Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: RNA Polymerase and RNA Initiation
Concentration of Free RNA Polymerase in Cells
Concentration of Free RNA Polymerase in Cells
It is necessary to know the concentration of free
intracellular RNA polymerase to design meaningful in vitro transcription experiments. One method of determining the
concentration utilizes the fact that theand β’ subunits of the E. coli RNA polymerase are larger than most
other polypeptides in the cell. This permits them to be easily separated from
other cellular proteins by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Consequently, after such electrophoresis, the amount of protein in theand β’ bands is compared to the total amount of protein
on the gel. The results are that a bacterial cell contains about 3,000
molecules of RNA polymerase. A calculation using the cell doubling time and
amounts of messenger RNA, tRNA, and ribosomal RNA in a cell leads to the
conclusion that about 1,500 RNA molecules are being synthesized at any instant.
Hence half the cell’s RNA polymerase molecules are synthesizing RNA. Of the
other 1,500 RNA polymerase molecules, fewer than 300 are free of DNA and are
able to diffuse through the cytoplasm. The remainder are temporarily bound to
DNA at nonpromoter sites.
How do we know these numbers? On first consideration,
a direct physical measurement showing that 300 RNA polymerase molecules are
free in the cytoplasm seems impossible. The existence, however, of a special
cell division mutant of E. coli makes this measurement
straight-forward (Fig. 4.5). About once per normal division, these mutant cells
divide near the end of the cell and produce a minicell that lacks DNA. This
cell contains a sample of the cytoplasm present in normal cells. Hence, to
determine the concentration of RNA polymerase free of DNA
Figure 4.5 The generation of a minicell lacking a chromosome.
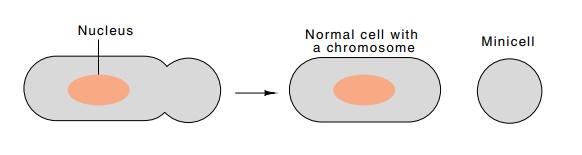
in cells, it is necessary only to determine the
concentration of ββ’ in the DNA-less minicells. Such
measurements show that the ratio of ββ’ to
total protein has a value in minicells of one-sixth the value found in
Related Topics