Chapter: Computer Networks : Data Link Layer
Backbone Networks
Backbone Networks
A
backbone network allows several LANs to be connected. In a backbone network, no
station is directly connected to the backbone; the stations are part of a LAN,
and the backbone connects the LANs. The backbone is itself a LAN that uses a
LAN protocol such as Ethernet; each connection to the backbone is itself
another LAN.
Although
much different architecture can be used for a backbone, we discuss only the two
most common: the bus and the star.
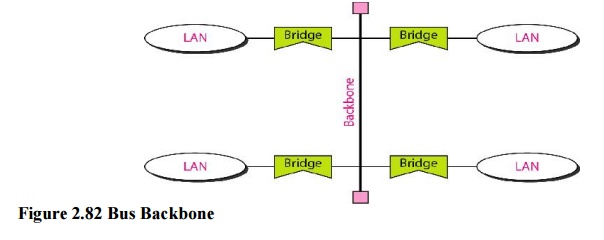
1. Bus Backbone
In a bus
backbone, the topology of the backbone is a bus. The backbone itself can use
one of the protocols that support a bus topology such as l0Base5 or l0Base2. In
a bus backbone, the topology of the backbone is a bus. Bus backbones are
normally used as a distribution backbone to connect different buildings in an
organization. Each building can comprise either a single LAN or another
backbone (normally a star backbone).
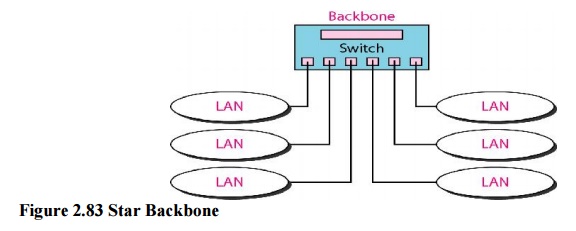
2. Star Backbone
In a star
backbone, sometimes called a collapsed or switched backbone, the topology of
the backbone is a star. In this configuration, the backbone is just one switch
that connects the LANs. In a star backbone, the topology of the backbone is a
star; the backbone is just one switch.
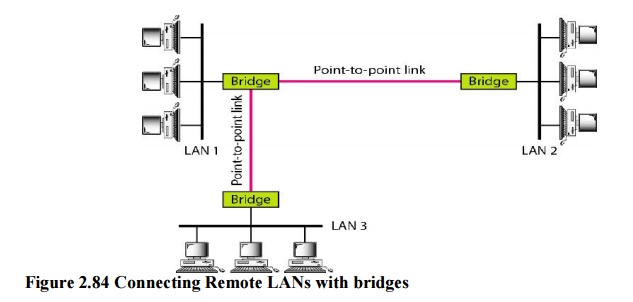
3. Connecting Remote LANs:
Another
common application for a backbone network is to connect remote LANs. This type
of backbone network is useful when a company has several offices with LANs and
needs to connect them. The connection can be done through bridges, sometimes
called remote bridges.
The bridges act as connecting devices
connecting LANs and point-to-point networks, such as leased telephone lines or
ADSL lines. The point-to-point network in this case is considered a LAN without
stations. The point-to-point link can use a protocol such as PPP.
Related Topics