Chapter: Computer Networks : Data Link Layer
Important Short Questions and Answers: Computer Networks - Data Link Layer
1. What are the responsibilities of data link
layer?
Specific
responsibilities of data link layer include the following.
a) Framing
b) Physical
addressing
c) Flow
control
d) Error
control
e) Access
control
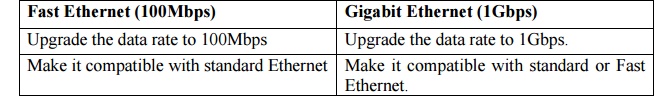
2. State the difference between Fast Ethernet
and Gigabit Ethernet.
3. What is the purpose of Network Interface Card?
A NIC is
a computer circuit board or card that is installed in a computer so that it can
be connected to a network. NIC provides a dedicated, full time connection to
the network.
4. What are Virtual LANs?
A VLAN
acts like an ordinary LAN, but connected devices don’t have to be physically
connected to the same segment. VLANs are considered likely to be used with
campus environment networks. Among many companies likely to provide products
with VLAN support are Cisco, Bay Networks and 3Com.
5. What are the functions of MAC?
MAC
sublayer resolves the contention for the shared media. It contains
synchronization, flag, flow and error control specifications necessary to move
information from one place to another, as well as the physical address of the
next station to receive and route a packet.
6. What are the functions of LLC?
The IEEE
project 802 models take the structure of an HDLC frame and divide it into 2
sets of functions. One set contains the end user portion of the HDLC frame –
the logical address, control information and data. These functions are handled
by the IEEE 802.2 logical link control (LLC) Protocol.
7. What is Ethernet?
Ethernet
is a multiple access network, meaning that a set of nodes send and receive
frames over a shared link.
8. Define Bluetooth.
Bluetooth
is a wireless LAN technology designed to connect devices of different functions
such as telephones, notebooks, computers, cameras, printers, coffee maker and
so on.
9. Why Ethernet is said to be 1-persistent
protocol?
The
Ethernet is said to be a 1-persistent protocol, because an adapter with a frame
to send transmits with probability one, whenever a busy line goes idle.
All the
nodes can distinguish between idle and a busy link and “collision detect” means
that a node listens as it transmits and can therefore detect when a frame it is
transmitting as interfered (collided) with a frame transmitted by another node.
11. Define flow control.
Flow
control refers to a set of procedures used to restrict the amount of data. The
sender can send before waiting for acknowledgment.
12. What is a buffer?
Each
receiving device has a block of memory called a buffer, reserved for storing
incoming data until they are processed.
13. Mention the categories of flow control.
There are
2 methods have been developed to control flow of data across communication links.
· Stop and
wait- send one from at a time.
· Sliding
window- send several frames at a time.
14. What is the function of stop and wait flow
control?
In this
method, the sender sends one frame and waits for an acknowledgement before
sending.
15. Mention the advantage and disadvantage of stop
and wait f low control.
Advantage:
simplicity and Disadvantage: inefficiency.
16. Define ARQ.
Error
control in the data link layer is based on Automatic repeat request (ARQ),
which means retransmission of data in 3 cases.
1. Damaged
frame
2. Lost
frame
3. Lost
acknowledgment.
17. Mention the function of go-back N-ARQ.
It is the
popular mechanism for continuous transmission error control. In the method, if
our frame is lost or damaged, all frames sent since the last frame acknowledged
are retransmitted.
18. What is selective reject ARQ?
In
selective reject ARQ only the specific damaged or lost frame is retransmitted.
If a frame is corrupted in transit, a NAK is returned and the frame is resent
out of sequence.
19. Define HDLC.
It is
bit-oriented data link protocols designed to support both half-duplex and full
duplex communication over point to point and midpoint links.
20. List the types of stations is HDLC.
HDLC
differentiates between 3 types of stations.
a) Primary
b) Secondary
c)
Combined
21. What are the different communication modes in
HDLC?
