Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school
Parts of a flower
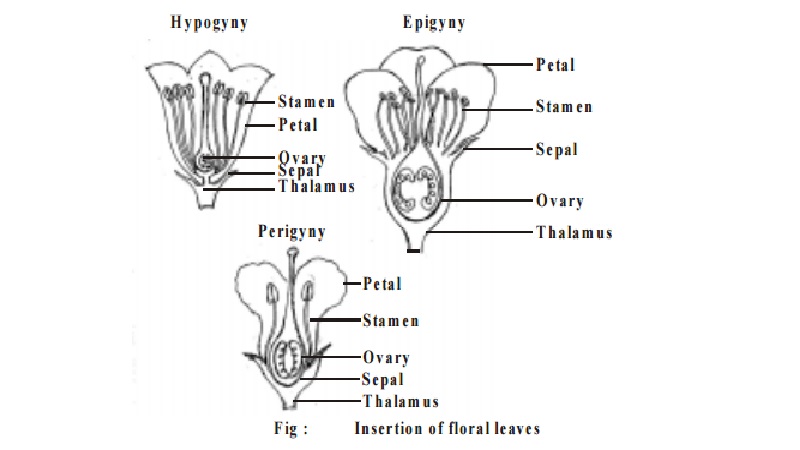
Parts of a flower
A typical flower consists of following parts:
1. Bracts and Bracteoles
3.Whorls of flower
Calyx
Corolla
Androecium
Gynoecium
Essential and Non-Essential Parts
Of the four parts of a flower, androecium and gynoecium are known as essential organs because they have a direct role in reproduction i.e. pollination and fertilization which lead to development of fruit and seeds from flower. The calyx and corolla do not have a direct role in these processes. Hence they are described as non-essential organs or accessory organs.
Bracts and Bracteoles
Bracts are special leaves at whose axil flowers develop. For example, in an axillary flower, the leaf from whose axil the flower develops becomes the bract. But bracts are not always present. If a bract is found, the flower is called bracteate; if it is absent then the flower is described as ebracteate. When bracts are present, they protect flower buds in the young stage. Sometimes small and thin bract-like structures are present on the pedicel between the flower and the bract. These are called bracteoles. the bracteoles may be one or two in number. Flowers having bracteoles are described as bracteolate and flowers where bracteoles are absent are calledebracteolate.
The receptacle (thalamus)
The thalamus is the short floral axis, with compressed nodes and internodes on which various floral leaves are inserted.
Variation of the Receptacle
In a few cases, internodes become distinct and elongated. The elongated internode between the calyx and corolla is theanthophore as in Caryophyllaceae.
The internode elongated between the corolla and the androecium is called the androphore eg. Passiflora (family - Passifloraceae).
The elongated internode between the androecium and the gynoecium is called the gynophore as in Capparis [Capparidaceae] When both androphore and gynophore are present, they are called gynandrophore or androgynophore e.g. Gynandropsis. When the thalamus is prolongated beyond the ovary, it is called the carpophore as in the Coriander, Foeniculum etc.
Calyx
The calyx is the outermost whorl of a flower composed of sepals. The sepals are usually green in colour, but sometimes, become brightly coloured then, said to be petaloid as in Caesalpinia pulcherrima. in Musseanda frondosa the sepals are transformed into large, yellow or white and leafy structure.
The primary function of the calyx is protective. It protects the inner parts of the flower from mechanical injury, rain and excessive sun shine, and from drying out in the bud condition. Green in colour, it can also do the phosynthetic function. When petaloid, it performs the function of attracting insects for pollination. When spiny, its function is defensive and as pappus, it helps in the dispersal of fruit.
The calyx may be regular or irregular. The sepals are free from one another and is said to be ploysepalous, when united united,gamosepalous.
Corolla
The corolla is the second accessory floral whorl consisting of petals.
The petals of the corolla are usually variously coloured and of delicate texture. They may be free (polypetalous) or united (gamopetalous). The primary function of the corolla is to attract insects for polinatioin and also serves to protect the essential organs.
Androecium
It is the third whorl of the flower. It is considered as the male part of the flower. The androecium is made up of stamens or microsporophylls. Each stamen has a slender stalk called filament, bearing the anther (microsporangial sorus). Usually the anther consists of two lobes. The two lobes of an anther are connected by a tissue called connective. Each anther lobe has two pollen sacs(microsporangia). Each pollen sac consists of innumerable Pollen grains (microspores).
Sterile stamen or staminode
In some plants, a stamen may not develop any fertile anther. Such sterile stamens are called staminodes eg. Cassia.
Gynoecium
Gynoecium is the collective term for the innermost central whorl of floral appendages. It is considered as the female part of the flower. A unit of gynoecium is called carpel. Following technical terms and related with gynoecium.
Related Topics