Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: Molecular Biology of Cancer
Oncogenes and Proto oncogenes
ONCOGENES AND
PROTO-ONCOGENES
Oncogenes were first discovered on
cancer-causing viruses, but they are found in all normal cells as well. The
original, unmutated wild-type allele of an oncogene is sometimes called the proto-oncogene. The wild-type
proto-oncogene promotes growth and division of the cell.During development of a
multicellular organism, cell division must be closely controlled. Once an organ
or tissue has reached its correct size, it should stop growing. In other words,
its cells should stop dividing. Clearly, mutations in genes that control cell
division are potentially very dangerous. These mutant versions are the
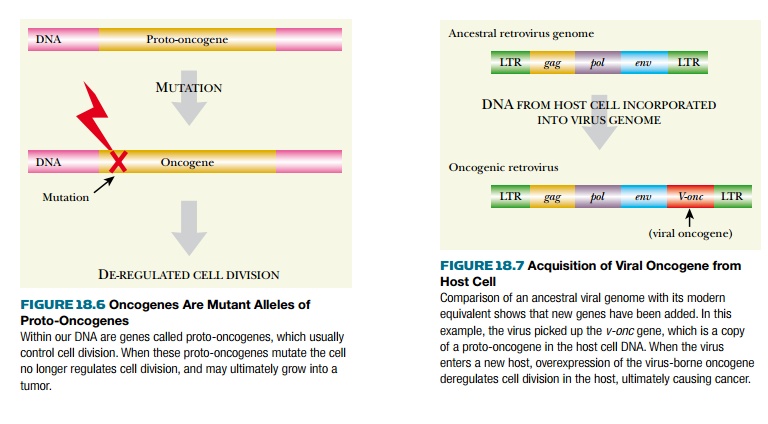
cancer-causing oncogenes (Fig. 18.6).
The genomes of cancer-causing
viruses also contain oncogenes. However, these oncogenes were originally
derived from those of the host cells that the viruses infect. Certain types of
viruses occasionally pick up cellular DNA and incorporate it into the viral
genome. Sometimes they pick up an oncogene and the result is a cancer-causing
or oncogenic virus (Fig. 18.7). The
virus-borne version of an oncogene is sometimes written v-onc to distinguish it
from the cellular version, c-onc. Although quite a few cancer
viruses are known, most human cancers are not due to viruses, but are due to
new mutations of cellular proto-oncogenes to the oncogene form.
Related Topics