Microbial Metabolism | Microbiology - Carbohydrate Catabolism | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Carbohydrate Catabolism
Carbohydrate Catabolism
Most
microorganisms oxidize carbohydrates as their primary source of cellular
energy. Carbohydrate catabolism is the breakdown of carbohydrate molecule to
produce energy and is therefore of great importance in cell metabolism. Glucose
is the most common carbohydrate energy source used by cells.
To
produce energy from glucose, microorganism use two general processes namely
Respiration and Fermentation
Cellular Respiration
Respiration
is defined as an ATP generating process in which organic molecules are oxidized
and the final electron acceptor is an inorganic compound. In aerobic
respiration, the final electron acceptor is Oxygen and in anaerobic respiration
the final electron acceptor is an inorganic molecule like NO3, SO42−
other than Oxygen.
The
aerobic respiration of glucose typically occurs in three principal stages. They
are
• Glycolysis
• Krebs cycle
• Electron transport chain
Glycolysis
Glycolysis
is the process of splitting of sugar molecule, where the glucose is
enzymatically degraded to produce ATP. Glycolysis is the oxidation of glucose
to pyruvic acid with simultaneous production of some ATP and energy containing
NADH. It takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Glycolysis occurs in the extra mitochondrial part of the cell cytoplasm. Glycolysis
was discovered by Emden, Meyerhof and Parnas. So, this cycle is shortly termed
as EMP pathway, in honour of these pioneer workers. This cycle occurs in
animals, plants and large number of microorganisms. Glycolysis does not require
oxygen, it can occur under aerobic or anaerobic condition. Glycolysis is a
sequence of ten enzyme catalyzed reactions.
Aerobic condition

Anaerobic condition
C6H12O6
+2 NAD + 2 ADP + 2 P → 2 CH3 COCOOH + 2 ATP + 2NADH+2H+ (Pyruvic acid)
Since
glucose is a six carbon molecule and pyruvate is a three carbon molecule, two
molecules of pyruvate are produced for each molecule of glucose that enters
Glycolysis. Net energy production from each glucose molecule is two ATP
molecules
The
Glycolysis pathway consists of two phases. They are
1. The preparatory/Investment phase, where ATP is consumed
2. The pay off phase where ATP is produced (Figure 4.4).
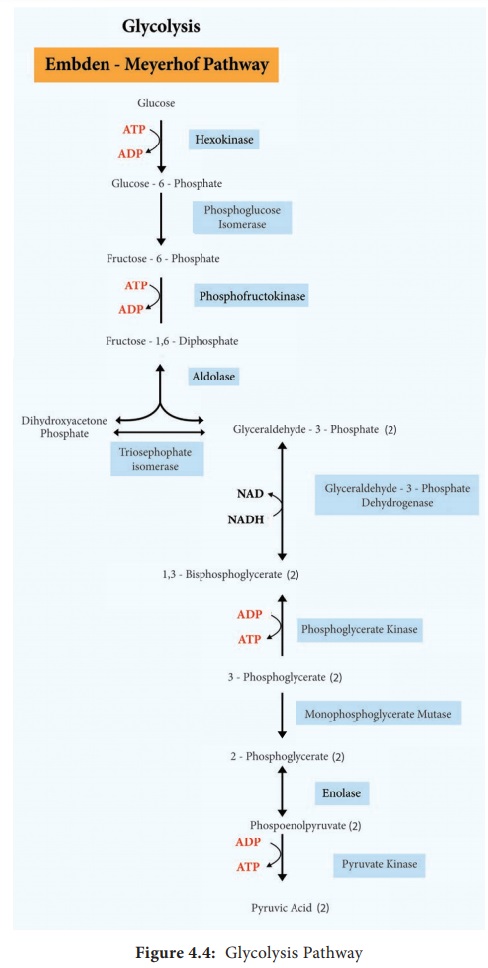
1. In the
preparatory stage, two molecules of ATP are utilized and then glucose is
phosphorylated, restructured, and split into two 3 carbon compounds namely
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and Dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
2. In pay
off phase or energy conserving stage, the two 3 carbon molecules are oxidized
in several steps to 2 molecules of pyruvic acid and two molecules of NAD+
are reduced to NADH, thus four molecules of ATP are formed by substrate level
phosphorylation.
Two
molecules of ATP are needed to initiate Glycolysis and four molecules of ATP
are generated at the end of the process. Therefore, the net gain of Glycolysis
is two ATP for each molecule of glucose oxidized.
Alternatives to Glycolysis
Many
bacteria have another pathway in addition to Glycolysis for the oxidation of
glucose. Some of the common pathways that occur in most of the bacteria are
• Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) or Hexose Mono Phosphate shunt
• Entner
–Doudoroff Pathway
HOTS: Does Glycolysis require Oxygen?
Strips used in Glu- cometer a chemical called glucose oxidase which
reacts with the glucose in the blood sample and is con-verts it into an acid
called gluconic acid.
Related Topics