Chapter: Environmental Science and Engineering
Mineral Resources
MINERAL RESOURCES
Minerals
are naturally occurring substances with definite chemical and physical
properties.
Uses of minerals
Mineral
is an element or inorganic compound that occurs naturally. The main uses of
minerals are as follows:
Development
of industrial plants and machinery Generation of energy e.g. coal, lignite,
uranium Construction, housing, settlements
Defense
equipments- weapons, settlement Transportation
Communication-telephone
wires, cables, electronic devices Medical system- particularly in Ayurvedic
System Formation of alloys for various purposes
Agriculture-
as fertilizers, seed dressings and fungicides Jewellery- e.g. Gold, silver,
platinum, diamond
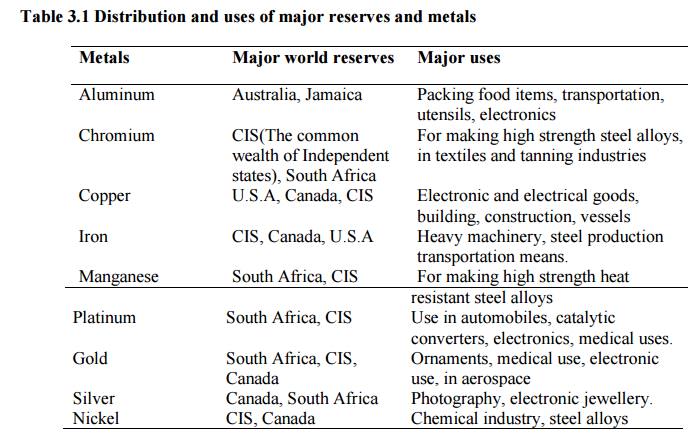
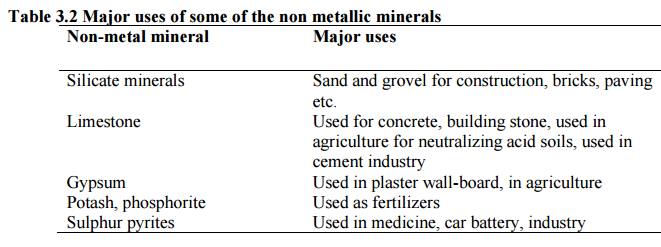
Table 3.1 Distribution and uses of major reserves
and metals
2 Environmental impacts of mineral extraction
Major
mines which are known for causing severe problems are given below: Jaduguda
Uranium Mine, Jharkhand- exposing local people to radioactive hazards.
Jharia
coal mines, Jharkhand- underground fire leading to land subsidence and forced
displacement of people.
Sukinda
chromite mines, Orissa- Seeping of hexavalent chromium into river posing
serious health hazard, Cr6+ being highly toxic and carcinogenic.
Kudremukh
iron ore mine, Karnataka- causing river pollution and threat to biodiversity.
East coast Bauxite mine, Orissa-Land encroachment and issue of rehabilitation
unsettled. North-Eastern Coal Fields, Assam-Very high sulphur contamination of
groundwater.
3 Impacts of mining: Mining is done to extract
minerals from deep deposits in soil. Environmental
damages caused by mining activities are as follows:
Devegetation and defacing of lands: Mining
requires removal of vegetation along with underlying soil mantle and overlying rock masses. This results in destruction
of landscape in the area. Subsidence of
land: Subsidence of mining areas results in tilting of buildings, cracks in
houses, buckling of roads, bending
of rail tracks and leaking of gas from cracked pipe lines leading to serious
disasters.
Groundwater contamination: Mining
pollutes the groundwater. Sulphur, usually present as an impurity in many ores is known to get converted into sulphuric
acid through microbial action, thereby making the water acidic.
Surface water pollution: The acid
mine drainage often contaminates the nearby streams and lakes. The acidic water, radioactive
substances like uranium, heavy metals also contaminate the water bodies and
kill aquatic animals.
Air pollution: In order to separate and purify
the metal from other impurities in the ore, smelting is done which emits enormous quantities of air pollutants. Oxides of
sulphur, arsenic, cadmium and lead etc. shoot up in the atmosphere near the
smelters and the public suffers from several health problems. Occupational Health Hazards: Miners working
in different type of mines suffer from asbestosis, silicosis, black lung disease.
4 Remedial measures
Adopting
eco-friendly mining technology
Utilization
of low grade ores by using microbial – leaching technique. In this method, the
ores are inoculated with the desired strains of bacteria like Thiobacillus
ferroxidans, which remove the impurities and leave the pure mineral.
Re-vegetating
mined areas with appropriate plants Gradual restoration of flora
Prevention
of toxic drainage discharge.
5 Case studies
1. Mining and quarrying in Udaipur
Soap
stones, building stone, and dolomite mines spread over 15,000 hectares in
Udaipur have caused many adverse impacts on environment.
About 150
tons of explosives are used per month in blasting. The Maton mines have badly
polluted the Ahar river.
The hills
around the mines are suffering from acute soil erosion.
The waste
water flows towards a big tank of “Bag Dara".
Due to
scarcity of water people are compelled to use this effluent for irrigation
purpose. The animals like tiger, lion, deer, and birds have disappeared from
the mining area.
2. Mining in Sariska and Tiger Reserve in Aravallis
The
Aravalli range is spread over about 692 Km in the North-west India covering
Gujrat, Rajasthan, Haryana, and Delhi.
The hill
is rich in mineral resources.
Mining
operations within and around the Sariska Tiger reserve has left many areas
permanently infertile and barren.
The
precious wild life is under serious threat.
Related Topics