Neural Control and Coordination : Zoology - Answer the following questions | 11th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Neural Control and Coordination
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Neural Control and Coordination
Answer the following questions
Zoology
Neural Control and Coordination
Evaluation
Answer the following questions
15. Why is the blind spot called so?
• The optic nerves and the retinal blood
vessels enter the eye slightly below the posterior pole which is devoid of photo
receptors hence this region is called blind spot.
16. Sam’s optometrist tells him that his intraocular pressure is high. What is this condition called and which fluid does it involve?
• The increase in the intraocular pressure
leads to the disease called Glaucoma.
• Any block in the canal of Schlemm increases the intraocular pressure of aqueous humor and leads to 'Glaucoma' where the optic nerve and the retina are compressed due to pressure.
17. The action potential occurs in response to a threshold stimulus; but not at sub threshold stimuli. What is the name of the principle involved?
• The increase in the intraocular pressure
leads to the disease called Glaucoma.
• Any block in the canal of Schlemm
increases the intraocular pressure of aqueous humor and leads to 'Glaucoma' where
the optic nerve and the retina are compressed due to pressure.
18. Pleasant smell of food urged Ravi to rush into the kitchen. Name the parts of the brain involved in the identification of food and emotional responses to odour.
• The hypothalamus contains a pair of
small rounded body called mamillary bodies that are involved in olfactory reflexes
and emotional responses to odour
• This is also act as centre for appetite
thirst and heat regulation
19. Cornea transplant in humans is almost never rejected. State the reason.
• The cornea is the only tissue in the
body that can be transplanted from one person to another with little or no possibility
of rejection. This is because cornea does not have blood vessels.
20. At the end of repolarization, the nerve membrane gets hyperpolarized. Why?
• If repolarization becomes more negative than the resting potential - 70mV to about - 90mV it is called hyperpolarization.
21. The choroid plexus secretes cerebrospinal fluid. List the function of it.
• CSF provides buoyancy to CNS structures,
CSF acts as a shock absorber for the brain and spinal cord.
• It nourishes the brain cells by transporting
constant supply of food and oxygen.
• It carries harmful metabolic wastes
from the brain to the blood
• Maintains a constant pressure inside
the cranial vessels.
22. What is the ANS controlling centre? Name the parts that are supplied by the ANS.
The
autonomic neural system is auto functioning and self governed. It is a part of peripheral
neural system that cardiac muscle. This system controls and coordinates the involuntary
activities of various organs. ANS controlling centre is in the hypothalamus.
The
components of ANS:-
1.
Preganglionic neuron:-
The
cell body is in the brain or spinal cord. Its myelinated axon exits the CNS as part
of cranial or spinal nerve and ends in an autonomic ganglion.
2.
Autonomic ganglion:-
It
consists of axon of preganglionic neuron and cell bodies of postganglionic neuron.
3.
Postganglionic neuron:-
It
conveys nerve impulses from autonomic ganglia to visceral effector organs.
The
autonomic neural system consists of sympathetic neural system and parasympathetic
neural system.
23. Why the limbic system is called the emotional brain? Name the parts of it.
The
limbic system is called "emotional brain because it plays a primary role in
the regulation of pleasure pain anger fear sexual feeling and affection.
The
main components of limbic system are olfactory bulbs
• Cingulalate gyrus
• Cingulalate gyrus
• Mammillary body
• Amygdale
• Hippo campus
• Hypothalamus.
24. Classify receptors based on type of stimuli.

25. Name the first five cranial nerves, their nature and their functions.
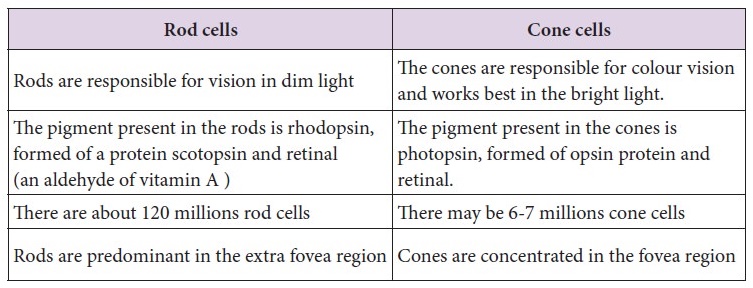
Rods
1. Helps in seeing
in dim light
2. Contains Rhodopsin
pigment
3. The protein retinol
and vitamins aldehyde combine to form scotoptin called Rhodopsin
4. There are 120
million rods are seen the retina
5. Rods are seen
richly over the surface of the foveal region.
Cones
1. Colour perception
in bright light
2. Contains photopsin
3. The protein opsin
and retinol combines to form photopsin.
4. 6-7 million cone
cells are seen on the retina
5. Cones are richly
present on the foveal region.
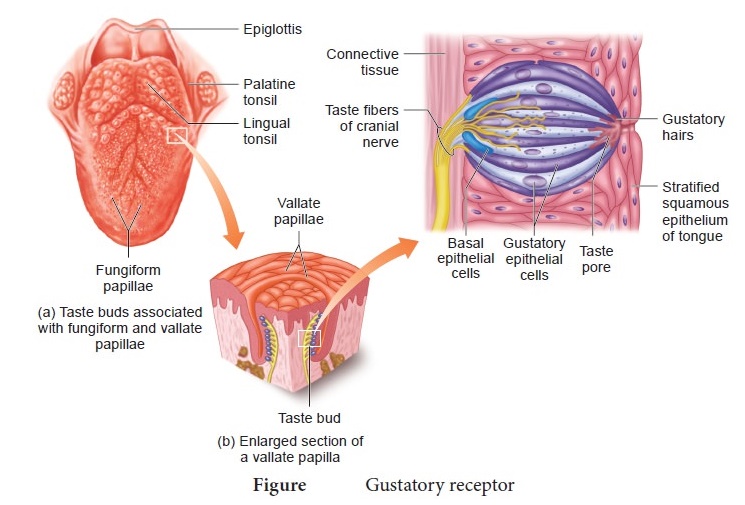
26. The sense of taste is considered to be the most pleasurable of all senses.
Describe the structure of the receptor involved with a diagram.
