Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Histamine, Serotonin, & the Ergot Alkaloids
H3- & H4-Receptor Antagonists
H3- & H4-RECEPTOR
ANTAGONISTS
Although
no selective H3 or H4 ligands are presently available for
general clinical use, there is great interest in their therapeutic potential. H3-selective
ligands may be of value in sleep disorders, narcolepsy, obesity, and cognitive
and psychiatric disorders. Tiprolisant, an inverse H3-receptor
agonist, has been shown to reduce sleep cycles in mutant mice and in humans
with narco-lepsy. Increased obesity has been demonstrated in both H1-
and H3-receptor knockout mice. As noted, several newer antipsychotic
drugs have significant affinity for H3 receptors.
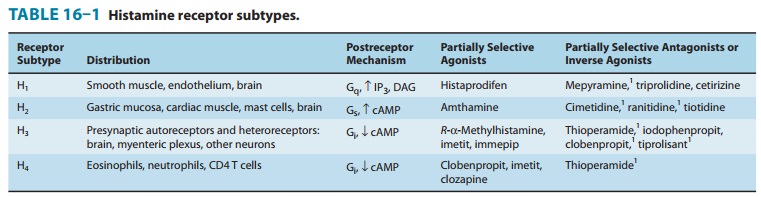
Because
of the homology between the H3 and H4 receptors, many H3
ligands also have affinity for the H4 receptor. H4
blockers have potential in chronic inflammatory conditions such as asthma, in
which eosinophils and mast cells play a prominent role. No selective H4
ligand is available for use in humans, but in addition to research agents
listed in Table 16–1, many H1-selective blockers (eg,
diphenhydramine, cetirizine, loratadine) show some affinity for this receptor.
Several studies have suggested that H4-receptor antagonists may be
useful in pruritus, asthma, allergic rhinitis, and pain conditions.
Related Topics