Chapter: Environmental Science and Engineering
Human Population and the Environment
HUMAN POPULATION AND THE ENVIRONMENT
1 Objectives
2 Family Welfare Programme
3 Family Planning Programme
4 Environment And Human Health
5 Human Rights
6 Value Education
7 Hiv /Aids
8 Womans And Child Welfare
9 Role Of Information Technology In Environment
10 Role Of Information Technology In Human Health
1 Objectives
Ø To get a
knowledge on human population and human rights.
Ø To
educate the students on value education.
Ø To equip
the students towards the modern technology with respect to environment and
human health.
1.1 Population density
Number of
individuals of the population per unit area or per unit volume.
1.2 Parameters affecting population size
ü Birth
rate
ü Death
rate or Mortality
ü Immigration
ü Emigration.
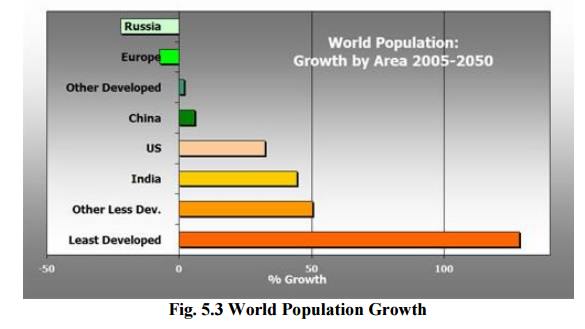
1.3 Population Growth
The rapid
growth of the global population for the past 100 years from the difference
between the rate of birth and death.
Table.5.1 Population statistics in India as on 2010
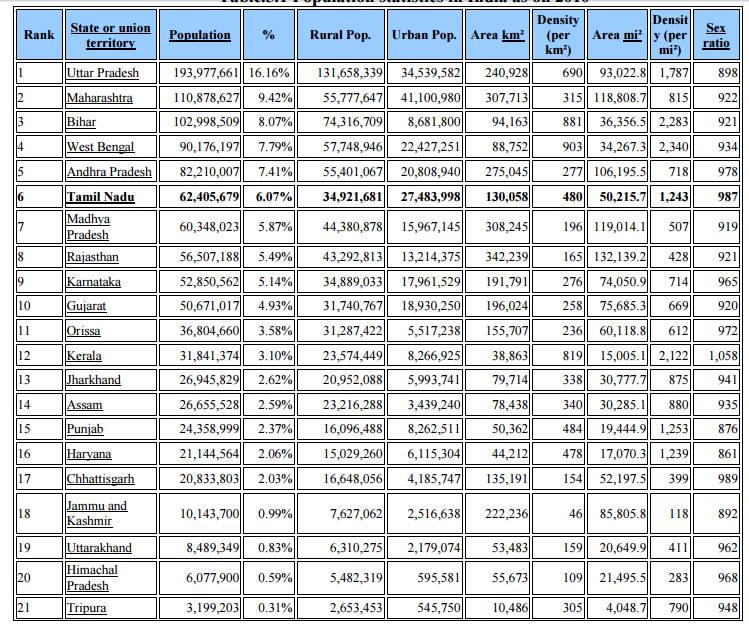
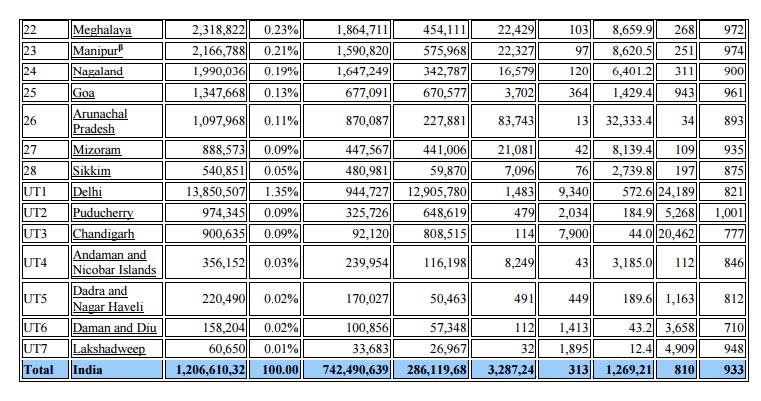
1.4 Causes of rapid population growth
v The rapid
population growth is due to decrease in death rate and increase in birth rate.
v Availability of antibiotics, immunization, increased food production, clean water and air decreases the famine-related deaths.
v In
agricultural based countries, children are required to help parents in the
field that is why population increases in the developing countries.
