Biotechnology - Methods of Gene Transfer | 12th Botany : Chapter 4 : Principles and Processes of Biotechnology
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 4 : Principles and Processes of Biotechnology
Methods of Gene Transfer
Methods of Gene Transfer
The next step after a recombinant DNA molecule has been generated
is to introduce it into a suitable host cell. There are many methods to
introduce recombinant vectors and these are dependent on several factors such
as the vector type and host cell.
For achieving genetic transformation in plants, the basic
pre-requisite is the construction of a vector which carries the gene of
interest flanked by the necessary controlling sequences, i.e., the promoter and
terminator, and deliver the genes into the host plant. There are two kinds of
gene transfer methods in plants. It includes:
·
Direct or vectorless gene transfer
·
Indirect or vector – mediated gene transfer
1. Direct or Vectorless Gene Transfer
In the direct gene transfer methods, the foreign gene of interest
is delivered into the host plant without the help of a vector. The following
are some of the common methods of direct gene transfer in plants.
a. Chemical mediated gene transfer: Certain chemicals like
polyethylene glycol (PEG) and dextran sulphate induce DNA uptake into plant
protoplasts.
b. Microinjection: The DNA is directly injected into the
nucleus using fine tipped glass needle or micro pipette to transform plant
cells. The protoplasts are immobilised on a solid support (agarose on a
microscopic slide) or held with a holding pipette under suction.
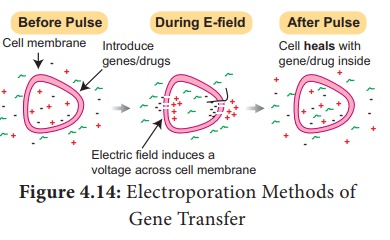
c. Electroporation Methods of Gene Transfer: A pulse of
high voltage is applied to protoplasts, cells or tissues which makes
transient pores in the plasma membrane through which uptake of foreign DNA
occurs.
d. Liposome mediated method of Gene Transfer: Liposomes the
artificial phospholipid vesicles are useful in gene transfer. The gene
or DNA is transferred from liposome into vacuole of plant
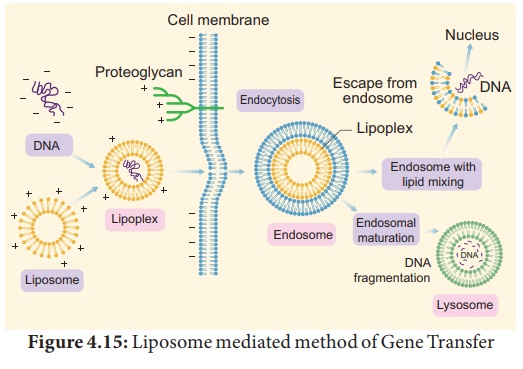
cells. It is carried out by encapsulated DNA into the vacuole.
This technique is advantageous because the liposome protects the introduced DNA
from being damaged by the acidic pH and protease enzymes present in the vacuole.
Liposome and tonoplast of vacuole fusion resulted in gene transfer. This
process is called lipofection.
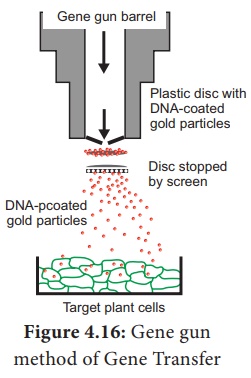
e. Biolistics: The foreign DNA is coated onto the
surface of minute gold or tungsten particles (1-3 µm) and bombarded onto the
target tissue or cells using a particle gun (also called as gene gun/micro
projectile gun/shotgun ). Then the bombarded cells or tissues
are cultured on selected medium to regenerate plants from the transformed
cells.(Figure 4.16)
2. Indirect or Vector-Mediated Gene Transfer
Gene transfer is mediated with the help of a plasmid vector is
known as indirect or vector mediated gene transfer. Among the various vectors
used for plant transformation, the Ti-plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens
has been used extensively. This bacterium has a large size plasmid, known as Ti
plasmid (Tumor inducing) and a portion of it referred as T-DNA (transfer DNA)
is transferred to plant genome in the infected cells and cause plant tumors
(crown gall). Since this bacterium has the natural ability to transfer T-DNA
region of its plasmid into plant genome, upon infection of cells at the wound
site, it is also known as the natural genetic engineer of plants.
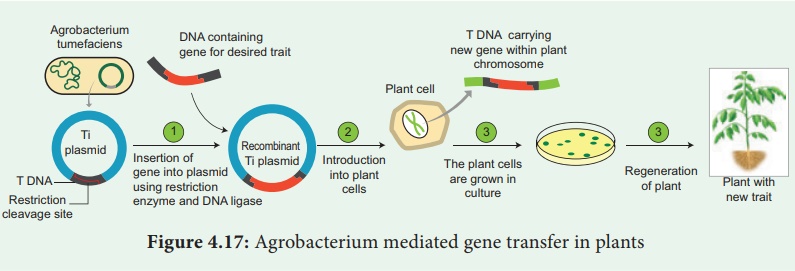
The foreign gene (e.g. Bt gene for insect resistance) and plant selection marker gene, usually an antibiotic gene like npt II which confers resistance to antibiotic kanamycin are cloned in the T DNA region of Ti-plasmid in place of unwanted DNA sequences.(Figure 4.17)
Related Topics