HDLC
supports 3 modes of communication between stations.
a) Normal
response mode (NRM)
b) Asynchronous
response mode (ARM)
c) Asynchronous
balanced mode (ABM)
22. Mention the types of frames in HDLC.
There are
3 types of HDLC frames.
a) Information
frames (I-frames)
b) Supervisory
frames (S-frames)
c) Unnumbered
frames (U-frames)
23. Give the usage of I, S, U frames.
I frames
– used to transport user data and control information relating to user data.
S frames
– used only to transport control information, primarily data link layer and
error controls.
U frames
– reserved for systems management.
24. Write the types of frame fields contained in
HDLC.
Each
frame in HDLC may contain up to 6 fields.
a) Beginning
flag field
b) An
address field
c) A control
field
d) An
information field
e) A frame
check sequence (FCS) field
f) An ending
flag field.
25. What is meant by bit stuffing?
Bit
stuffing is the process of adding one extra 0 whenever there are 5 consecutive
in the data so that the receiver doesn’t mistake the data for a flag.
26. Define LAN.
A Local
Area Network (LAN) is a data communication system that allows a number of
independent devices to communicate directly with each other in a limited
geographic area.
27. Mention the various architecture in a LAN.
LAN is
dominated by 4 architectures.
a) Ethernet
b) Token bus
c) Token
ring
d) Fiber
distributed data interface (FDDI)
28. Define a standard 802.3
IEEE
802.3 supports a LAN standard originally developed by Xerox and later extended by
a joint venture between digital equipment corporations. Intel Corporation and
Xerox. This was called ‘Ethernet’.
29. List the most command kinds of Base band 802.3
LAN.
a) 10 Base 5
b) 10 Base 2
c) 10 Base T
d) 1 Base 5
e) 100 Base
T
30. Mention the different kinds of Ethernet
networks.
a)
Switched Ethernet
b) Fast
Ethernet
c)
Gigabit Ethernet
31. Describe the three HDLC station types?
The three
HDLC station types are:
Primary station: The primary station has the
complete control of the link. The Primary stationsends commands to the
secondary station.
Secondary station: The
secondary station sends responses.
Combined station: The
combined station is one which acts either as a primary or a Secondary,depending
upon the nature and direction of the transmission. Combined station sends both
commands and responses.
32. What is piggy backing?
Piggy
backing means combining data to sent and acknowledgement of the frame received
in one single frame. Piggy backing can save bandwidth because the overhead from
a data frame and an ACK frame can be combined in to just one frame
33. Name the four types of S-frames?
The four
types of S-frames are
Receive
ready (RR).T0 e value of the code sub field is 00
Receive
not ready (RNR). The value of the code sub field is 10
Reject
(REJ). The value of the code sub field is 01
Selective
reject (SREJ). The value of the code sub field is 11
34. Name the five categories of U-frames?
The five
categories of U-frames are Mode setting, unnumbered exchange, Disconnection,
Initialization mode &Miscellaneous mode
Glossary:
Access point (AP): A central base station in a BSS.
Acknowledgment (ACK): A response sent by the receiver to indicate the successful receipt
ofdata.
ALOHA: The original random
multiple access method in which a station can send a frame anytime it has one
to send.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM): A wide area protocol featuring high data rates andequal-sized
packets (cells); ATM is suitable for transferring text, audio, and video data.
ATM LAN: A LAN using ATM technology.
ATM layer: A layer in ATM that provides routing, traffic management,
switching, andmultiplexing services.
Automatic Repeat Request (ARQ):An error-control method in which correction is made
byretransmission of data.
Autonegotiation:A Fast Ethernet feature that allows two devices to negotiate
the mode or datarate.
Backward Explicit Congestion Notification
(BECN):A bit in the Frame Relay packet
thatnotifies the sender of congestion.
Basic Service Set (BSS): The building block of a wireless LAN as defined by the IEEE
802.11standard.
Bluetooth: A wireless LAN technology designed to connect devices of different
functions suchas telephones and notebooks in a small area such as a room.
Bursty Data: Data with varying instantaneous transmission rates.
Data Link Control The responsibilities of the data link layer: flow control and error control.
