Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Deficiency of Vitamins
DEFICIENCY OF VITAMINS
1. Vitamin A:
(Retinol)
The important deficiency states due to lack of vitamin A in the diet
are:
1.
Night Blindness: In the early stages of
vitamin A deficiency, the individual
cannot see well in dim light. In advanced deficiency, the subject cannot see
objects in dim light.
2.
Xerosis Conjunctiva: The
conjunctiva is dry, thickened, wrinkled
and pigmented. The pigmentation gives conjunctiva a smoky appearance.
3.
Xerosis Cornea: When dryness spreads
to cornea, it takes on a hazy,
lusterless appearance.
4.
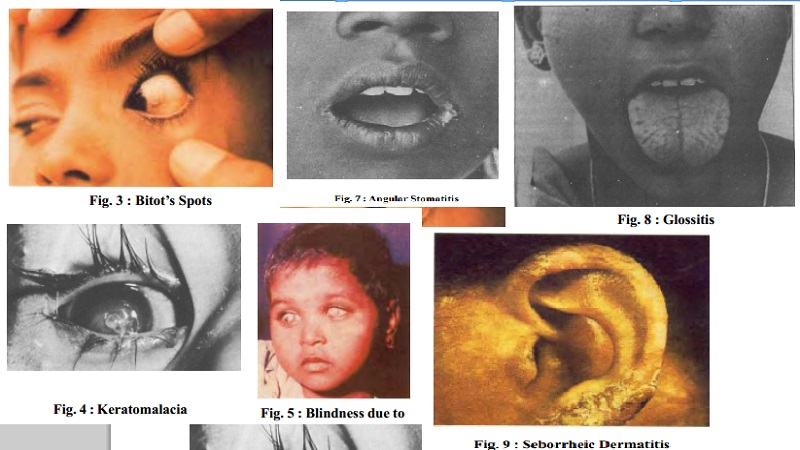
Bitot's Spots: Greyish glistening
white plaques, formed of desquamated thickened conjuctival epithelium, usually
triangular in shape and firmly adhering to the conjuctiva.
5.
Keratomalacia : When xerosis of the
conjuctiva and cornea is not treated, it may develop into a condition known as keratomalacia.
6.
Follicullar Hyperkeratosis: The skin
becomes rough and dry.
Under the national prophylaxis programme against nutritional blindness
2,00,000 IU of vitamin A in oil is administered every six months to preschool
children to eliminate vitamin A deficiency.
2. Vitamin D (7 - dehydro cholestrol)
i. Rickets
The chief signs in fully developed active rickets are found in the chest
wall (beading), waists and ankles (thickening) and various deformities (knock -
knees and bow legs). The child is restless, fretful and pale with flabby and
toneless muscles, which allow the limbs to assume unnatural postures.
Development is delayed so that the teeth often erupt late and there is failure
to sit up, stand, crawl and walk at the normal ages. There is usually a
protuberant abdomen so called potbelly.
ii. Osteomalacia
3. Vitamin E
(Tocopherol)
Vitamin E deficiency in animals causes several disorders such as
reproduction failure, liver necrosis, etc,
4. Vitamin K
Vitamin K deficiency leads to haemorrhagic conditions.
5. Vitamin C (Ascorbic
Acid)
Severe Vitamin C deficiency results in the development of the disease scurvy. The disease is characterized by
General weakness followed by shortness of breath, pain in bones, joints
and muscles of the extremities.
Swollen and tender joints, haemorrhages in various tissues and pain in
joints.
Bleeding gums and loose teeth.
In infantile scurvy, the infant screams if picked up or moved or
handled. There is pain and tenderness of the limbs.
6. Vitamin B1
(Thiamine)
Thiamine
deficiency causes the disease, beriberi, in human beings. Two forms of beriberi
namely wet beriberi and dry beriberi occurs in adults. The
first symptoms are anorexia (loss of appetite) with heaviness and weakness of
the legs. There is pain and numbness in the legs. The subjects feel weak and
get easily exhausted. Oedema is the important feature of wet beriberi. The calf
muscles are swollen. The pulse is fast and bouncing. The heart becomes weak and
death occurs due to heart failure. In infantile beriberi, the first symptoms
are restlessness, sleeplessness and cardiac failure.
7. Vitamin B2 or Riboflavin
Riboflavin deficiency is characterized by
a)Angular stomatitis:
The lesions at the angles of the mouth are termed as angular stomatitis.
b) Glossitis
The tongue in general is acutely inflamed called as glossitis.
c) Skin lesions occur on the nasolabial folds and on the ears as shown in the picture
below.
Cheilosis which is the dry chapped appearance of the lips.
Behavioural abnormalities occur in riboflavin deficient children.
8. Vitamin B3
(Niacin)
Niacin deficiency causes the disease pellagra in humans.
Pellagra is also called Disease of 3D's. Because the disease
has the symptoms of diarrhoea, dermatitis and depression. The disease is
characterized by the following.
Glossitis and
diarrhoea - These are the two outstanding symptoms. Nausea and vomiting are seen
in most cases.
The dermatitis is the most characteristic symptom of the disease.
The commonest sites are the back of the fingers and hands, the forearms, and
the neck. The following pictures show dermatitis on hands and neck.
c) Milder mental
disturbances consisting of irritability, depression, inability to concentrate
and poor memory are common in niacin deficiency.
9. Vitamin B6
or Pyridoxine
Pyridoxine deficiency results in
the following
Hypochromic microcytic anaemia.
Sleep disturbances, irritability and depression
Angular stomatitis, glossitis and cheilosis in pregnant and lactating
mothers.
10. Pantothenic Acid
The visible signs of deficiency include nausea,
vomiting, tremor of the outstretched hands, irritability and burning feet
syndrome.
11. Folic Acid
Folic acid deficiency causes megaloblastic anaemia mainly in
pregnant women of low income groups.
12. Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 deficiency causes perinicious anemia in humans. Soreness and inflammation of the tongue are commonly observed. Parasthesia (numbness and tingling) occurs in fingers and toes. Persons living exclusively on vegetarian diets develop vitamin B12 deficiency.
Related Topics