Microbial Metabolism | Microbiology - Generation of ATP | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Generation of ATP
Generation of ATP
Much of
energy released during oxidation reduction reaction is trapped within the cell
by the formation of ATP. A phosphate group is added ADP with the input of
energy to form ATP. The addition of a phosphate to a chemical compound is
called phosphorylation.
Organism
uses three different mechanisms of phosphorylation to generate ATP from ADP.
They are
Substrate Level Phosphorylation
It is a
metabolic reaction that results in the formation of ATP or GTP by the direct
transfer of a phosphoryl group to ADP or GDP from another phosphorylated
compound
Alkaline phosphatas is a heat sensitive enzyme in milk which is
used as an indicator in Pasteurization.
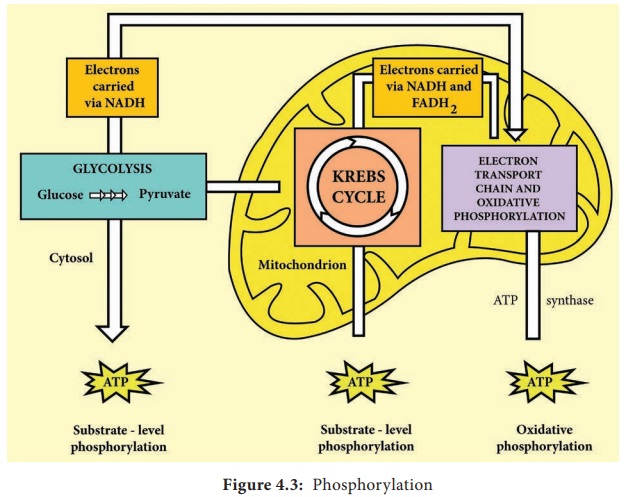
Oxidative Phosphorylation
In this
reaction, electrons are transferred from organic compounds to molecules of
Oxygen (O 2) or other inorganic molecules through a series of
different electron carriers (Example: NAD+ and FAD) . Then the
electrons are passed through a series of different electron carriers to oxygen.
The process of oxidative phosphorylation occurs during electron transport chain
(Figure 4.3).
Photophosphorylation
It occurs
only in photosynthetic cells which contain light trapping pigments. Example: In
photosynthesis, photosynthetic pigment, Chlorophyll is involved in the
synthesis of organic molecules especially sugars, with the energy of light from
the energy poor building blocks like Carbon dioxide and water. In phototropic
bacteria (purple, green sulphur bacteria, Cyanobacteria), photosynthetic
pigments bateriochlorophylls are involved in ATP production.
Related Topics