Chapter: Modern Medical Toxicology: Miscellaneous Drugs and Poisons: Gastrointestinal and Endocrinal Drugs
Corticosteroids - Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Anti-inflammatory Drug
Corticosteroids
Glucocorticoids
have been employed in the treatment of asthma for a long time, and are
especially useful in the management of severe chronic asthma or severe acute
exacerbations. These drugs are usually given systemically, but the development
of aerosol formulations in recent years has greatly improved the efficacy as
well as safety.
Inhaled Corticosteroids
Examples
include beclomethasone dipropionate, triamcinolone acetonide, flunisolide,
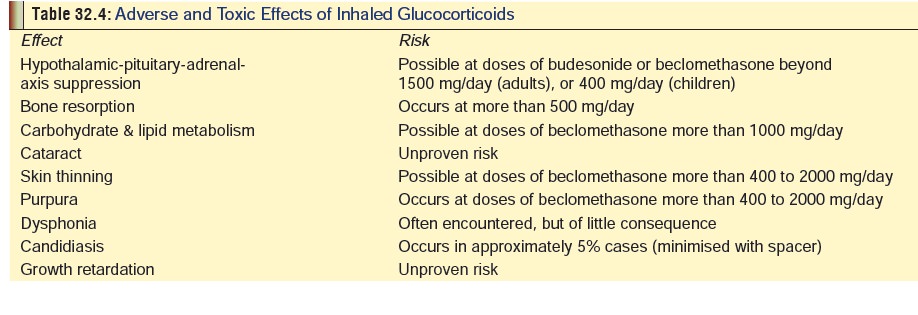
budesonide dipropionate, and flutica-sone propionate. Adverse and toxic effects
have been listed in Table 32.4. Of
all the inhaled corticosteroids, fluticasone is said to be the safest, being
associated with a low incidence of adverse effects. Treatment involves
cessation of inhaled glucocorticoids. Oropharyngeal candidiasis can be
prevented by rinsing the mouth and throat with water after each use and by
employing spacer or reservoir devices attached to the dispenser.
Cromolyn and Nedocromil
Cromolyn was first synthesised in
1965 and has been in use in the management of asthma since 1973. It is the
first-line drug for the treatment of mild to moderate asthma. It is also used
as eye drops in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis. A related compound,
Nedocromil was released for use recently.
Mode of action is through inhibition
of pulmonary mast cell degranulation in response to a variety of stimuli, and
suppression of activating effects of chemoattractant peptides on human
neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes. Cromolyn and nedocromyl are
administered by inhalation using either solution (delivered by aerosol spray or
nebuliser), or powdered drug (delivered by turbo-inhaler). Only about 1% of an
oral dose of cromolyn is absorbed. After inhalation, peak plasma concentrations
occur within 15 minutes. The biological half-life ranges from 45 to 100
minutes.
![]() Adverse effects are uncommon with
both cromolyn and nedocromil. Occasional effects reported include cough,
bronchospasm, laryngeal oedema, joint pain, headache, rash, angioedema, and
nausea. Nedocromil may leave behind a bad taste.
Adverse effects are uncommon with
both cromolyn and nedocromil. Occasional effects reported include cough,
bronchospasm, laryngeal oedema, joint pain, headache, rash, angioedema, and
nausea. Nedocromil may leave behind a bad taste.
Related Topics