Chapter: Basic Concept of Biotechnology : Animal Biotechnology
Cloning
Cloning
The
procedure for obtaining organisms with the same genetic information. You need
to collect an egg cell from a donor (a female sheep, mouse or cat). Then you
need to carefully remove the nucleus from the cell and collect another cell
from the skin, udder or other tissue from another male or female donor of the
same species (i.e. fromanother sheep, mouse or cat). From this cell, you also
need to remove the cell nucleus and place it in the empty egg. The egg obtained
in such a way needs to be treated with a gentle electric shock. The egg should
begin to divide and grow into a multicellular embryo. At this stage, the embryo
needs to be implanted into the uterus of a surrogate mother. If the pregnancy
develops and the animal is born (Fig. 12).
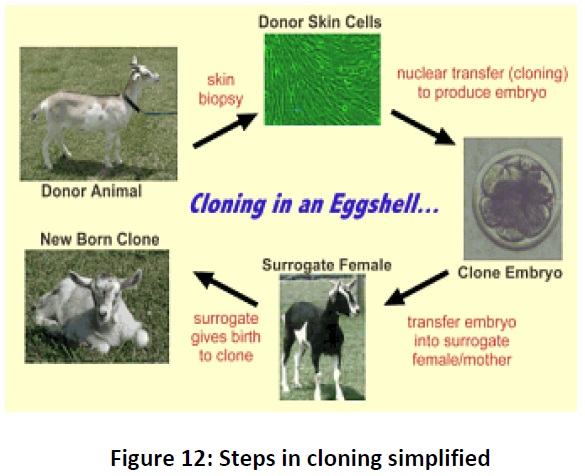
Creating
a clone of your favorite animal seems like a great way to insure your pet will
be with you forever. Although this might be a goal of cloning, it is not the
primary focus of biotech specialists. Commercialization of cloning allows
desirable traits to be reliably propagated. Animal breeders are able to clone
animals with superior traits such as cows with high milk production or champion
racehorses. Embryo twinning (splitting embryos in half) was the first method of
cloning used to produce identical twin cattle. Since the twins are the result
of mixing the genetic material from two parents, the exact genetic make-up of
the animal is not known until it has matured. Dolly (the veryfamous sheep that
was the first mammal ever cloned in the lab), however, was created from a single
cell, not an embryo. DNA from a donor cell is inserted into an egg that has had
its own DNA removed. It is a very delicate and difficult process. So far,
animals successfully cloned include sheep, goats, pigs, cattle, cats, deer and
dogs.
One
can imagine future uses of cloning that could include using preserved DNA to
help maintain endangered species or even recover extinct species!
Ø
Limits
to Cloning: The donor cell must come from a livingorganism: an
organism is also shaped by its environment, success rate for cloning is very
low and clones may be old before their time.
Ø
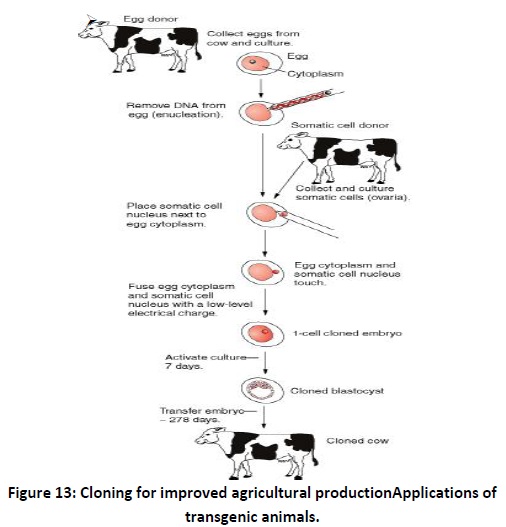
The
future of cloning: preservation of endangered
animals,studying the effect of drugs etc on duplicates, improve agricultural
production (Fig. 13)
Related Topics