Chapter: Computer Networks : Data Link Layer
Connecting Devices
Connecting Devices:
The
connecting devices are divided into five different categories based on the
layer in which they operate in a network.
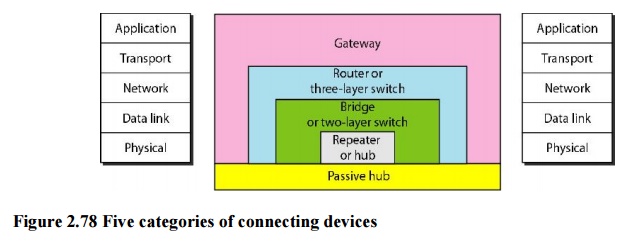
The five
categories contain devices which can be defined as:
1. Those
which operate below the physical layer such as a passive hub.
2. Those
which operate at the physical layer (a repeater or an active hub).
3. Those
which operate at the physical and data link layers (a bridge or a two-layer
switch).
4. Those
which operate at the physical, data link & network layers (a router or a
3-layer switch).
5. Those
which can operate at all five layers (a gateway).
1. Passive Hubs
A passive
hub is just a connector. It connects the wires coming from different branches.
In a star-topology Ethernet LAN, a passive hub is just a point where the
signals coming from different stations collide; the hub is the collision point.
This type of a hub is part of the media; its location in the Internet model is below
the physical layer.
2. Repeaters
A
repeater is a device that operates only in the physical layer. Signals that
carry information within a network can travel a fixed distance before
attenuation endangers the integrity of the data.
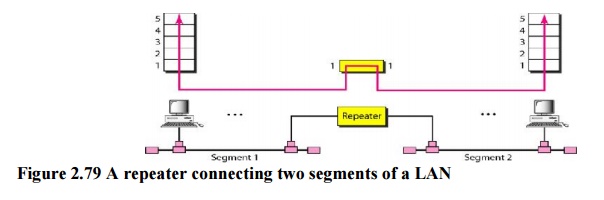
A repeater
receives a signal and, before it becomes too weak or corrupted, regenerates the
original bit pattern. The repeater then sends the refreshed signal. A repeater
can extend the physical length of a LAN.
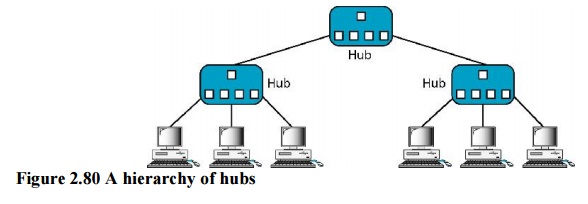
3. Active Hubs
An active
hub is actually a multipart repeater. It is normally used to create connections
between stations in a physical star topology. However, hubs can also be used to
create multiple levels of hierarchy. The hierarchical use of hubs removes the
length limitation of 10Base-T (100 m).
4. Bridges
A bridge
operates in both the physical and the data link layer. As a physical layer
device, it regenerates the signal it receives. As a data link layer device, the
bridge can check the physical (MAC) addresses (source and destination)
contained in the frame
5. Filtering
A bridge
has filtering capability. It can check the destination address of a frame and
decide if the frame should be forwarded or dropped. If the frame is to be
forwarded, the decision must specify the port. A bridge has a table that maps
addresses to ports.
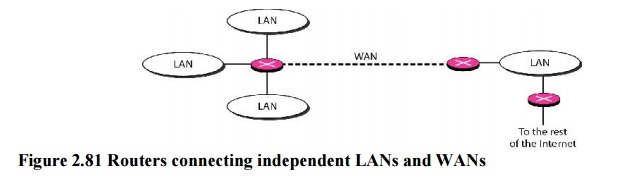
6. Routers
A router
is a three-layer device that routes packets based on their logical addresses
(host-to-host addressing). A router normally connects LANs and WANs in the
Internet and has a routing table that is used for making decisions about the
route. The routing tables are normally dynamic and are updated using routing
protocols.
7. Three-Layer Switches
A
three-layer switch is a router, but a faster and more sophisticated. The
switching fabric in a three-layer switch allows faster table lookup and
forwarding.
Related Topics