Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Reproductive and Obstetrics
Physiology - Gynaecology
Gynaecology
Physiology
·
GnRH:
· 10 amino acids – only lasts seconds Þ requires portal circulation
· Pulsitile release
·
Stimulates release of FSH + LH
· Inhibited by progesterone (strongest inhibitor), PRL, inhibin, testosterone, oestrogen, stress
· FSH:
acts on germ cells
·
LH: acts on supporting tissue:
·
Male: Leydig cells ® testosterone
·
Female: Thecal cells ®
testosterone ® acted on by aromatase (produced by granulosa cells) ®
oestradiol
·
Oestrogen: three types:
·
Oestradiol: ovary
·
Produced by follicles
·
® Mucus
·
-ive feedback on FSH
·
Above a threshold ® LH
·
Unopposed oestradiol causes
endometrial hyperplasia – growth without the maturing effect of progesterone
·
Oestriol: placenta
·
Oestrone: metabolised from
androgens (eg testosterone) by adipose tissue · Female
fetus has several million eggs, by puberty has 300 – 400 eggs · Follicle
at ovulation is 2 cm
·
Infection control:
·
Sperm carry bacteria and viruses
into uterus. If mucus inhibits sperm ® ¯infection, which would otherwise
cause inflammation and ¯chances of implantation
·
Oestrogen ® Vaginal epithelium thickens during cycle ® glycogen ® lactobacilli
®acidity ® ¯other bacteria
·
Menstrual Cycle:
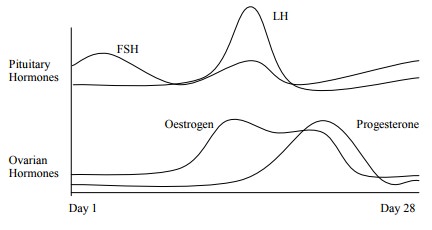
·
Inhibin from developing follicle
suppresses FSH compared with LH ® LH surge
· Phases for uterus endothelium: menstrual ® proliferative/follicular ® secretory/ progestational
·
Human Chorionic Gonadatrohpin
(hCG) from implanted zygote signals corpus luteum to continue progesterone
production.
Related Topics