Preparation of Karyotype, Applications of Karyotyping - Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Karyotyping | 12th Zoology : Chapter 4 : Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 4 : Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Karyotyping
Karyotyping
Karyotyping is a
technique through which a complete set of chromosomes is separated from a cell
and the chromosomes are arranged in pairs. An idiogram refers to a diagrammatic
representation of chromosomes.
Preparation of Karyotype
Tjio and Levan (1960)
described a simple method of culturing lymphocytes from the human blood.
Mitosis is induced followed by addition of colchicine to arrest cell division
at metaphase stage and the suitable spread of metaphase chromosomes is
photographed.
The individual
chromosomes are cut from the photograph and are arranged in an orderly fashion
in homologous pairs. This arrangement is called a karyotype. Chromosome
banding permits structural definitions and differentiation of chromosomes.
Applications of Karyotyping:
·
It helps in gender identification.
·
It is used to detect the chromosomal aberrations like deletion,
duplication, translocation, nondisjunction of chromosomes.
·
It helps to identify the abnormalities of chromosomes like
aneuploidy.
·
It is also used in predicting the evolutionary relationships
between species.
·
Genetic diseases in human beings can be detected by this
technique.
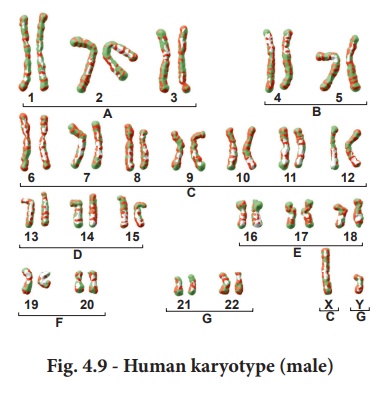
Human Karyotype
Depending upon the
position of the centromere and relative length of two arms, human chromosomes
are of three types: Metacentric, sub metacentric and acrocentric. The
photograph of chromosomes are arranged in the order of descending length in
groups from A to G (Fig. 4.9).
Related Topics