1.5 Characteristics of population growth
§ Exponential
growth
§ Doubling
time
§ Infant
mortality rate
§ Total
fertility rate
§ Replacement
level
§ Male/female
ratio
§ Demographic
transition.
1.6 Variation of population based on age structure
2. Pyramid
shaped – India, Bangladesh, and Ethiopia.
3. Bell shaped
– France, USA, and UK.
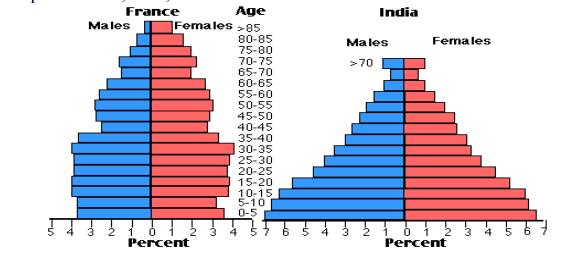
Fig. 5.1 Bell and Pyramid shaped
Population structure
3. Urn shaped - Germany, Italy,
and Japan.
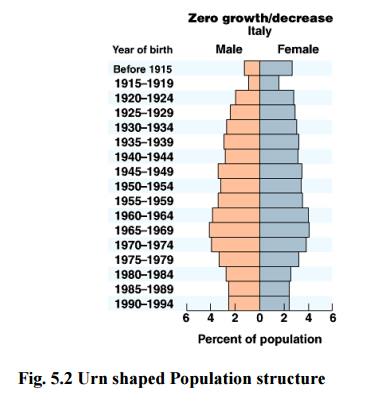
1.7 Population Explosion
The
enormous increase in population due to low death rate and high birth rate.
1.8 Causes
Modern
medical facilities, life expectancy, illiteracy.
1.9 Effects
Poverty,
Environmental degradation, over –exploitation of natural resources, threat,
communal war.
1.10 Remedy
Through
birth control programmes.
2 FAMILY WELFARE PROGRAMME
2.1 Objectives
o Slowing down the population explosion
o Over exploitation of natural resources
3 FAMILY PLANNING PROGRAMME
3.1Objectives
o Reduce
infant mortality rate. o Encourage late marriages.
o Improve women’s health.
o Control of communal diseases.
4 ENVIRONMENT AND HUMAN HEALTH
1. Physical
Hazards – Radioactive and UV radiations, Global warming, Chlorofluro carbons,
Noise etc.
2. Chemical
Hazards – Combustion of Fossil fuels, industrial effluence, pesticides, heavy
metals.
3. Biological
Hazards- Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites.
5 HUMAN RIGHT
v Human
right to freedom
v Human
right to property
v Human
right to freedom of religion
v Human
right to culture and education
v Human
right to constitutional remedies
v Human
right to equality
v Human
right against exploitation
v Human
right to food and environment
v Human
right to good health.
v To
promote interdependence among Asian countries in all areas of cooperation by
identifying Asia's common strengths and opportunities which will help reduce
poverty and improve the quality of life for Asian people whilst developing a
knowledge-based society within Asia and enhancing community and people
empowerment;
v To expand
the trade and financial market within Asia and increase the bargaining power of
Asian countries in lieu of competition and, in turn, enhance Asia's economic
competitiveness in the global market;
v To serve
as the missing link in Asian cooperation by building upon Asia's potentials and
strengths through supplementing and complementing existing cooperative
frameworks so as to become a viable partner for other regions;
v To
ultimately transform the Asian continent into an Asian Community, capable of
interacting with the rest of the world on a more equal footing and contributing
more positively towards mutual peace and prosperity.
6 VALUE EDUCATION
Education
It is
nothing but learning about the particular thing through knowledge. We can
identify our values and ourselves with the help of knowledge and experience.
6.1Types
1. Formal
education-Self related learning process.
2. Value
education – Analyze based on instruments.
3. Value-based
environment education- Based on environment.
6.2 Objectives
ü To
improve the integral growth of human begins.
ü To create
attitudes and improvement towards sustainable lifestyle.
ü To
increase awareness about our national history our cultural heritage,
constitutional rights, national integration, community develo9pment and
environment.
