Microbial Metabolism | Microbiology - Metabolism | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 4 : Microbial Metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism
The term
Metabolism refers to the sum of all bio chemical reactions that occur within a
living cell. Chemical reaction either release energy or require energy.
Metabolism can be viewed as an energy balancing act. It can be divided into two
classes of chemical reactions namely Catabolism
and Anabolism.
Catabolism: It is called catabolic or degradative reactions because complex organic compounds are broken
down into simples ones. Catabolic reactions are generally hydrolytic reactions.
It is enzyme regulated chemical reaction that release energy and they are
exergonic Example: Break down of sugar into Carbon dioxide and water in cells
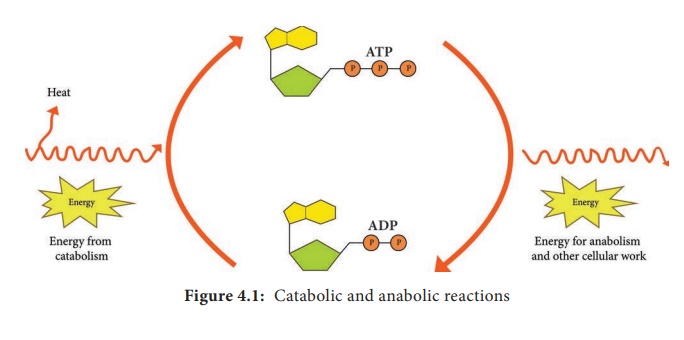
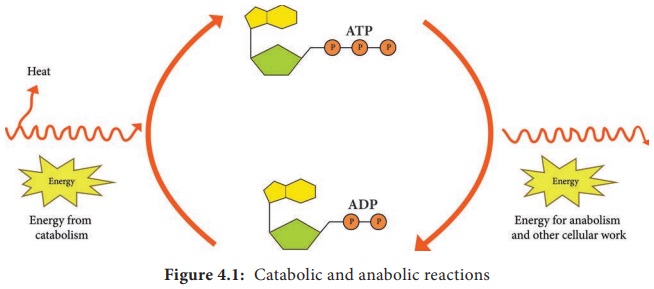
Anabolism: It is called anabolic or biosynthetic reactions because complex organic molecules are
formed from simples ones. Anabolic process often involves dehydration, are bio-
synthetic reactions (Figure 4.1). It is enzyme regulated energy requiring
reaction and they are endergonic. Examples: Formation of proteins from amino
acids.
Catabolic
reactions furnish the energy needed to drive anabolic reactions. This coupling
of energy requiring and energy releasing reactions is made possible through the
molecule Adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP).
Related Topics