Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 9 : Tissue and Tissue System
Anatomy and Primary Structure of a Monocot Leaf - Grass Leaf
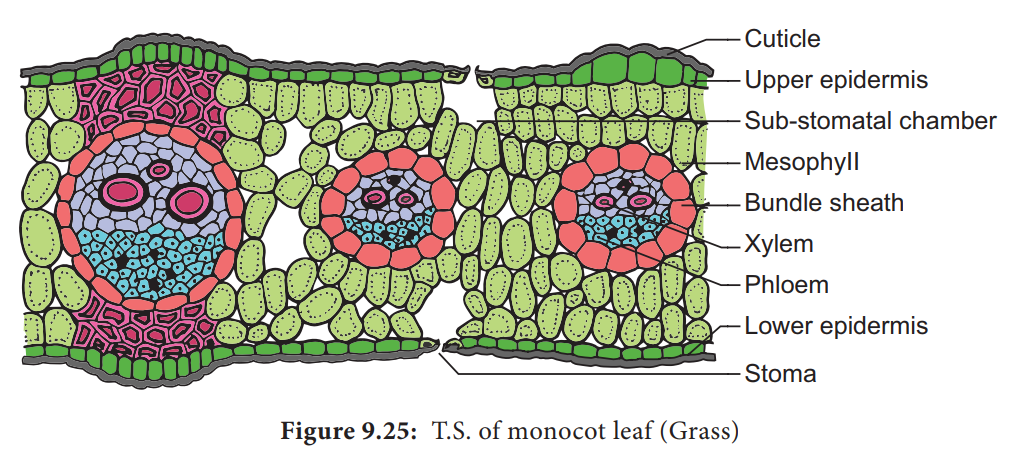
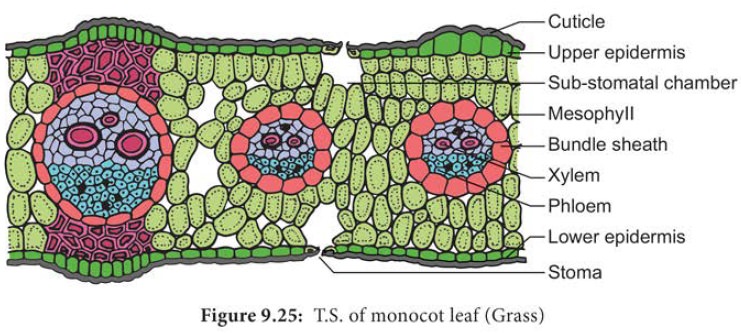
Anatomy of a Monocot Leaf – Grass Leaf
A transverse section of a grass leaf reveals the following internal structures.
Epidermis
The leaf has upper and lower epidermis. They are made up of a single layer of thin walled cells. The outer walls are covered by thick cuticle.
The number of stomata is more or less equal on both the epidermis. The stomata is surrounded by dumb – bell shaped guard cells. The guard cells-contain chloroplasts, whereas the other epidermal cells do not have them.
Some special cells surround the guard cells. They are distinct from other epidermal cells.
These cells are called subsidiary cells.
Some cells of upper epidermis are large and thin walled. They are called bulliform cells or motor cells. These cells are helpful for the rolling and unrolling of the leaf according to the weather change.
Some of the epidermal cells of the grass are filled with silica. They are called silica cells.
Mesophyll
The ground tissue that is present between the upper and lower epidermis of the leaf is called mesophyll. Here, the mesophyll is not differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma. All the mesophyll cells are nearly isodiametric and thin walled. These cells are compactly arranged with limited intercellular spaces. They contain numerous chloroplasts.
Vascular Bundles
Vascular bundles differ in size. Most of the vascular bundles are smaller in size. Large bundles occur at regular intervals.Two patches of sclerenchyma are present above and below the large vascular bundles. These sclerenchyma patches give mechanical support to the leaf. The small vascular bundles do not have such sclerenchymatous patches. Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and closed . Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a parenchymatous bundle sheath. The cells of the bundle sheath generally contain starch grains. The xylem of the vascular bundle is located towards the upper epidermis and the phloem towards the lower epidermis.In C4grasses, the bundle sheath cells are living and involve in C4 photosynthesis. This sheath is called Kranz sheath.
Related Topics