ü To create
and develop awareness about the values and their significance and role.
ü To know
about various living and non- living organisms and their interaction with
environment.
6.3 Types of values
v Universal
values-Importance of the human conditions.
v Cultural
values-Right, wrong, good and bad.
v Individual
values-Individual personality and experiences.
v Global
values-Human civilization.
v Spiritual
values-Self-restraint, discipline.
7 HIV /AIDS
AIDS is
the abbreviated form for Acquired Immuno
Deficiency Syndrome caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immune deficiency Virus).
7.1 Origin of HIV/AIDS
1. Through
African Monkey
African
monkey or Chimpanzees To human.
2. Through
Vaccine Programme
(a)Polio,
small pox vaccine from monkey’s kidney-Africa.
(b)
Hepatitis-B viral vaccine-Los Angles and New York.
7.2 Factors influencing modes of Transmission of
HIV
1. Unprotected
sex with infected person.
2. Using
needles or syringes from HIV positive person.
3. During
pregnancy, breast feeding HIV transmits from mother to infant babies.
4. Blood
transfusion during accident and pregnancy.
5. Biologically
the male to female transmission is 2 to 4 time more efficient than female to
male transmission.
6. Women’s
cervical tissue is more vulnerable to HIV than men.
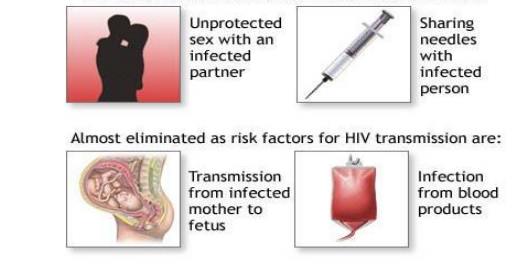
7.3 Factors not influencing transmission of HIV
1. Tears,
food, air, cough, handshake and normal kissing.
2. Mosquito
flies and insect bites.
3. Sharing
of utensils, clothes, toilets and bathroom.
Effects
·
Death
·
Loss of labor
·
Inability to work
·
Lack of energy.
7.4 Functions of HIV in human body
White
blood cells (WBC) are responsible for the formation of antibodies called
T-helper cells’-helper cells are the key infection fighters in the immune
system. Once HIV cells are enter into the boy they destroy the T-cells and
cause many infection diseases.
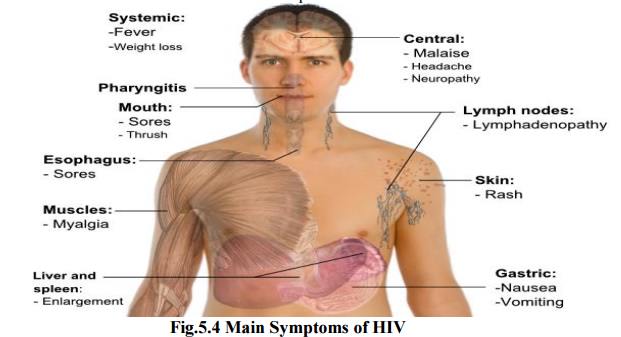
7.5 Symptoms
I.Minor symptoms
ü Persistent
cough for more than one month.
ü General
skin disease.
ü Viral
infection.
ü Fungus
infection in mouth and throat.
ü Frequent
fever, headache and fatigue.
II.
Major
symptoms
ü Diarrhea
for more than one month.
ü TB for
more than one month.
ü Fall of
hairs.
ü 10% of
body weight loss within short period.
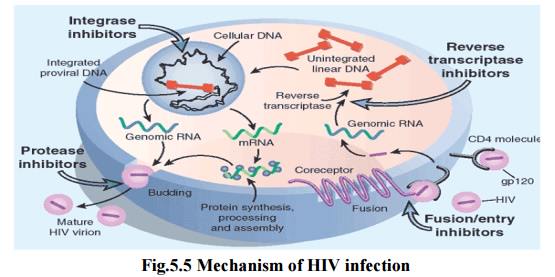
7.6 Mechanism of Infection
7.7 Control and Preventive measures
1. Education.
2. Prevention
of Blood borne HIV transmission.
3. Primary
health care.
4. Counseling
services.
5. Drug
treatment.
