Zoology - Neural Control and Coordination: Important Questions | 11th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Neural Control and Coordination
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 10 : Neural Control and Coordination
Neural Control and Coordination: Important Questions
Neural
Control and Coordination
Evaluation
Choose the followings:
1. Which structure in the ear
converts pressure waves to action potentials?
a.
Tympanic membrane
b. Organ of Corti
c.
Oval window
d.
Semicircular canal
2. Which of the following pairings
is correct?
a. Sensory nerve – afferent
b.
Motor nerve - afferent
c.
Sensory nerve – ventral
d.
Motor nerve – dorsal
3. During synaptic transmission of
nerve impulse, neurotransmitter (P) is released from synaptic vesicles by the
action of ions (Q). Choose the correct P and Q.
a. P = Acetylcholine, Q = Ca++
b.
P = Acetylcholine, Q = Na+
c.
P = GABA, Q=Na+
d.
P = Cholinesterase, Q = Ca++
4. Examine the diagram of the two
cell types A and B given below and select the correct option.

a.
Cell-A is the rod cell found evenly all over retina
b.
Cell-A is the cone cell more concentrated in the fovea centralis
c. Cell-B is concerned with colour
vision in bright light
d.
Cell-A is sensitive to bright light intensities
5.
Assertion: The imbalance in
concentration of Na+, K+ and proteins generates action
potential.
Reason:
To maintain the unequal distribution of Na+ and K+, the
neurons use electrical energy.
a.
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of the
Assertion.
b.
Both Assertion and Reason are true but the Reason is not the correct
explanations of Assertion.
c.
Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
d. Both Assertion and Reason are
false.
6. Which part of the human brain is
concerned with the regulation of body temperature?
a.
Cerebellum
b.
Cerebrum
c.
Medulla oblongata
d. Hypothalamus
7. The respiratory centre is
present in the
a. Medulla oblongata
b.
Hypothalamus
c.
Cerebellum
d.
Thalamus
8. Match the following human spinal
nerves in column I with their respective number in column II and choose the
correct option
column I : column II
P. Cervical nerves : i. 5 pairs
Q. Thoracic nerve : ii. 1 pair
R. Lumbar nerve : iii. 12 pair
S. Coccygeal nerve : iv. 8 pair
a. ( P-iv ),( Q-iii ),( R-i ),(
S-ii )
b.
( P-iii ), ( Q-i ), ( R-ii ), ( S-iv )
c.
( P-iv ),( Q-i ),( R-ii ),( S-iii )
d.
( P-ii ), ( Q-iv ), ( R-i ), ( S-iii )
9. Which of the following cranial
nerve controls the movement of eye ball ?
a.
trochlear nerve
b. optic nerve
c.
Olfactory nerve
d.
vagus nerve.
10. The abundant intracellular
cation is
a.
H+
b. K+
c.
Na+
d.
Ca++
11. Which of the following
statements is wrong regarding conduction of nerve impulse?
a.
In a resting neuron, the axonal membrane is more permeable to K+ ions and
nearly impermeable to Na+ ions.
b.
Fluid outside the axon has a high concentration of Na+ ions and low
concentration of K+, in a resting neuron.
c.
Ionic gradient s are maintained by Na+ K+ pumps across
the resting membrane, which transport 3Na ions outwards for 2K+ into
the cell.
d. A neuron is polarized only when
the outer surface of the axonal membrane possess a negative a charge and its
inner surface is positively charged.
12. All of the following are
associated with the myeline sheath except
a.
Faster conduction of nerve impulses
b. Nodes of Ranvier forming gaps
along the axon
c.
Increased energy output for nerve impulse conduction
d.
Saltatory conduction of action potential
13. Several statements are given
here in reference to cone cells which of the following option indicates all
correct statements for cone cells ?
Statements
(i) Cone cells are less sensitive
in bright light than Rod cells
(ii) They are responsible for
colour vision
(iii) Erythropsin is a photo
pigment which is sensitive to red colour light
(iv) They are present in fovea of
retina
a.
(iii), (ii) and (i)
b. (ii) , (iii) and (iv)
c.
(i), (iii) and (iv)
d.
(i), (ii) and (iv)
14. Which of the following
statement concerning the somatic division of the peripheral neural system is
incorrect?
a.
Its pathways innervate skeletal muscles
b.
Its pathways are usually voluntary
c.
Some of its pathways are referred to as reflex arcs
d. Its pathways always involve four
neurons
15. When the potential across the
axon membrane is more negative than the normal resting potential, the neuron is
said to be in a state of
a.
Depolarization
b. Hyperpolarization
c.
Repolarization
d.
Hypopolarization
16.
Why is the blind spot called so?
17.
Sam’s optometrist tells him that his intraocular pressure is high. What is this
condition called and which fluid does it involve?
18.
Why are we getting running nose while crying?
19.
The action potential occurs in response to a threshold stimulus; but not at sub
threshold stimuli. What is the name of the principle involved?
20.
Pleasant smell of food urged Ravi to rush into the kitchen. Name the parts of
the brain involved in the identification of food and emotional responses to
odour.
21.
Cornea transplant in humans is almost never rejected. State the reason.
22.
At the end of repolarization, the nerve membrane gets hyperpolarized. Why?
23.
Label the parts of the neuron.
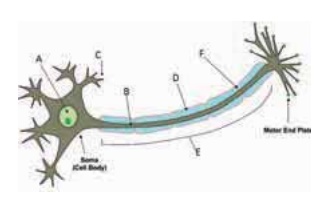
24.
The choroid plexus secretes cerebrospinal fluid. List the function of it.
25.
What is the ANS controlling centre? Name the parts that are supplied by the
ANS.
26.
Why the limbic system is called the emotional brain? Name the parts of it.
27.
Classify receptors based on type of stimuli.
28.
Name the first five cranial nerves, their nature and their functions.
29.
The sense of taste is considered to be the most pleasurable of all senses.
Describe
the structure of the receptor involved with a diagram.
30.
Describe the structures of olfactory receptors?
Glossary
Ampulla
– The widened opening for each of the semicircular canals, containing sensory
innervations.
Depolarization
– The loss of electric potential difference between the inside and outside the
nerve cell due to a change in permeability and migration of sodium ions to the
interior.
Neurotransmitters
– Also known as chemical messengers, are chemicals that transmit signals across
a neuromuscular junction, from one neuron to another "target" neuron,
muscle cell, or gland cell.
Nissl’s granules
– Endoplasmic reticulum with free ribosomes, found in the cytoplasm of neuronal
cell body, but absent in the axon. These are the site of protein synthesis.
Nodes of Ranvier
– Periodic gap in the insulating sheath (myelin) on the axon of certain neurons
that serves to facilitate the rapid conduction of nerve impulses.
Properioception
– The ability to sense stimuli arising within the body regarding position,
motion and equilibrium.
Schwann cells
– It is also called neurilemma cell, produce the myelin sheath around neuronal
axons in the peripheralneural system. Schwann cells are named after German
physiologist Theodor Schwann, who discovered them in the 19th century.
Septum pellucidum
– Located in the midline of the brain, between the two cerebral hemispheres. It
separates the lateral ventricles I and II.
Threshold stimulus
– The minimum stimulus needed to achieve an action potential.
Related Topics