Lactic acid, Alcohol | Microbial Metabolism | Microbiology - Fermentation | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Fermentation
Fermentation
In 1856
fermentation, reaction was first demonstrated by Louis Pasteur in yeast. The
study of fermentation and its practical uses is named as Zymology. Any energy
releasing metabolic process that takes place only under anaerobic condition is
called fermentation. It can also be defined as a metabolic process that release
energy from a sugar or other organic molecule. It does not require oxygen or an
electron transport system, and uses an organic molecule as the final electron
acceptor. Fermentation reaction yields only a small amount of energy (2 ATP).
Anaerobes
do not use an electron transport chain to oxidize NADH to NAD+ and
therefore use fermentation as alternative method to maintain a supply of NAD+
for the proper function of normal metabolic pathways. Facultative anaerobes can
use fermentation under anaerobic condition and carryout aerobic respiration
when oxygen is present. Fermentation reoxidizes NADH to NAD+ by converting
pyruvic acid into various organic acids.
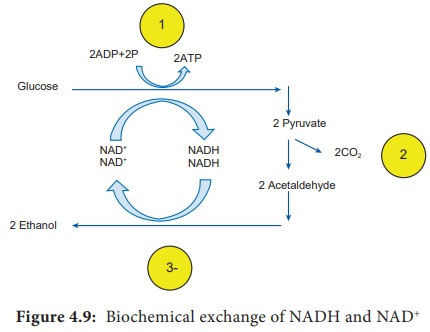
During
fermentation, NADH is converted back into the coenzyme NAD+ so that
it can be used again for Glycolysis (Figure 4.9). Organic electron acceptors
such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde react with NADH to form NAD+,
producing CO2 and organic solvent like ethanol. Fermentation can be
classified as Lactic acid fermentation and alcohol fermentation.
Aquifex (water maker) of Aquificae is a diverse collection of
bacteria that live in harsh environmental settings.These can produce water by
oxidizing hydrogen.
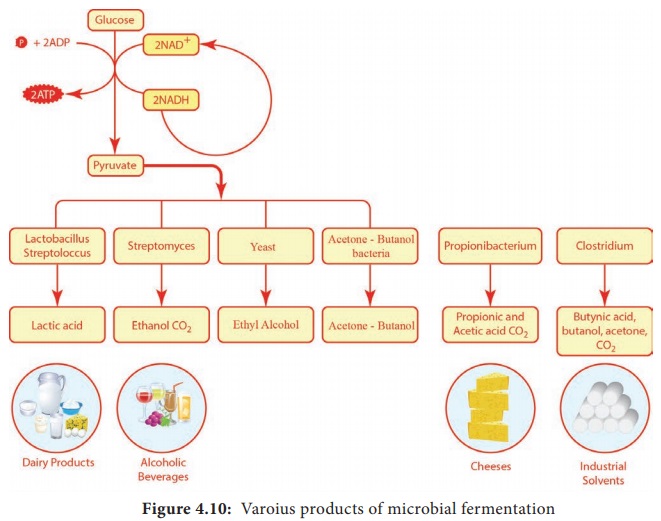
Lactic acid fermentation
During
Glycolysis, in the first step of lactic acid fermentation, a molecule of
glucose is oxidized to 2 molecules of pyruvic acid and it generates the energy.
In the next step pyruvic acid is reduced by NADH to form lactic acid. Lactobacillus and Streptococcus are some of the lactic acid producing genera (Figure 4.10).
Milk is
converted into fermented products such as curd, yogurt and cheese. The
fermentation of lactose in milk by these bacteria produces lactic acid which
acts on milk protein to give yogurt its texture and characteristic tart
flavour. Here lactase enzyme is produce by the bacteria which convert the
lactose into lactic acid.Builds up of Lactic acid in muscle cells causes muscle
cramp.
Homolactic acid fermentation
In this
type of fermentation, organism produces lactic acid alone. So it is referred to
as homolactic fermentation.
Glucose +
2ADP + 2P → Lactic acid +2ATP
Heterolactic acid fermentation
In this
type of fermentation, organism produces Lactic acid as well as other acids or
alcohol. So it is known as hetero fermentation or heterolactic and often uses
the pentose phosphate pathway.
G + ADP + ![]() → Lactic acid + ethanol + CO2 + ATP
→ Lactic acid + ethanol + CO2 + ATP
HOTS: Why do cells need to ferment when they get 2ATPs from
Glycolysis?
Alcohol Fermentation
Alcohol
fermentation begins with the Glycolysis which yields two molecules of pyruvic
acid and two molecules of ATPs. In the next step, the two molecules of pyruvic
acid are converted to two molecules of acetaldehyde and two molecules of CO2.
The acetaldehydes are then reduced by NADH to form ethanol. The ethanol and CO2
produced by the yeast Saccharomyces is used in alcoholic beverages and to raise
bread dough respectively.
Related Topics