Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 6 : Solid State
Classification of crystalline solids
Classification
of crystalline solids:
1. Ionic solids:
The structural units of
an ionic crystal are cations and anions. They are bound together by strong
electrostatic attractive forces. To maximize the attractive force, cations are
surrounded by as many anions as possible and vice versa. Ionic crystals possess
definite crystal structure; many solids are cubic close packed. Example: The
arrangement of Na+ and Cl- ions in NaCl crystal.
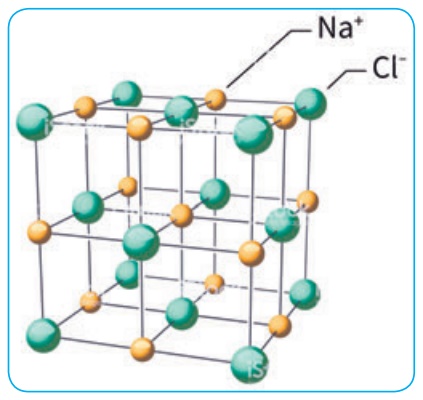
Characteristics:
·
Ionic solids have high melting points.
·
These solids do not conduct electricity, because the ions are
fixed in their lattice positions.
·
They do conduct electricity in molten state (or) when dissolved in
water because, the ions are free to move in the molten state or solution.
·
They are hard as only strong external force can change the relative
positions of ions.
2. Covalent solids:
In covalent solids, the
constituents (atoms) are bound together in a three dimensional network entirely
by covalent bonds. Examples: Diamond, silicon carbide etc. Such covalent
network crystals are very hard, and have high melting point. They are usually
poor thermal and electrical conductors.

3. Molecular solids:
In molecular solids, the
constituents are neutral molecules. They are held together by weak van der
Waals forces. Generally molecular solids are soft and they do not conduct
electricity. These molecular solids are further classified into three types.
(i) Non-polar molecular solids:
In non polar molecular
solids constituent molecules are held together by weak dispersion forces or
London forces.
They have low melting
points and are usually in liquids or gaseous state at room temperature.
Examples: naphthalene, anthracene etc.,
(ii) Polar molecular solids
The constituents are
molecules formed by polar covalent bonds. They are held together by relatively
strong dipole-dipole interactions. They have higher melting points than the
non-polar molecular solids. Examples are solid CO2 , solid NH3
etc.
(iii) Hydrogen bonded molecular solids
The constituents are
held together by hydrogen bonds. They are generally soft solids under room
temperature. Examples: solid ice (H2O), glucose, urea etc.,
3. Metallic solids:
You have already studied
in XI STD about the nature of metallic bonding. In metallic solids, the lattice
points are occupied by positive metal ions and a cloud of electrons pervades
the space. They are hard, and have high melting point. Metallic solids possess
excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. They possess bright lustre.
Examples: Metals and metal alloys belong to this type of solids, for example
Cu,Fe,Zn, Ag ,Au, Cu-Zn etc.
Related Topics