Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Respiratory Care Modalities
Incentive Spirometry (Sustained Maximal Inspiration) - Noninvasive Respiratory Therapies
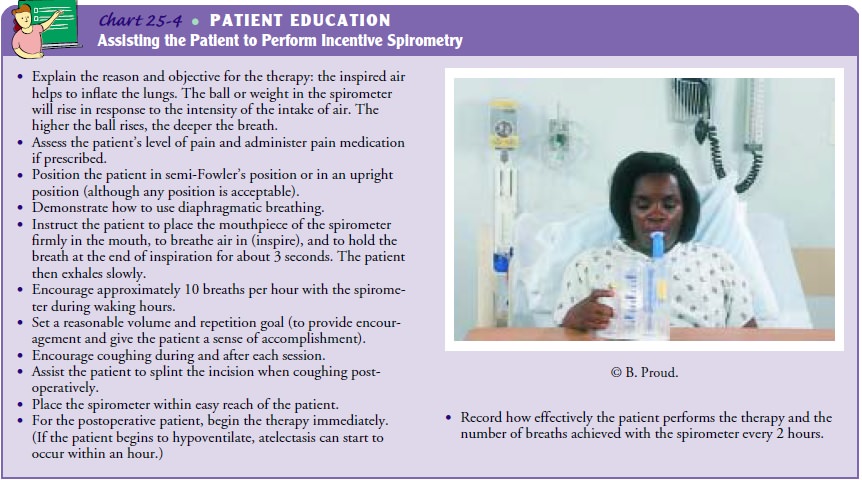
INCENTIVE SPIROMETRY (SUSTAINED MAXIMAL INSPIRATION)
Incentive spirometry is
a method of deep breathing that pro-vides visual feedback to help the patient
inhale slowly and deeply to maximize lung inflation and prevent or reduce
atelectasis. Ide-ally, the patient assumes a sitting or semi-Fowler’s position
to en-hance diaphragmatic excursion (Chart 25-4). However, this procedure may
be performed with the patient in any position.
Incentive
spirometers may be one of two types: volume or flow. In the volume type, the
tidal volume of the spirometer is set according to the manufacturer’s
instructions. The purpose of the device is to ensure that the volume of air
inhaled is increased gradually as the patient takes deeper and deeper breaths.
The pa-tient takes a deep breath through the mouthpiece, pauses at peak lung
inflation, and then relaxes and exhales. Taking several nor-mal breaths before
attempting another with the incentive spirom-eter helps avoid fatigue. The
volume is periodically increased as tolerated.
A
flow spirometer has the same purpose as a volume spirom-eter, but the volume is
not preset. The spirometer contains a number of movable balls that are pushed
up by the force of the breath and held suspended in the air while the patient
inhales. The amount of air inhaled and the flow of the air are estimated by how
long and how high the balls are suspended.
Indications
Incentive
spirometry is used after surgery, especially thoracic and abdominal surgery, to
promote the expansion of the alveoli and to prevent or treat atelectasis. As a
preventive measure, incentive spirometry may be more effective than IPPB
because it maximizes the amount of air inhaled while maintaining relatively low
airway pressures.
Nursing Management
Nursing
management of the patient using incentive spirometry includes placing the
patient in the proper position, teaching the technique for using the incentive
spirometer, setting realistic goals for the patient, and recording the results
of the therapy.
Related Topics