Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Mendelian disorders | 12th Zoology : Chapter 4 : Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 4 : Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Mendelian disorders
Mendelian
disorders
Alteration or mutation
in a single gene causes Mendelian disorders. These disorders are transmitted to
the offsprings on the same line as the Mendelian pattern of inheritance. Some
examples for Mendelian disorders are Thalassemia, albinism, phenylketonuria ,
sickle cell anaemia, Huntington's chorea, etc., These disorders may be dominant
or recessive and autosomal or sex linked.
Thalassemia
Thalassemia is an
autosomal recessive disorder. It is caused by gene mutation resulting in
excessive destruction of RBC’s due to the formation of abnormal haemoglobin
molecules. Normally haemoglobin is composed of four polypeptide chains, two alpha
and two beta globin chains. Thalassemia patients have defects
in either the alpha or beta globin chain causing the production of abnormal
haemoglobin molecules resulting in anaemia.
Thalassemia is
classified into alpha and beta based on which chain of haemoglobin molecule is
affected. It is controlled by two closely linked genes HBA1 and HBA2 on
chromosome 16. Mutation or deletion of one or more of the four alpha gene
alleles causes Alpha Thalassemia. In Beta Thalassemia, production
of beta globin chain is affected. It is controlled by a single gene (HBB) on
chromosome 11. It is the most common type of Thalassemia and is also known as
Cooley’s anaemia. In this disorder the alpha chain production is increased and
damages the membranes of RBC.
Phenylketonuria
It is an inborn error of
Phenylalanine metabolism caused due to a pair of autosomal recessive
genes. It is caused due to mutation in the gene PAH (phenylalanine hydroxylase
gene) located on chromosome 12 for the hepatic enzyme “phenylalanine
hydroxylase” This enzyme is essential for the conversion of phenylalanine to
tyrosine. Affected individual lacks this enzyme, so phenylalanine accumulates
and gets converted to phenylpyruvic acid and other derivatives. It is
characterized by severe mental retardation, light pigmentation of skin and
hair. Phenylpyruvic acid is excreted in the urine.
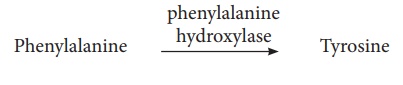
Albinism
Albinism is an inborn
error of metabolism, caused due to an autosomal recessive gene. Melanin pigment
is responsible for skin colour. Absence of melanin results in a condition
called albinism. A person with the recessive allele lacks the tyrosinase enzyme
system, which is required for the conversion of dihydroxyphenyl alanine (DOPA)
into melanin pigment inside the melanocytes. In an albino, melanocytes are
present in normal numbers in their skin, hair, iris, etc., , but lack melanin
pigment.

Huntington’s chorea
It is inherited as an
autosomal dominant lethal gene in man. It is characterized by involuntary
jerking of the body and progressive degeneration of the nervous system,
accompanied by gradual mental and physical deterioration. The patients with
this disease usually die between the age of 35 and 40.
Related Topics