Data Link Layer The second layer in
the Internet model. It is responsible for node-to-nodedelivery.
Encryption Converting a message into an unintelligible form that is
unreadable unlessdecrypted.
Ethernet: A local area network using the CSMA/CD access method.
Extended Service Set (ESS): A wireless LAN service composed of two or more BSSs with APsas
defined by the IEEE 802.11 standard.
Fast Ethernet: Ethernet with a data rate of 100 Mbps.
Forward Explicit Congestion Notification
(FECN): A bit in the Frame Relay packet thatnotifies the destination
of congestion.
Forwarding: Placing the packet in its route to its destination.
Frame Relay: A packet-switching specification defined for the first two layers
of the Internetmodel. There is no network layer. Error checking is done on
end-to-end basis instead of on each link.
Gigabit Ethernet: Ethernet with a 1000 Mbps data rate.
Go-Back-N ARQ: An error-control method in which the frame in error and all
following framesmust be retransmitted.
High-level Data Link Control (HDLC): A bit-oriented data link protocol defined by the ISO.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers (IEEE): A group consisting of
professionalengineers which has specialized societies whose committees prepare
standards in members' areas of specialty.
Interframe space (IFS): In wireless LANs, a time interval between two frames to control
accessto the channel.
Logical link control (LLC): The upper sublayer of the data link layer as defined by
IEEEProject 802.2.
Medium access control (MAC) sublayer: The lower sublayer in the data link layer defined bythe IEEE 802
project. It defines the access method and access control in different local
area network protocols.
Network Address Translation (NAT): A technology that allows a private network to use a setof private
addresses for internal communication and a set of global Internet addresses for
external communication.
Network Allocation Vector (NAV): InCSMA/CA,the amount of
time that must pass before astation can check for an idle line.
Normal Response Mode (NRM): In HDLC, a communication mode in which the secondarystation must have permission from the primary station before transmission can proceed.
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP): A simple two-step authentication protocol used inPPP.
Piconet: A Bluetooth network.
Piggybacking: The inclusion of acknowledgment on a data frame.
Poll: In the
primary/secondary access method, a procedure in which the primary station asks
asecondary station if it has any data to transmit.
P-Persistent: A CSMA persistence strategy in which a station sends with
probabilitypif it findsthe line idle.
Preamble: The 7-byte field of an IEEE 802.3 frame consisting of alternating
1s and 0s that alertand synchronize the receiver.
Project 802: The project undertaken by the IEEE in an attempt to solve LAN
incompatibility.Routing Table: A table containing information a router
needs to route packets. The informationmay include the network address, the
cost, the address of the next hop, and so on.
Scatternet:A combination of piconets.
Select: In the poll/select access method, a procedure in which the primary
station asks asecondary station if it is ready to receive data.
Selective-Repeat ARQ: An error-control method in which only the frame in error is resent.
Sliding Window: A protocol that allows several data units to be in transition
before receiving anacknowledgment.
Sliding Window ARQ: An error-control protocol using sliding window concept.
Slotted ALOHA: The modified ALOHA access method in which time is divided into
slots andeach station is forced to start sending data only at the beginning of
the slot.
Standard Ethernet: The conventional Ethernet operating at 10 Mbps.
Stop-and-Wait Protocol: A protocol, in which the sender sends one frame, stops until itreceives
confirmation from the receiver, and then sends the next frame.
Switched Ethernet: An Ethernet in which a switch, replacing the hub, can direct a
transmissionto its destination.
Throughput: The number of bits that can pass through a point in one second.
Unicast Address: An address belonging to one destination.
Virtual Circuit (VC): A logical circuit made between the sending and receiving computer.
Virtual Circuit Switching: A switching technique used in switched WANs.
Virtual Link: An OSPF connection between two routers that is created when the physical link isbroken. The link between them uses a longer path that probably goes through several routers.
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN): A technology that divides a physical LAN into virtualworkgroups
through software methods.
X.25: An ITU-T standard
that defines the interface between a data terminal device and a
packet-switching network
Related Topics