Science - Effect of Pressure on Gases | 9th Science : Matter Around Us
Chapter: 9th Science : Matter Around Us
Effect of Pressure on Gases
Effect of Pressure on Gases
When you are blowing air into a balloon, you fill
it with air particles moving with high speed. These particles colloide at the
sides of the balloon and the applied pressure on it keeps the balloon inflated.
In a similar way all gases exert pressure. The
pressure depends on the temperature of the gas and the volume it occupies.

Higher the temperature, higher will be the kinetic
energy of the particles and faster will be the motion of the gas particles. They
start hitting harder and more o en on the walls of the container and pressure
increases. Similarly when the volume decreases the gas gets compressed. The
particles of the gas have only lesser space to move around. Therefore they
start hitting on the walls of the container more and pressure increases.

We have seen that in gases the particles are apart
and there is only very weak forces of attraction between them. If pressure is
applied on a gas the particles are brought in close contact with each other.
The attractive forces eventually become strong enough to hold the particles
close together, and the gas condenses to the liquid state.
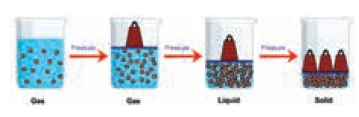
If the pressure is increased still further, the particles are brought in very close to each other that the attractive forces are strong enough to hold them in place in three-dimensional arrangement. The liquid then becomes a solid.

But, increase in pressure alone cannot bring about change of states from gas to liquid to solid. Apart from high pressure, low temperature is also necessary for a gas to be converted into liquid. You may learn more about this in higher classes.
So far we have been discussing the classification
of matter on the basis of their physical states. Now let us see how we can
classify matter on the basis of chemical composition.
To Summarise
Related Topics