Parts of Flower | Botany - Gynoecium | 11th Botany : Chapter 4 : Reproductive Morphology of Angiosperm
Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 4 : Reproductive Morphology of Angiosperm
Gynoecium
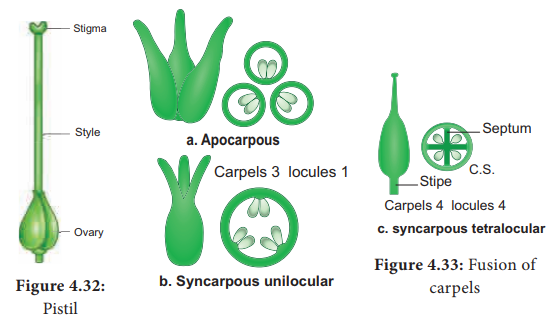
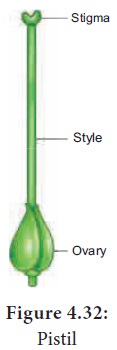
Gynoecium
Gynoecium or pistil is the female reproductive part of the flower.
A pistil consists of an expanded basal portion called the ovary, an elongated section called a style and an apical structure that receives pollen called a stigma. Ovary with stipe is called stipitate ovary.
Carpel: They are components of a gynoecium. Gynoecium is made of one or more carpels. Carpels may be distinct or connate.
1. Number of carpel
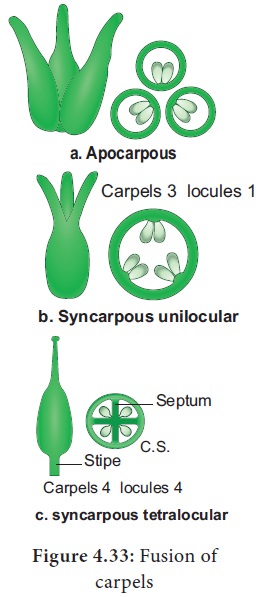
2. Fusion of carpels
![]()
![]()
![]()
It is an important systematic character. Apocarpous gynoecium is generally thought to be ancestral condition in Angiosperms.

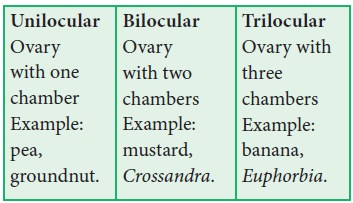
3. Number of locules
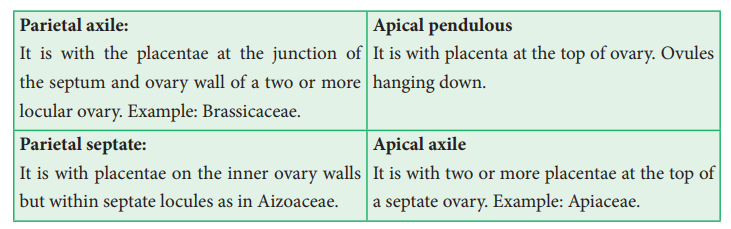
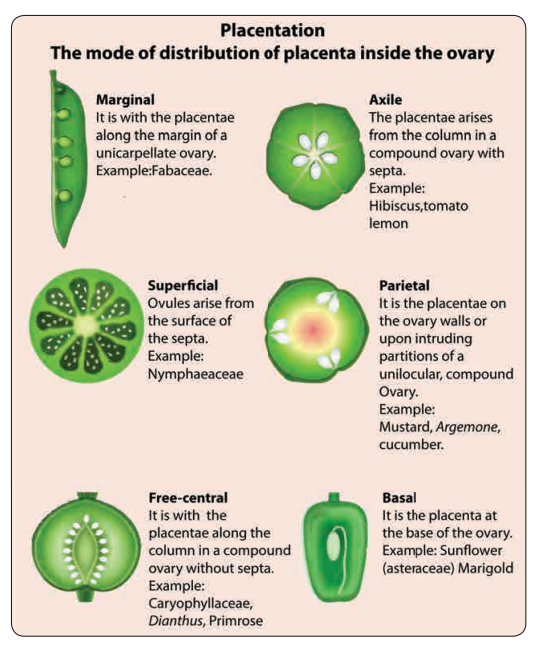
Ovary bears ovules on a specialized tissue called placenta. A septum is a crosswall or partition of ovary. The walls of ovary and septa form a cavity called locule.
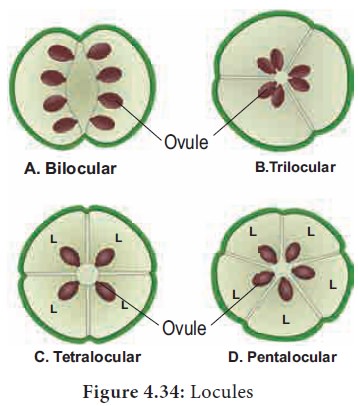
Number of locules
Like that tetralocular and pentalocular ovaries are present according to the locule numbers four and five. More than one locule ovaries are called plurilocular.
4. Style and stigma
1 Style is a stalk like structure of a pistil connecting ovary and stigma.
a. Simple: Single unbranched style. Example: Hibiscus.
b. Bifid: A style branched into two.
![]()
![]()
![]() Example: Asteraceae
Example: Asteraceae