• The sense of taste is considered to
be the most pleasurable of all senses.
• The tongue is provided with many small
projections called papillae.
• Taste buds are located mainly on the
papillae.
• Taste buds are flask shaped. There
are two major types.
• Gustatory epithelial cells or taste
cells.
• Basal epithelial cells or repairing
cells.
• Long micro villi called gustatory
hairs project from the tip of the gustatory cells and extends through a taste pore
to the surface of the epithelium.
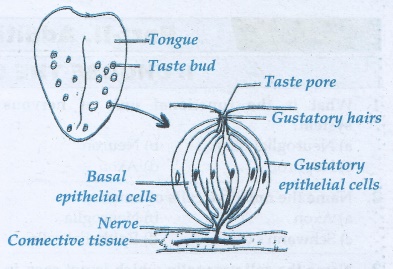
• Gustatory hairs are the sensitive
portion of the gustatory cells and they have sensory dendrites which send the signal
to the brain.
• The basal cells that act as stem cells
divide and differentiate into new gustatory cells.
27. Describe the structures of olfactory receptors?
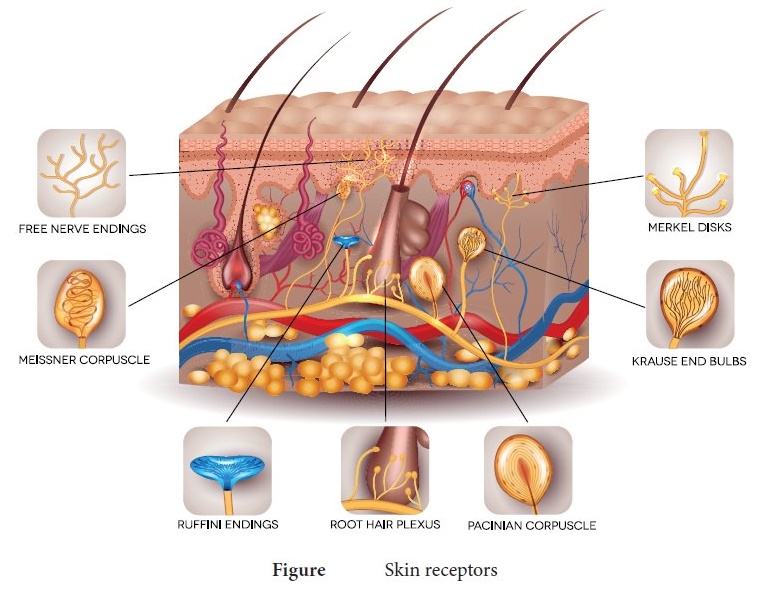
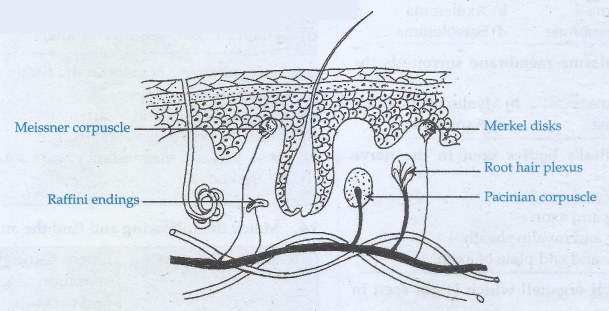
• Skin senses this skin is the largest
sense organ.
• All over the skin sensory receptors
of pressure heat cold and pain.
Following
are the sensory receptors of skin.
Tactile
merkel disc.
• It is a light touch receptor lying
in the deeper layer of epidermis.
Hair
follicle receptors:
• These are light touch receptor lying
around the hair follicles.
Meissner's
corpuscles:
• These are small light pressure receptors
found scattered in the dermis and monitoring vibration due to pressure.
• It allows to detect different textures,
temperature, hardness and pain.
Ruffini
endings:
This
lie in the dermis responds to continuous pressure.
Krause
end bulbs:
These
are thermoreceptors that sense temperature
Q. Why are we getting running nose while crying?
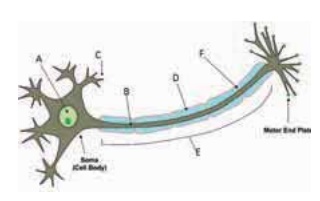
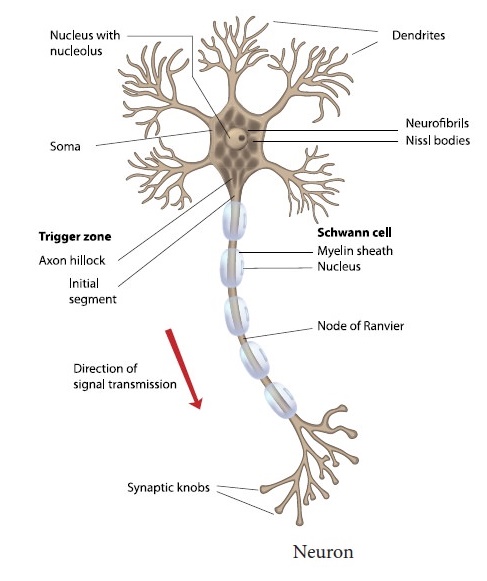
Q. Label the parts of the neuron.
Related Topics