
Here food gets cooked by hot air inside the oven. Foods baked are generally brown and crisp on the top and soft and porous in the centre, (eg) cakes and breads. The temperature that is normally maintained in the oven is between 120 o C-260 o C.
Fat as medium of cooking
Sauteing
This method involves cooking in just enough of oil to cover the base of the pan. Foods cooked by sauteing are generally vegetables used as side dishes in a menu.
Shallow fat frying
Here food is cooked on a tava with little oil (eg) chapathi, cutlets, etc.
Deep fat frying
Food is totally immersed in hot oil and cooked. The temperature maintained is 180 o - 220 o C (eg.) Samosa, Bajji, etc. The taste of the food is improved along with texture.
Other cooking methods
Braising
Braising is a combined method of roasting and stewing in a pan with a tight fitting lid. Meat is cooked by this method.
Microwave cooking
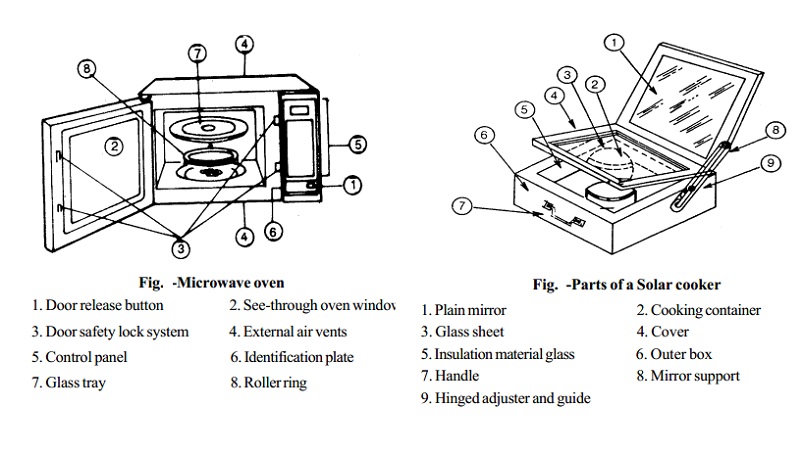
1. Door release button
2. See-through oven window
3. Door safety lock system
4. External air vents
5. Control panel
6. Identification plate
7. Glass tray
8. Roller ring
Electromagnetic waves from a power source called magnetron are absorbed by the food and food becomes hot at once. Microwave cooking enhances the flavour of food because it cooks quickly with little or no water and thus preserves the natural colour of vegetables and fruits.
SOLAR COOKING
1. Plain mirror 2. Cooking container
3. Glass sheet 4. Cover
5. Insulation material glass 6. Outer box
7. Handle 8. Mirror support
9. Hinged adjuster and guide
Solar cooker works on solar energy. Solar cooker consists of well insulated box, the inside of which is painted dull black and is covered by one or more transparent covers, the purpose of which is to trap the heat inside the solar cooker. The temperature maintained is around 140 o C. Cost of the cooker and the maintenance cost is low. It takes longer time and special vessels need to be used.
Related Topics