Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school
Androecium And Gynoecium
Sterile stamen or staminode :
In some plants, a stamen may not develop any fertile anther. Such sterile stamens are called staminodes eg. Cassia.
Androecium
It is the third whorl of the flower. It is considered as the male part of the flower. The androecium is made up of stamens or microsporophylls. Each stamen has a slender stalk called filament, bearing the anther (microsporangial sorus). Usually the anther consists of two lobes. The two lobes of an anther are connected by a tissue called connective. Each anther lobe has two pollen sacs(microsporangia). Each pollen sac consists of innumerable Pollen grains (microspores).
Sterile stamen or staminode
In some plants, a stamen may not develop any fertile anther. Such sterile stamens are called staminodes eg. Cassia.
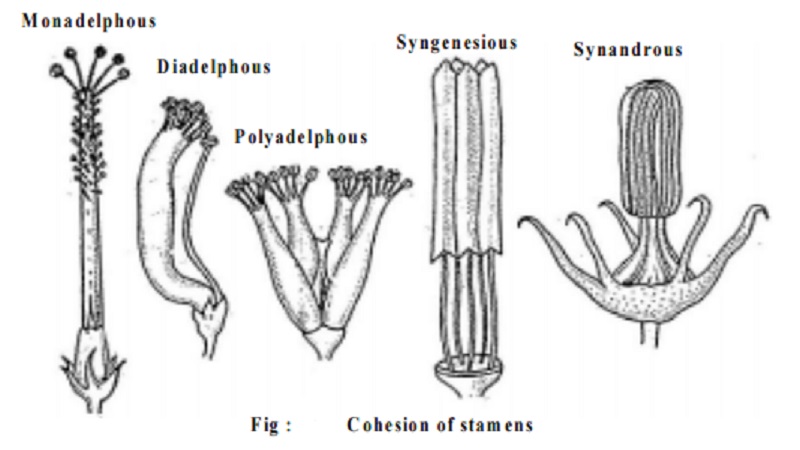
1. Cohesion of Stamens
Monadelphous: All the stamens of a flower are united in one bundle by fusion of their filaments only. The anthers are free, eg. Hibiscus, Abutilon, etc.
Diadelphous: All the stamens of a flower are united in two bundles by fusion of their filaments only. The anthers are free, eg.Clitoria
Polyadelphous: Filaments of all the stamens unite to form more than two bundles. The anthers are free, eg. Citrus.
Syngenesious: Anthers of all the stamens of the flower unite to forma cylinder around the style. The filaments are free, eg.Asteraceae.
Synandrous: Anthers as well as the filaments are fused throughout their whole length, eg. Cucurbitaceae
Polyandrous: Stamens are indefinite and free, eg. Ranunculus.
2. Adhesion of stamens
Epipetalous: Stamens adhre to the petals by their filaments and hence appearing to arise from them, eg. Solanum, Ocimum, etc.
Epitepalous (Epiphyllous): When stamens united with the perianth leaves, the stamens are said to be Epitepalous. eg.Asphodelus. (Spider lilly)
Gynandrous: Stamens adhere to the carpels either throughout their length of by their anthers only. eg. Calotropis.
3. Length of stamens
i. Didynamous: Out of four stamens in a flower, two are long and two are short, eg.
Ocimum
ii. Tetradynamous: Out of six stamens in a flower, two outer are short and four inner are long, eg. Mustard.
4. Position of stamens
i. Inserted: Stamens shorter than corolla tube.ii. Exerted: Stamens longer than the corolla tube, protruding outwards.
Number of antherlobes
Dithecous: Anthers have two lobes with four microsporangia or pollen sacs.
Monothecous: Anthers have only one lobe with two microsporangia.
Fixation of anthers
Basifixed (Innate): Filament is attached to the base of the anther, eg. Brassica.
Adnate: Filament is continued from the base to the apex of anther, eg. Verbena.
Dorsifixed: Filament is attached to the dorsal side of the anther, eg. Citrus.
Fixation of anthers
Basifixed (Innate): Filament is attached to the base of the anther, eg. Brassica.
Adnate: Filament is continued from the base to the apex of anther, eg. Verbena.
Dorsifixed: Filament is attached to the dorsal side of the anther, eg. Citrus.
Versatile: Anther is attached lightly at its back to the slender tip of the filament so that it can swing freely, eg. Grass
Gynoecium
Gynoecium is the collective term for the innermost central whorl of floral appendages. It is considered as the female part of the flower. A unit of gynoecium is called carpel. Following technical terms and related with gynoecium.
1. Number of Carpel
Monocarpellary: Gynoecium consists of a single carpel; eg. Fabaceae
Bicarpellary: Ovary consists of two carpels; eg. Rubiaceae
Tricarpellary: Ovary consists of three carpels; eg. Liliaceae
Tetracarpellary: Ovary comprises of four carpels; eg. Melia
Multicarpellary: Gynoecium consists of many carpels eg. Papaver
2. Cohesion of Carpels
Apocarpous: Gynoecium made up of two or more carpels which are free; eg. Polyalthia.
Syncarpous: Gynoecium consists of two or more carpels which are fused; eg. Hibiscus.
3. Number of locules
Depending on the number of chambers, the ovary may be described as unilocular, bilocular, trilocular etc.
Study Material, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, brief detail
11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school : Androecium And Gynoecium |
Related Topics
11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school