7.8 Scenario in India
Large
number of cases has been reported in Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
7.9 World Scenario
Nearly
90% of the HIV affected peoples live in developing countries.13% of world’s
population live in Africa. About 3 million people so far died due to HIV in 2003.In
the world AIDS ranking India is in 2nd place.
7.10 HIV symbol and World AIDS day

8 WOMANS AND CHILD WELFARE
5.8.1
Objectives
v To
provide education
v To impart
vocational training
v To
generate awareness
v To
improve employment opportunities
v To restore dignity, equality and respect.

9 ROLE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN ENVIRONMENT
1. Remote sensing
Components
- A platform, aircraft, a balloon, rocket and satellite.
Functions
·
Origin of electro magnetic energy
·
Transmission of energy
·
Interaction of energy
·
Detection of energy
·
Preprocessing of data
·
Data analysis and interpretation
·
Integration and other applications.
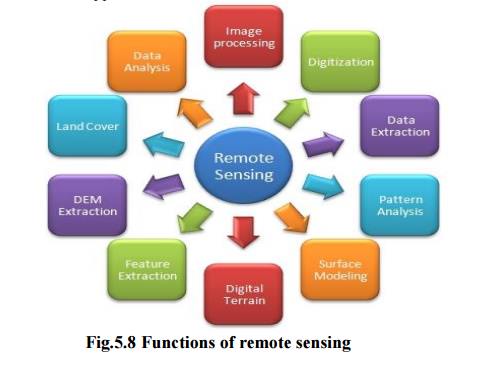
Applications
In
agriculture, forestry, land cover, water resources.
2. Data Base- Collection of inter related
data on various subjects.
Applications
§ Ministry
of environment and forest
§ National
management information system
§ Environmental
information system.
3. Geographical information system (GIS)
It is a
technique of superimposing various thematic maps using digital data on a large
number of inter-related aspects.
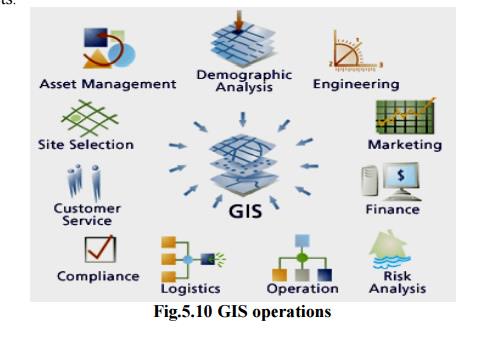
Application
Ø Thematic
maps are super imposed using soft wares.
Ø Interpretation
of polluted zones
Ø To check
unplanned growth and related environmental problems.
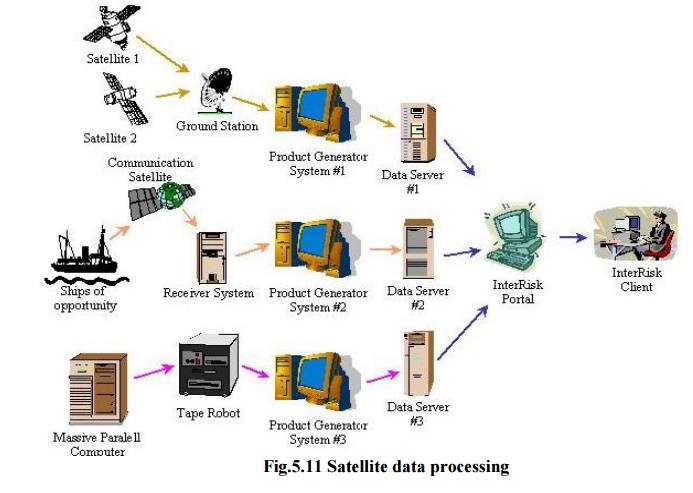
4. Satellite data
v Helps in providing reliable information and
data about forest cover
v Provide
information about forecasting weather
v Reserves
of oil, minerals can be discovered.
5. World Wide Web
It
provides Current data.
Applications
·
Online learning
·
Digital files or photos, animations on
environmental studies.
10 ROLE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN HUMAN HEALTH
The health service technology involves three
systems Ø Finance
and accounting
Ø Pathology
Ø Patient Administration –
clinical system.
Applications
§ Data regarding birth and death
rates
§ To monitor the health of the
people effectively
§ The information regarding the
outbreak of epidemic diseases.
§ Online Consultation
§ Drugs and its replacement.
Related Topics