Microbiology - Microbial Metabolism | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Microbial Metabolism
Microbial Metabolism
Learning Objectives
After
studying this chapter the students will be able to,
• Identify
the role of ATP in cellular activities.
• Define
metabolism and describe the fundamental differences between catabolism and
anabolism.
• Explain
oxidation – reduction reaction.
• List
and provide examples of three types of phosphorylation reactions that generates
ATP.
• Describe
the Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein and its pathways (Glycolysis, Krebs cycle,
electron transport chain)
• Electron
transport chain and chemiosmotic model for ATP generation.
• Understand
about the types of fermentation and its products.
• Describe the mechanism of enzymatic activity and
significance of microbial enzymes.
Chapter Outline
1. Metabolism
2. Energy of Chemical Reaction
3. Generation of ATP
4. Carbohydrate Catabolis
5. Tricarboxylic Acid Cyc
6. Electron Transport Chai
7. Lipid Catabolism
8. Protein Metabolism
9. Fermentation
10. Enzymes
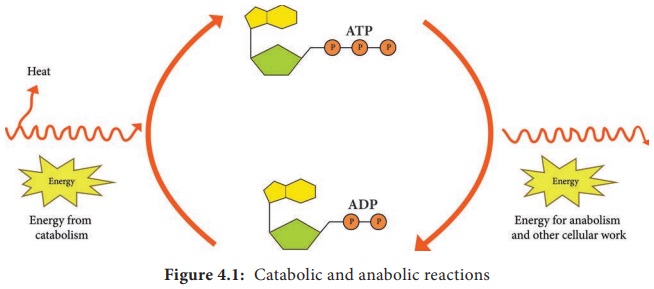
All living organisms are constantly in need of energy to function.
The life support activity of even the most structurally simple organism
involves a large number of complex biochemical reactions. Living
cells carry out three major types of processes namely Chemical Process, Transport
Process and Mechanical Process.
In chemical processes, energy is required
to synthesize complex biological molecules from much simpler molecules.
Transport processes require energy to take up nutrients, eliminate waste, and
maintain ion balance. Mechanical processes require energy to change the
physical location of structures within cells. Even during resting state, a
substantial amount of energy is needed for fundamental functions of cells. All
living system obeys the laws of thermodynamics. This law analyzes energy
changes in a collection of matter called system (a cell or a plant).
The
energy exchanges between the system and the surrounding balance each other. All
chemical reactions in cells involve energy transformation. (For example:
Photosynthetic bacteria transform radiant energy into chemical energy) . In
living cells thermodynamic changes are essential for biological function such
as growth, reproduction, photosynthesis andrespiration. Microorganisms obtain
energy and nutrients for their survival and reproduction through metabolism.
The microbial species and ecological niche can often be differentiated from
each other based on metabolic characteristics. The metabolic reaction often
allows the use of micro organisms in fermentation process and biogeochemical
cycle.
Three fourth of the energy is derived from carbohydrate that we consume and Glucose is the major fuel for all living organisms.
Related Topics