Zoology - Principles of Inheritance and Variation: Summary | 12th Zoology : Chapter 4 : Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 4 : Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Principles of Inheritance and Variation: Summary
Summary
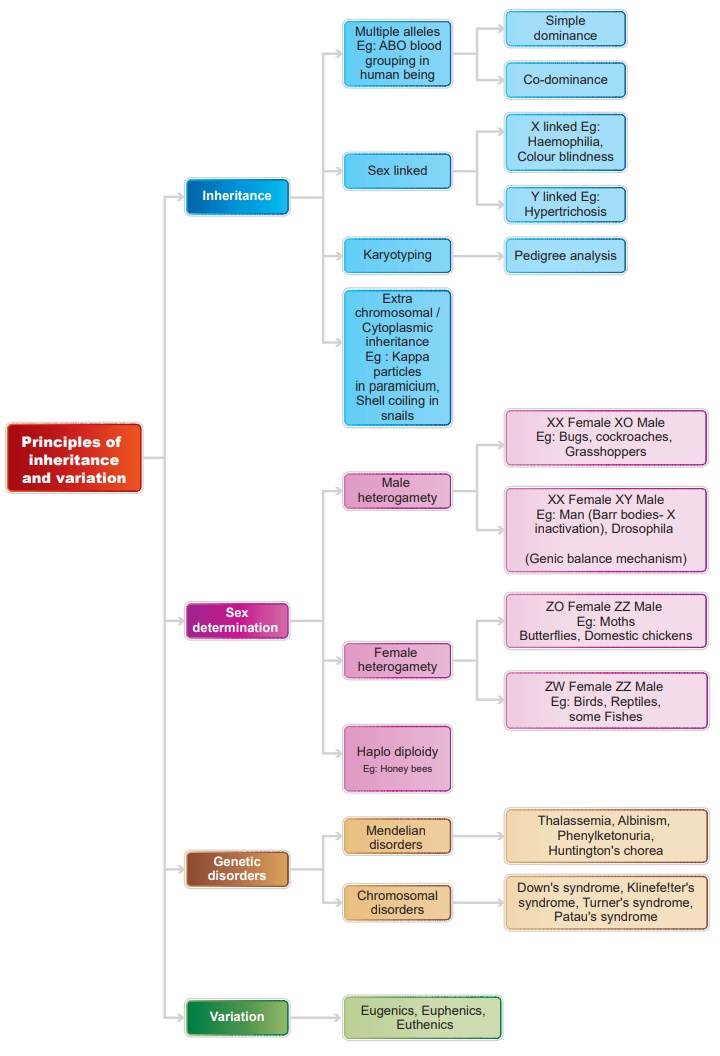
Genetics is a branch of biology that deals with the study of heredity and variation. It describes how characteristics and features pass on from the parents to their offsprings in successive generations. Variation is the degree by which progeny differ from their parents. A set of three or more alleles of the same gene occupying the same locus in a given pair of homologous chromosomes controlling a particular trait is called Multiple allele. ABO blood grouping in man is a good example for multiple allelism. Apart from A and B antigens, the RBC’s of humans contain a special type of antigen called Rh antigen/Rh factors. Erythroblastosis foetalis, also called haemolytic disease of the newborn, in which the red blood cells of a foetus are destroyed due to maternal immune reaction resulting from a blood group incompatibility between the foetus and the mother.
The mechanism of
determination of male and female individuals in a species is called sex
determination. The chromosomes are different in two sexes and referred to as
allosomes; the remaining chromosomes are named autosomes. In human beings a
normal female has 22 pairs of autosomes and a pair of sex chromosomes (44A +
XX) and a male has 22 pairs of autosomes and a pair of sex chromosomes (44A +
XY). In birds, reptiles and some fishes, sex chromosomes are ZZ in males and ZW
in females. In moths and butterflies, sex chromosomes are represented as ZZ in
males and ZO in females. Sex in Drosophila is determined polygenically. The sex
of an individual depends upon the ratio of X chromosomes to autosome sets. The inheritance
of a trait that is determined by a gene located on one of the sex chromosomes
is called sex linked inheritance. Haemophilia, colourblindness, muscular
dystrophy are some examples for X linked inheritance in human beings.
Pedigree analysis is the
study of traits as they have appeared in a given family line for several
generations. The genetic disorders are of two types- Mendelian and chromosomal.
Alternations or mutation in single gene causes Mendelian disorders like,
thalassemia, albinism, phenylketonuria, and Huntington’s chorea. Chromosomal
abnormalities arise due to chromosomal non-disjunction, translocation,
deletion, duplication and inversion. Downs syndrome, Klinefelter’s syndrome,
Turner’s syndrome and Patau’s syndrome are some of the chromosomal disorders.
Downs syndrome is due to trisomy of chromosome 21. Presence of trisomic
condition of chromosome 13 results in Patau’s syndrome. In Turner’s syndrome
the sex chromosome is XO and in Klinefelter’s syndrome the condition is XXY. An
idiogram refers to a diagrammatic representation of chromosomes.
The cytoplasmic extra nuclear genes have a characteristic pattern of inheritance which does not resemble genes of nuclear chromosomes and are known as Extrachromosomal/ Cytoplasmic inheritance. The betterment of human race can be achieved by methods like Eugenics, Euthenics and Euphenics.
Related Topics