Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Drug Receptors & Pharmacodynamics
Cytokine Receptors
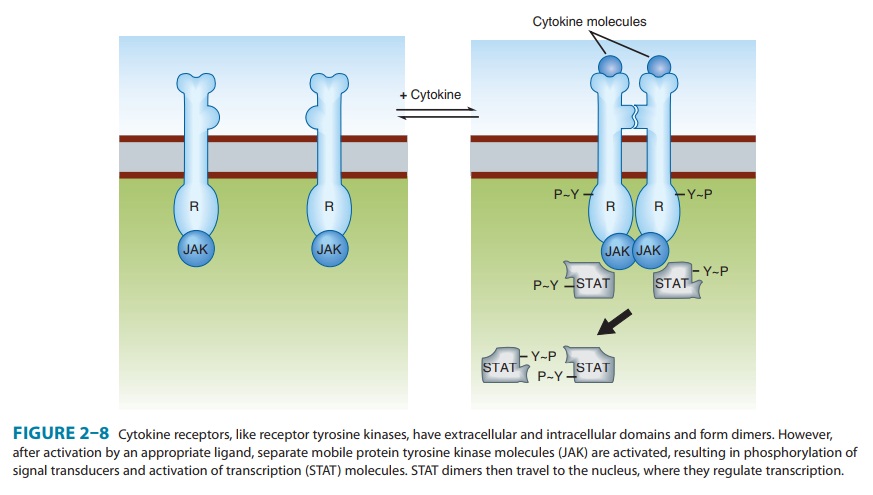
Cytokine Receptors
Cytokine
receptors respond to a heterogeneous group of peptide ligands, which include
growth hormone, erythropoietin, several kinds of interferon, and other
regulators of growth and differentiation. These receptors use a mechanism
(Figure 2–8) closely resembling that of receptor tyrosine kinases, except that
in this case, the protein tyrosine kinase activity is not intrinsic to the
receptor molecule. Instead, a separate protein tyrosine kinase, from the
Janus-kinase (JAK) family, binds noncovalently to the receptor. As in the case
of the EGF receptor, cytokine receptors dimerize after they bind the activating
ligand, allowing the bound JAKs to become activated and to phosphorylate
tyrosine residues on the receptor. Phosphorylated tyrosine residues on the
receptor’s cytoplasmic surface then set in motion a complex signaling dance by
binding another set of proteins, called STATs (signal transduc-ers and
activators of transcription). The bound STATs are them-selves phosphorylated by
the JAKs, two STAT molecules dimerize (attaching to one another’s tyrosine
phosphates), and finally the STAT/STAT dimer dissociates from the receptor and
travels to the nucleus, where it regulates transcription of specific genes.
Related Topics