Chapter: 11th Microbiology : Chapter 13 : Immunology
Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis is the formation and development of blood cells of all types. In humans, hematopoiesis begins in the yolk sac in the first weeks of embryonic development. In the third month of gestation, the stem cells migrate from the yolk sac to the fetal liver and then to the spleen. Hematopoiesis continues in these two organs from the third to the seventh month of gestation. As gestation continues, the site of hematopoiesis gradually shifts to the bone marrow such that it becomes the principle site at the time of birth.
As hematopoietic stem cells can give rise to all of the different types of blood cells, they are often known as pluripotent stem cells. The different types of blood cells and their lineage relationships are summarized in Figure 13.10. We shall be concerned here only with the cells derived from the myeloid progenitor and the common lymphoid progenitor.
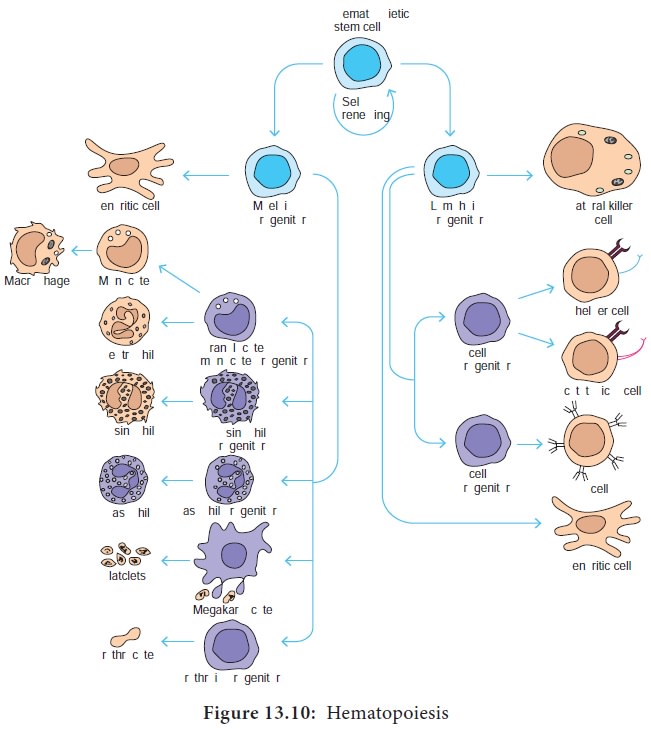
The myeloid progenitor gives rise to erythrocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes, mast cells and platelets. The common lymphoid progenitor gives rise to B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells.
Related Topics