Chapter: Biology of Disease: Diet and Disease
Minerals and Trace Elements - Diet and Nutrition
MINERALS AND TRACE ELEMENTS
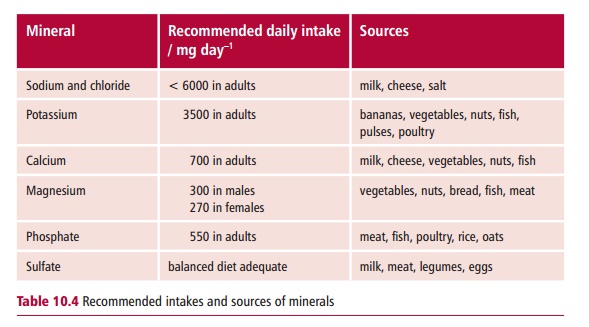
Minerals and trace elements are inorganic dietary
substances required to maintain good health. Minerals include calcium,
magnesium, sodium, potassium, phosphate, chloride and sulfate. They are present
in the body in amounts larger than 5 g and some are required in dietary
quantities of more than 100 mg per day and are provided by a variety of foods (Table 10.4).
Both groups have diverse functions. Minerals play
roles in promoting growth and are important constituents of body tissues such
as bone, teeth, hair, skin and nails, and as cofactors in some enzymes and
other proteins. Sodium, potassium and chloride are required to maintain the
electrolyte and osmotic composition of intra- and extracellular fluids,
generate electrochemical gradients across plasma membranes and for nerve
conductance and muscle contraction. Calcium is an essential component of bone
and teeth, is required for muscle contraction and is a second messenger for
some hormones and neurotransmitters. Magnesium is a cofactor for many enzymes,
especially those utilizing nucleotides involved in energy metabolism and
nucleic acid synthesis. Like calcium, phosphate is needed for bone and teeth
formation and is also a component of nucleic acids and phospholipids. It
activates a number of enzymes, especially some involved in energy metabolism
and is
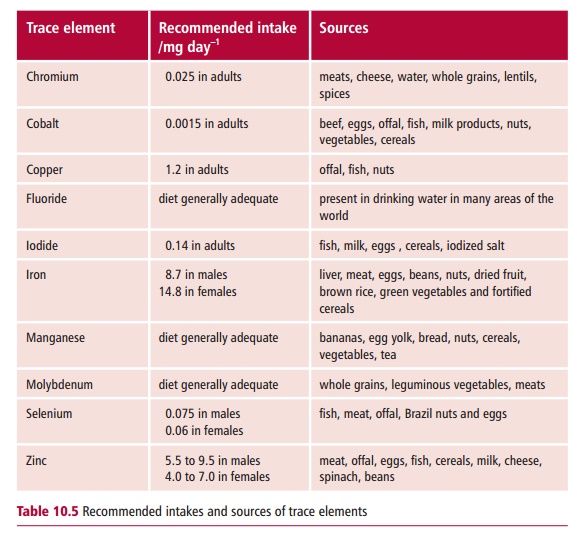
Compared with minerals, trace elements are required
in much smaller quantities, but like them are supplied by a variety of foods (Table 10.5). Trace elements include
iron, cobalt, copper, molybdenum, chromium, manganese, zinc, selenium, iodide
and fluoride. They are present in the body at concentrations less than 100
parts per million and are required in milligrams or even micrograms per day and
a number are toxic in excess.
Trace elements have specific and diverse functions.
Chromium helps maintain blood glucose concentration by acting as a cofactor for
insulin activity. The role of cobalt as a component of vitamin B12, has already
been mentioned. Copper is also an essential cofactor for a number of enzymes,
including those involved in collagen and elastin synthesis and some redox
proteins. Copper is also required for iron absorption and metabolism and
hemoglobin synthesis. Fluoride is necessary for the ‘hardening’ of bone and
teeth. All the thyroid hormones contain iodine as described. Iron is a
component of the prosthetic group, heme found in hemoglobin and myoglobin,
where it maintains its oxidation state and binds a dioxygen molecule. Iron is
also found in the heme of cytochromes and in nonheme iron proteins involved in
electron transfer, where, of course, its oxidation state does alter. Manganese
is essential for the activities of a number of enzymes. For example, pyruvate
carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase function in gluconeogenesis;
arginase is a key enzyme of the urea cycle that detoxifies ammonia produced
during amino acid metabolism and superoxide dismutase is a major antioxidant
defence. Enzymes that contain molybdenum are common and catalyze several
reactions in purine metabolism, for example xanthine oxidase, and maintains the
synthesis of sex hormones. Selenium is a cofactor in, for example, glutathione
peroxidases, and zinc in carbonic anhydrase and RNA polymerase.
Related Topics