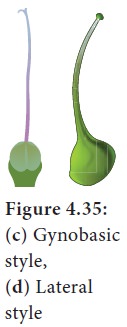
c. Gynobasic style: arising from base of the ovary. Example: Lamiaceae (Ocimum), Ovu characteristic of Boraginaceae.
d. Lateral style: Style arises from the side of ovary. Example: Mangifera.
2. Stigma: A stigma is a structure present at the tip of a pistil which receives the pollen grains.
a) Discoid: A disk-shaped stigma is called discoid.
b) Capitate: Stigma appearing like a head. Example: Alchemilla
c) Globose: Stigma is spherical in shape is called globose.
d) Plumose stigma: Stigma feathery which is unbranched or branched as in Asteraceae, Poaceae.
3. Pistillode: A reduced sterile pistil. Example: ray floret of head infloresence in Helianthus.
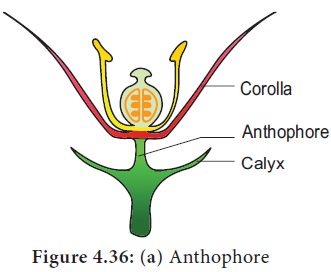
5. Extension of the condensed internode of the receptacle
1. Anthophore: The internodal elongation between calyx and corolla. Example: caryophyllaceae (Silene conoidea)
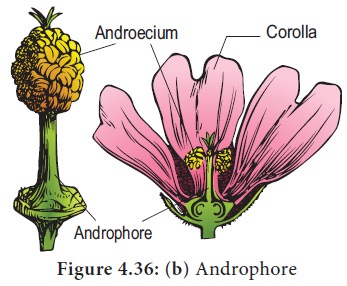
2. Androphore: The internodal elongation between the corolla and androecium. Example: Grewia.
3. Gynophore: The internodal elongation between androecium and gynoecium. Example: Capparis.
Saffron flower stigma is costly. One gram of saffron is around Rs.300. In traditional texts ascribe a few medicinal properties to saffron stigma.It is also used as a flavoring substance.
4. Gynandrophore or Androgynophore: The unified internodal elongation between corolla and androecium and androecium and gynoecium. Example: Gynandropsis.

6. Ovary position
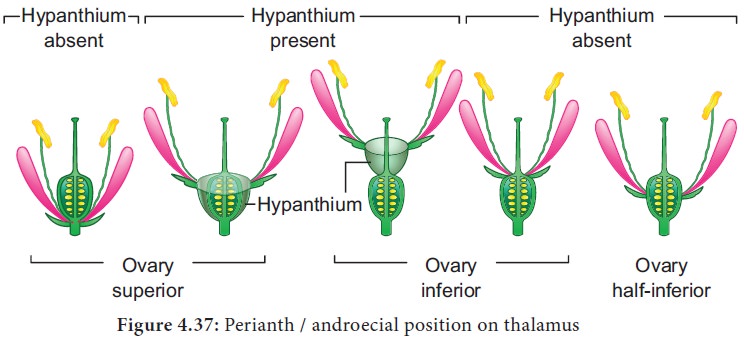
Hypanthium: (staminal disk); a fleshy, elevated often nectariferous cup like thalamus.
The position or attachment of ovary relative to the other floral parts. It may be classified into
1. Superior ovary: It is the ovary with the sepals, petals and stamens attached at the base of the ovary.
2. Inferior ovary: It is the ovary with the sepals, petals and stamens attached at the apex of the ovary.
3. Half-inferior ovary: It is the ovary with the sepals, petals and stamens or hypanthium attached near the middle of the ovary.

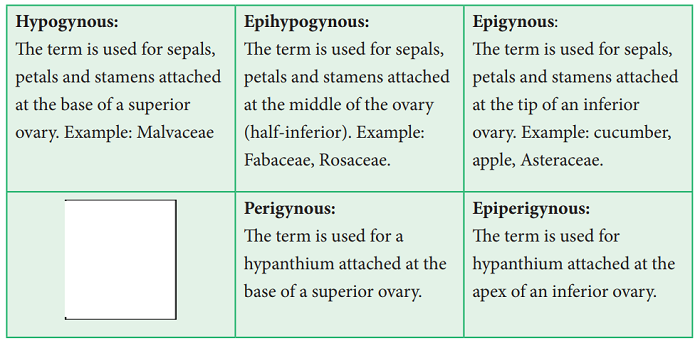
7. Perianth / androecial position on thalamus:
It describes placement of the perianth and androecium relative to the ovary and to a hypanthium, if present.
Related Topics