Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Respiratory Care Modalities
Adjusting the Ventilator and Assessing the Equipment
ADJUSTING THE VENTILATOR
The
ventilator is adjusted so that the patient is comfortable and breathes “in sync”
with the machine. Minimal alteration of the normal cardiovascular and pulmonary
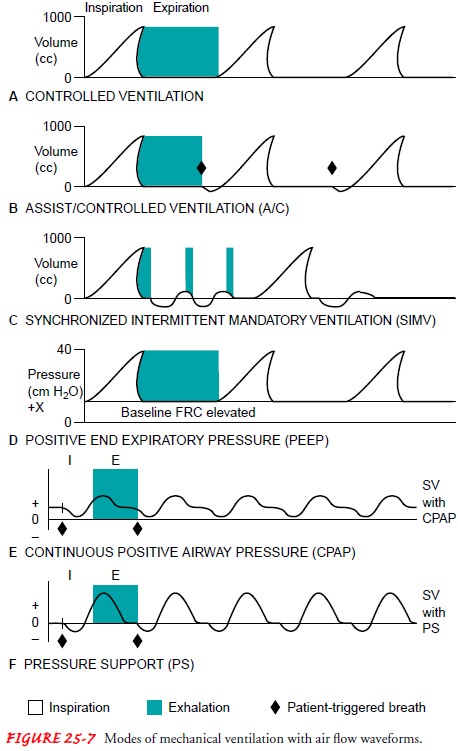
dynamics is desired. Modes of mechanical ventilation are described in Figure
25-7. If the volume ventilator is adjusted appropriately, the patient’s
ar-terial blood gas values will be satisfactory and there will be little or no
cardiovascular compromise. Chart 25-12 discusses how to achieve adequate
mechanical ventilation for each patient.

ASSESSING THE EQUIPMENT
The
ventilator needs to be assessed to make sure that it is func-tioning properly
and that the settings are appropriate. Even though the nurse is not primarily
responsible for adjusting the settings on the ventilator or measuring
ventilator parameters (usually the responsibility of the respiratory
therapist), the nurse is responsible for the patient and therefore needs to
evaluate how the ventilator affects the patient’s overall status.
In
monitoring the ventilator, the nurse should note the following:
·
Type of ventilator (such as
volume-cycled, pressure-cycled, negative-pressure)
·
Controlling mode (such as controlled ventilation, assist–control
ventilation, synchronized intermittent manda-tory ventilation)
·
Tidal volume and rate settings
(tidal volume is usually 10 to 15 mL/kg; rate is usually 12 to 16/min)
·
FiO2
(fraction of inspired oxygen)
setting
·
Inspiratory pressure reached and
pressure limit (normal is 15 to 20 cm H2O;
this increases if there is increased airway resistance or decreased compliance)
·
Sensitivity (a 2-cm H2O
inspiratory force should trigger the ventilator)
·
Inspiratory-to-expiratory ratio
(usually 1 3 [1 second of in-spiration to 3 seconds of expiration] or 1 2)
·
Minute volume (tidal volume × respiratory rate, usually 6 to 8 L/min)
·
Sigh settings (usually 1.5 times the
tidal volume and ranging from 1 to 3 per hour), if applicable
·
Water in the tubing, disconnection
or kinking of the tubing
·
Humidification (humidifier filled
with water) and temper-ature
·
Alarms (turned on and functioning
properly)
·
PEEP and/or pressure support level,
if applicable. PEEP is usually 5 to 15 cm H2O
Related Topics