Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Reproductive and Obstetrics
Labour
Labour
·
Definition:
o Regular contractions (usually 3 in 10 minutes, lasting 40 – 50 seconds)
o Cervical change:
§ More anterior
§ Effaced: depth of „rim‟ normally 2 cm, 50% effaced = 1 cm
§ Dilated
§ Soft (hard = like forehead, normal = like nose, soft = like chin)
o +/- Show (mucus plug) or ROM (rupture of membranes)
·
80% of all pregnancies last 38 -
42 weeks. 10% are preterm. 10% beyond the start of the 43rd week (although biggest cause is
inability to reliably date conception)
· How does it start:
o Uterus: distension, gap junctions in smooth muscle, oxytocin receptors
o Cervical ripening: PGE breaks down collagen + effect of Braxton-Hicks
contractions
o Fetus: ?vasopressin released in response to transient hypoxia, ?other
hormones
· Examination:
o Mother: monitor BP (hypo ® ?blood loss, hyper ® ?pre-eclampsia), pulse, temperature (eg infection if prolonged period post-rupture)
o Foetal position: by abdominal inspection and palpation. 2/3rds of babies head first with back on the left. Descent – what portion of the head is below the pelvis (eg 3/5ths)
o Fundal height
o Foetal welfare:
§ CTG for 20 minutes (but incidence of fetal distress in early labour is low. Continuous monitoring ® interventions)
§ Intermittent auscultation every 15 – 30 minutes following a contraction. Approx every 5 minutes in 2nd stage.
·
Fetal position – Definitions:
o Lightening:
§ = Baby dropping. ® ¯SFH, development of lower segment of the uterus, descent of fetal head into pelvis
§ 1st pregnancy: 2 – 3 weeks before
§ 2nd pregnancy: may not be till 2nd stage of labour – uterus has lost some of its tone – doesn‟t push baby down so well
o Fetal lie: relation of fetal spine to mother‟s spine. Longitudinal
(cephalic or breech), transverse, oblique (unstable lie)
o Fetal presentation: portion of the fetus in the birth canal:
§ Cephalic (96%): vertex, sinceput, brow, face
§ Breech (3%): Frank (extended – „foot in mouth‟), Complete (knees and
hips flexed),
§ Incomplete (footling). Only worry
after 36 weeks – it can turn fairly easily before then
§ Transverse or oblique (1%)
o Fetal Attitude: “posture” of the fetus, eg extended neck
o Fetal Position: Relation of occiput (vertex) to the maternal pelvis.
Left or Right, Anterior, Posterior, or Transverse, eg
§ LOA = left occiput anterior (face down, 8 o‟clock) – most common position
§ LOT = left occiput transverse
§ OA = occiput anterior (6 o‟clock)
· LOP = left occiput
posterior (face up)
· Sutures:
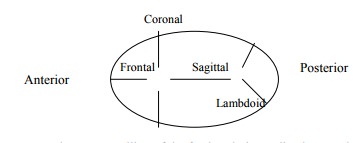
o Caput succedaneum: swelling of the fetal scalp immediately over the os
o Moulding: Overlapping cranial bones in cephalic presentation. May ¯BPD (biparietal parameter) by 0.5 – 1.0 cm
o Crowning: encirclement of largest diameter of the fetal head by the
vulvar ring
·
Adequate sized pelvis has:
o Wide pubic angle (skeleton can fit a fist)
o > 10 cm between ischial spines
o Can‟t reach sacral prominence (top of sacrum) on vaginal exam
· Delivery of the baby:
o Engagement: time when BPD passes through the pelvic inlet. Abdominal,
2/5 is palpable. If engaged, you know the pelvic inlet is big enough
o Descent: Extension of fetal body.
o Flexion of neck
o Internal rotation. Head rotates from 8 o‟clock to 6 o‟clock. Usually
descent through pelvis transverse, then need to rotate face downwards
o Extension: once head reaches vulva, occiput in direct contact with symphasis. Ritgen Manoeuvre – upward pressure on chin through perineum from below, downward pressure on occiput (stop anterior tear)
o External Rotation/Restitution – occiput goes back to original position (transverse) – now realigned again with shoulder. Check for nuchal cord (around neck), clear nasopharynx
o Expulsion: anterior shoulder, followed by posterior shoulder. Clamp and
cut cord, with baby below the level of the placenta if possible or if prem
o Episiotomy: NOT routine. In NZ do them medio-lateral at time of
Crowning. 1st degree = superficial, 4th degree = deep, including rectal sphincter and mucosa
· Stages of labour:
o Stage 1: Cervical effacement and dilation - Friedman phase – plot on a
partogram: · Latent phase (cervical softening). 20 hours in nullip, 14 hours in multip
· Active Phase: Acceleration phase and deceleration phase (= transition). Cervix dilates 1.0 – 1.2 cm/hr (Primiparous), 1.5 cm/hour (multiparous) to a maximum of 10cm dilated
o Stage 2: begins at 10 cm dilated and ends with delivery of the baby. 2 hours in primip, 45 minute – 1 hour in multip.
o Stage 3: separation and expulsion of the placenta · Active
management of 3rd stage
· Especially if risk of PPH (big baby/twins/previous PPH/anything that makes the uterus big eg polyhydramnios).
·
Give 5 – 10 units Syntocinon (IV
if risk of PPH, IM otherwise) when shoulder delivers
·
Can use syntometrin (oxytocin + a
little ergometrine – contraindicated if hypotension)
· If PPH then IV infusion following bolus (T½ of Syntocinon is 3 – 5 minutes)
·
Complications of Syntocinon:
hyperstimulation (® fetal hypoxia), uterine rupture, water intoxication (Syntocinon is like
ADH), uterine muscle fatigue (® post-delivery uterine
§ atony ® risk of PPH)
§ Signs of placental separation: sudden rush of blood, uterus rises, cord lengthens
§ OK to wait if no heavy bleeding. Gentle traction on chord with supra-pubic pressure (stops uterus coming down) or fundal massage and maternal bearing down without traction
§ Can manually deliver (place hand into uterus and separate) – if no
haemorrhage then wait for anaesthesia
o Then inspection, repair, rectal exam
· Cord prolapse: Cord comes through cervix before head. C-section usually indicated. In meantime try to control pressure on cord – don‟t push it back up. Risk if transverse lie
·
Pain Relief:
o Inhalation agent (eg nitrous oxide)
o Epidural: complications – hypotension, urinary retention, total spinal
block, prolonged expulsive effort
o TENS
o Narcotics eg pethidine: action lasts 3 hours and can cause fetal
respiratory distress – don‟t give if delivery expected within 3 hours
Related Topics