Chemistry - Calculation of unit cell dimensions and density | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 6 : Solid State
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 6 : Solid State
Calculation of unit cell dimensions and density
Calculations involving unit cell dimensions:
X-Ray diffraction analysis is the most powerful tool for the determination of crystal structure. The inter planar distance between two successive planes of atoms can be calculated using the following equation form the X-Ray diffraction data 2dsinθ = nλ
The above equation is known as Bragg’s equation.
Where
λ is the wavelength of X-ray used for diffraction.
θ is the angle of diffraction
By knowing the values of θ, λ and n we can calculate the value of d.
d = n λ /2sin θ
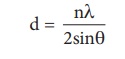
Using these values the edge of the unit cell can be calculated.
Calculation of density:
Using the edge length of a unit cell, we can calculate the density ( ρ ) of the crystal by considering a cubic unit cell as follows.
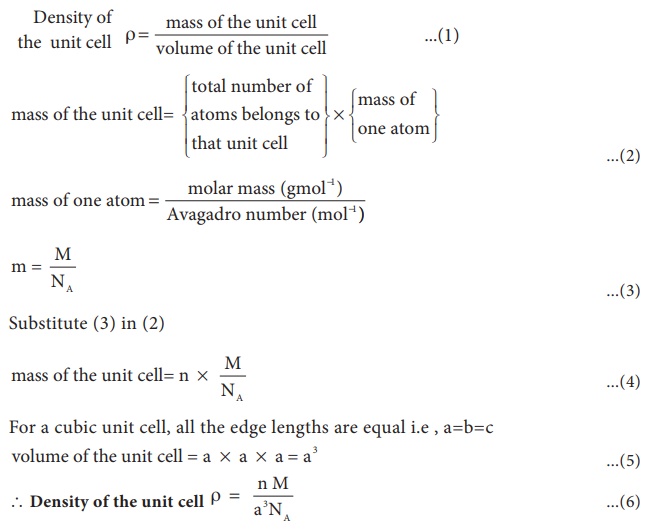
Equation (6) contains four variables namely ρ , n , M and a . If any three variables are known, the fourth one can be calculated.
Example 2
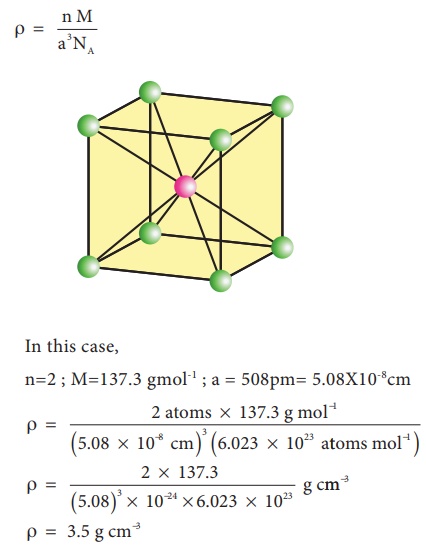
Barium has a body centered cubic unit cell with a length of 508pm along an edge. What is the density of barium in g cm-3?
Solution:
In this case,
n=2 ; M=137.3 gmol-1 ; a = 508pm= 5.08X10-8cm
Related Topics